Abstract
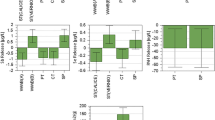
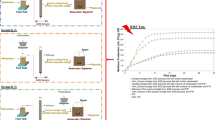
Fluidized bed pyrolysis has been recognized as an innovative technology for sewage sludge treatment. The physical and attrition properties of sewage sludge are changed through the fluidized bed pyrolysis. The minimum fluidization velocities and attribution rate constants for sewage sludge and sludge based-char were obtained from pressure drop and attribution tests. As a result, sewage sludge with 20% moisture content and char were classified as Geldart B solids and the superficial gas velocity for bubbling fluidization was 0.2142-0.8755 m/s. In addition, attribution of the sewage sludge and char was more affected by particle size than by material type. The equations for the overall attrition rate constants are K a × 105 = 1.09U − 14.82 for sludge and ln k a = 0.1(U−U mf )− 13.63 for char, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Takahashi, S. Kato, E. Sarai, T. Ichioka, S. Htayakawa and H. Miyajiri, Chemosphere, 44, 23 (2001).
Y. S. Yun and G. B. Lee, Energy Engg. J., 13(1), 82 (2004).
F. Rozada, L. F. Calvo, A. I. Garcia, J. M. Villacorta and M. Otero, Bioresource Technology, 87, 221 (2003).
J. E. Gwyn, AIChE J., 15(1), 35 (1969).
W. L. Forsythe and W. R. Hertwig, Ind. Eng. Chem., 41, 1200 (1949).
D. Kunii and O. Levenspiel, Fluidization engineering, Butter worth-Heinemann (1991).
B. Cagnon, X. Py, A. Guillot and F. Stoeckli, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 57, 273 (2003).
Y. M. Chang, C. M. Chou, K. T. Su, C. Y. Hung and C. H. Wu, Waste Management, 25, 249 (2005).
J. L. Cook, S. J. Khang, S. K. Lee and T. C. Keener, Powder Technology, 89, 1 (1996).
D. Geldart and J. Baeyens, Powder Technology, 42, 67 (1985).
M.-R. Kim, J.-G. Jang and J.-K. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22, 61 (2005).
S.-S. Lee, J.-S. Yoo, G.-H. Moon, S.-W. Park, D.-W. Park and K.-J. Oh, Am. Chem. Soc., Div. Fuel Chem., 48 (2003).
C. L. Lin and M. Y. Wey, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 20, 1123 (2003).
C. L. Lin and M. Y. Wey, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22, 154 (2005).
L. Lin, J. T. Sears and C. Y. Wen, Powder Technology, 27, 105 (1980).
Y.-S. Park, H.-S. Kim, D. Shun, K.-S. Song and S.-K. Kang, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 17, 284 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choung, Y.H., Cho, K.C., Choi, W.J. et al. Attribution of sewage sludge and sludge-based char in a fluidized bed reactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24, 660–663 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0021-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0021-y