Abstract
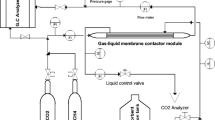
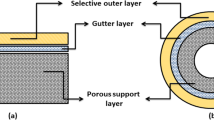
In this study, removal of SO2 from gas stream was carried out by using microporous polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) asymmetric hollow fiber membrane modules as gas-liquid contactor. The asymmetric hollow fiber membranes used in this study were prepared polyvinylidene fluoride by a wet phase inversion method. Water was used as an internal coagulant and external coagulation bath for all spinning runs. An aqueous solution containing 0.02 M NaOH was used as the absorbent. This study attempts to assess the influence of PEG additive, absorbent flow rate, SO2 concentration, gas flow rate and gas flow direction on the SO2 removal efficiency and overall mass transfer coefficient. The effect of liquid flow rate on SO2 removal efficiency shows that at very low liquid flow rate, the NaOH available at the membrane surface for reacting with SO2 is limited due to the liquid phase resistance. As liquid flow rate is above the minimum flow rate which overcomes the liquid phase resistance, the SO2 absorption rate is controlled by resistance in the gas phase and the membrane. The SO2 absorption rate with inlet SO2 concentration was sharply increased by using hollow fiber membranes compared to a conventional wetted wall column because the former has higher gas liquid contacting area than the latter. The mass transfer coefficient is independent of pressure. When the gas mixture was fed in the shell side, the removal efficiency of SO2 declined because of channeling problems on the shell side. Also, the addition of PEG in polymer dopes increased SO2 removal efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Lancia, D. Musmarra and F. Pepe, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 36, 197 (1997).
Z. Qi and E. L. Cussler, J. Membr. Sci., 23, 321 (1985).
S. Karoor and K. Sirkar, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 32, 674 (1993).
R. Wang, H. Y. Zhang, P. H. M. Feron and D. T. Liang, Sep. Purif Technol., 46, 33 (2005).
K. Li, J. F. Kong, D. Wang and W. K. Teo, AIChE J., 45, 1211 (1999).
I. Cabasso, K. O. Robert, E. Klein and J. K. Smith, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 21, 1883 (1977).
H. Yasuda and J. T. Tsai, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 18, 805 (1974).
D. Wang, K. Li and W. K. Teo, J. Membr. Sci., 163, 211 (1999).
H. K. Lee, H. D. Jo, W. K. Choi, H. H. Park, C. W. Lim and Y. T. Lee, Desalination, 200, 604 (2006).
H. K. Lee, B. R. Deshwal and K. S. Yoo, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22, 208 (2005).
D. Wang, W. K. Teo and K. Li, Sep. Purif. Technol., 27, 33 (2002).
H. Kreulen, C. A. Smolders, G. F. Versteeg and W. P. M. van Swaaij, J. Membr. Sci., 78, 217 (1993).
D. Wang, K. Li and W. K. Teo, J. Membr. Sci., 178, 13 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented at the 6th Korea-China Workshop on Clean Energy Technology held at Busan, Korea, July 4–7, 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, HH., Lim, CW., Jo, HD. et al. Absorption of SO2 using PVDF hollow fiber membranes with PEG as an additive. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24, 693–697 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0028-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0028-4