Abstract
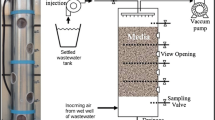
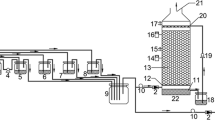
Hydrogen sulfide is heavier than air and is colorless, toxic and flammable, the gas odor threshold of which is about 0.47 ppbv, which causes nuisance odor at concentrations as low as about 8ppbv and corrosion problems in sewer systems. The transient behavior of biofilter packed with mixed media (of granular activated carbon and compost) inoculated with a pure culture of Thiobacillus sp. IW was observed at a height of four sampling ports to treat wasteair containing hydrogen sulfide in this investigation, which shall be used as control to be compared with the performance of a biofilter-involved integrated system for the treatment of waste-air containing hydrogen sulfide in a subsequent investigation. Unlike the previous studies of the other investigators, various process conditions were applied to successive biofilter runs in order to monitor and correlate each corresponding unsteady behavior of the biofilter at the height of each sampling port. During 10 days (20 times) after start-up of a biofilter hydrogen sulfide was continuously adsorbed on the media and that the adsorption of hydrogen sulfide was under way since the inlet loads of 1st and 2nd stage operations were very low. Afterwards it was obvious that the breakthrough curves at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th (exit) sampling ports responded rapidly to the change of operating conditions of a biofilter so that the breakthrough curve at each sampling port responded rapidly to approach a new state of saturation, which suggests that the adsorption capacity of biofilter-media may be relatively small or its affinity to hydrogen sulfide may be relatively high, compared to such volatile organic compound as ethanol. Up to the 3rd stage of operation the removal efficiency continued to be nearly 100%. However it began to decrease as inlet load increased. At the end of last stage of the biofilterrun removal efficiency was decreased and maintained at 94%. The maximum elimination capacity was observed to be ca. 95 g/m3/h, which was higher than that of the biofiltration-work of any other previous investigator except for that of the biofiltration-work with use of each of two inorganic packing materials (porous ceramics, calcinated and formed obsidian).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buisman, C. J., Geraats, B.G., Ljspeert, P. and Lettinga, G., “Optimization of sulphur production into a biotechnological sulphide-removing reactor,” Biotechnol. Bioeng., 35, 50 (1990).
Cho, K.-S., Ryu, H.W. and Lee, N.Y., “Biological deodorization of hydrogen sulfide using porous lava as a carrier of Thiobacillus thioxidants,” Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 90, 25 (2000).
Chung, Y.-C., Huang, C. and Tseng, C.-P., “Biodegradation of hydrogen sulfide by a laboratory-scale immobilized Pseudomonas putida CH11 biofilter,” Biotechnology Progress, 12, 773 (1996a).
Chung, Y.-C., Huang, C. and Tseng, C.-P., “Operation optimization of Thiobacillus thioparus CH11 in a biofilter for hydrogen sulfide removal,” Journal of Biotechnology, 52, 31 (1996b).
Chung, Y.-C., Huang, C. and Tseng, C.-P., “Biological elimination of H2S and NH3 from wastegases by biofilter packed with immobilized heterotrophic bacteria,” Chemosphere, 43, 1043 (2001).
Cox, H. H. and Deshusses, M. A., “Co-treatment of H2S and toluene in a biotrickling filter,” Chemical Engineering Journal, 87, 101 (2002).
Eckhart, A., Proceedings of biological treatment of industrial waste gases, Dechema, Heidelberg, Germany, Mar. 24–26, 2pp (1987).
Elias, A., Barona, A., Arreguy, A., Rios, J., Aranguiz, I. and Penas, J., “Evaluation of a packing material for the biodegradation of H2S and product analysis,” Process Biochemistry, 37, 813 (2002).
Hirai, M., Kamamoto, M., Yani, M. and Shoda, M., “Comparison of the biological H2S removal characteristics among four inorganic packing materials,” Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 91, 396 (2001).
Hirai, M., Ohtake, M. and Shoda, M., “Removal kinetics of hydrogen sulfide, methanethiol and dimethyl sulfide by peat biofilters,” J. Ferment. Bioeng., 70, 334 (1990).
Islander, R. I., Devinny, J. S., Mansfield, F., Postyn, A. and Shin, H., “Microbial ecology of crown corrosions in sewers,” J. Environ. Eng., 117, 751 (1990).
Lee, T. J., Kwon, O.Y. and An, S. J., “Removal of odor causing compounds using adsorption of crushed refused-tire and phenol oxidizing bacteria, Cryptococcus Terreus A,” J. KSEE, 22, 1601 (2000).
Lim, K. H. and Lee, E. J., “Biofilter modeling for waste air treatment: Comparisons of inherent characteristics of biofilter models,” Korean J. Chem. Eng., 20, 315 (2003).
Lim, K. H. and Park, S.W., “The treatment of waste-air containing mixed solvent using a biofilter; 1. Transient behavior of biofilter to treat waste-air containing ethanol,” Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21, 1161 (2004).
Lim, K.H., “The treatment of waste-air containing mixed solvent using a biofilter; 2. Treatment of waste-air containing ethanol and toluene in a biofilter,” Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22, 228 (2005).
Ottengraf, S. P. P., Exhaust gas purification, Biotechnology (H. J. Rehm, G. Reed, eds), VCH, Weinheim, Germany, Vol. 8, pp.426–452 (1986).
Oyarzun, P., Arancibia, F., Canales, C. and Aroca, G. E., “Biofiltration of high concentration of hydrogen sulfide using Thiobacillus thioparus,” Process Biochemistry, 00, 1 (2003).
Sorial, G. A., Smith, F. L., Suidan, M. T. and Biswas, P., “Evaluation of trickle bed biofilter media for toluene removal,” Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 45, 801 (1995).
Wani, A. H., Branion, M.R. and Lau, A. K., “Effects of periods of starvation and fluctuating hydrogen sulfide concentration on biofilter dynamics and performance,” Journal of Hazardous Materials, 60, 287 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, KH., Park, SW. Transient behavior of biofilter inoculated with Thiobacillus sp. IW to treat waste-air containing hydrogen sulfide. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 23, 965–971 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-006-0016-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-006-0016-0