Abstract
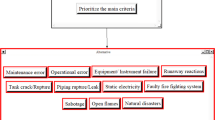
In recent years, China’s increased interest in environmental protection has led to a promotion of energy-efficient dual fuel (diesel/natural gas) ships in Chinese inland rivers. A natural gas as ship fuel may pose dangers of fire and explosion if a gas leak occurs. If explosions or fires occur in the engine rooms of a ship, heavy damage and losses will be incurred. In this paper, a fault tree model is presented that considers both fires and explosions in a dual fuel ship; in this model, dual fuel engine rooms are the top events. All the basic events along with the minimum cut sets are obtained through the analysis. The primary factors that affect accidents involving fires and explosions are determined by calculating the degree of structure importance of the basic events. According to these results, corresponding measures are proposed to ensure and improve the safety and reliability of Chinese inland dual fuel ships.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Wei, 2013. Speed up the application of dual fuel (diesel/natural gas) power technology to ships in Yangzi River. China Water Transport, 13(8), 3–5. (in Chinese)
Du Yanan, 2012. Consequences analysis of affiliated pipeline leakage of dual fuel ships. Master thesis, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, 117–120. (in Chinese)
Fan Hongjun, Zhang Hui, Xu Jianyong, 2013. Pool fire danger distance analysis of barge. J. China Shipbuilding (Chinese edition), 52(4), 77–82. (in Chinese)
Fay JA, 2003. Model of spills and fires from LNG and oil tanker. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B96, 171–188.
Huang Zhenghua, Li Jianhu, 2012. Assessment of fire risk of gas pipeline leakage in cities and towns. Procedia Engineering, 3(1), 77–82.
Lei Shi, Jian Shuai, Kui Xu, 2014. Fuzzy fault tree assessment based on improved AHP for fire and explosion accidents for steel oil storage tanks. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 8(7), 529–538.
Li Jianhua, Huang Zhenghua, 2012. Fire and explosion risk analysis and evaluation for LNG ships. Procedia Engineering, 6(3), 70–76.
Li Yueyang, Guan Yifeng, 2013. The desgn of dual fuel (diesel/natural gas) ships gas fuel system, J. Jiangsu Ship, 30(5), 17–19. (in Chinese)
Liao Suliang, Han Li, Liu Xinpeng, Guo Kaihua, 2014. Safety quantitative risk analysis of LNG filling ships. Chinese Safety Science and Technology (Chinese edition), 10(11), 187–192. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2014.11.032
Mattarelli E, Rinaldini CA, Golovitchev V, 2014. CFD-3D analysis of a light duty dual fuel (diesel/natural gas) combustion engine. J. Energy Procedia, 10(9), 929–937.
Ren Wei, Pan Xinxiang, Liu Xinjian, 2011. Safety assessment of main engine debugging during sea trial of newly-built ship based on FSA. J. China Shipbuilding, 52(1), 20–25. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2011.01.019
Shi Guozheng, Zhang Hui, Fan Hongjun, 2013. Fuel injection mode research of LNG ship. J. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 6(14), 16–24.
Tu Hangming, 2012. Risk assessment studies of gas fuel ship power system. Master thesis. Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, 59–63. (in Chinese)
Wang Daqing, Zhang Peng, Chen Liqiong, 2014. Fuzzy fault tree quantitative analysis of LNG storage tank leakage with consideration of event interdependencies. J. China Safety Science Journal, 24(1), 1390–1398. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2014.01.016
Xu Jianyong, Gan Shaowei, 2014. Development status and key technologies outline of LNG ships. Wuhan Specifications Institute, Wuhan. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements Special Fund (No.SBA2015020077)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Y., Zhao, J., Shi, T. et al. Fault tree analysis of fire and explosion accidents for dual fuel (diesel/natural gas) ship engine rooms. J. Marine. Sci. Appl. 15, 331–335 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-016-1366-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-016-1366-6