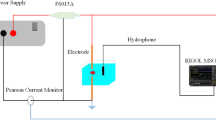
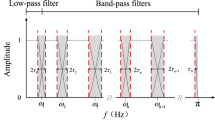
Abstract
After an aerial object enters the water, physical changes to sounds in the water caused by the accompanying bubbles are quite complex. As a result, traditional signal analyzing methods cannot identify the real physical object. In view of this situation, a novel method for analyzing the sounds caused by an aerial object’s entry into water was proposed. This method analyzes the vibrational mode of the bubbles by using empitical mode decomposition. Experimental results showed that this method can efficiently remove noise and extract the broadband pulse signal and low-frequency fluctuating signal, producing an accurate resolution of entry time and frequency. This shows the improved performance of the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao Xiaoling, Tang Weilin (1981). Investigations of the impact noise. Journal of Harbin Shipbuilding Engineering Institute, (1), 27–39. (in Chinese)
Deng Yongjun, Wang Wei, Qian Chengchun, Wang Zhong, Dai Dejun (2001). Boundary problem processing in EMD and hilbert transform. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(3), 257–263. (in Chinese)
Hu Qiao, Hao Baoan, Lv Linxia, Chen Yalin, Sun Qi (2007). Application of empirical mode energy entropy to target-detection of underwater acoustic signals. Classification and Identification Technology of Underwater Targets, 26(5), 181–183. (in Chinese)
Huang Daji, Zhao Jinping, Su Jilan (2003). Practical implementation of the Hilbert-Huang transform algorithm. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 25(1), 1–11. (in Chinese)
Huang NE, Shen Zheng, Long SR, Wu MC, Shih HH, Zheng Quanan, Yen NC, Chi CT, Liu HH (1998). The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear non-stationary time series analysis. Proceeding of the Royal Society of London Series A, 454, 903–995.
Li Ying, Wang Bangfeng, Sun Yafei, Shi Yifeng (2005). Analysis and application of empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectrum. Journal of Transducer Technology, 24(5), 71–76. (in Chinese)
Long Sisheng, Zhang Tiebao, Long Feng (2005). Causs and solutions of overshoot and undershooot and end swing in Hilbert-Huang transform. Acta Seismolo Gica Sinica, 27(5), 561–568. (in Chinese)
Oonincx PJ, Hermand JP (2004). Empirical mode decomposition of ocean acoustic data with constraint on the frequency range. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Underwater Acoustics, Delft, The Netherlands.
Sun Peng, Liu Pingxiang, Xu Bailing (2005). The research on the detection of transient signal. Ship Science and Technology, 27(3), 72–76. (in Chinese)
Tan Shanwen, Qin Shuren, Tang Baoping (2004). The filtering character of Hilbert-Huang transform and its application. Journal of Chongqing University, 27(2), 9–12. (in Chinese)
Yang Shixi, Hu Jinsong, Wu Zhaotong, Yan Gongbiao (2004). Study of empirical mode decomposition based on high-order spline interpolation. Journal of Zhejiang University, 38(3), 267–270. (in Chinese)
Zhang Yushan, Liang Jianwen, Hu yuxiang (2003). Application of auto-regressive model to process boundary problem in EMD. Progress in Natural Science, 13(10), 1054–1059. (in Chinese)
Zhong Youming, Jin Tao, Qin Shuren (2005). New envelope algorithm for Hilbert-Huang transform.. Jounal of Data Acquisition & Processing, 20(1), 13–17. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yang Li was born in 1982. She graduated from Harbin Engineering University and received the M.S. degree in 2009. She is now a PhD candidate for underwater acoustic engineering at Harbin Engineering University. Her main interests are focused on acoustic signal processing and underwater target recognition.
Si-Chun Li was born in 1963. She is a professor at Harbin Engineering University. She received the PhD degree in underwater acoustic engineering from Harbin Engineering University in 2008. Her current research interests include underwater acoustic signal processing, signal detection, passive target feature extraction and target recognition.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Li, Sc., Piao, Sc. et al. Application of empirical mode energy to the analysis of fluctuating signals. J. Marine. Sci. Appl. 9, 99–104 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-010-9030-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-010-9030-z