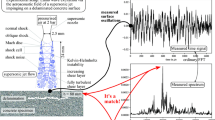
Abstract
This paper presents an air-coupled impact echo (IE) technique that relies on the phase spectrum of the collected data to find the frequencies corresponding to the reflections from delaminations. The proposed technique takes advantage of the fact that the IE compression wave is not a propagating wave, but it is the 1st order symmetrical (S1) mode Lamb wave at zero group velocity (S1-ZGV). Therefore, it searches the phase spectra of the data collected by multiple sensors to locate the frequency corresponding to the lowest phase difference. As a result, the technique reduces the effect of propagating waves, including the direct acoustic wave and ambient noise. It is named the Constant Phase IE (CPIE). The performance of the CPIE is experimentally compared with the regular amplitude spectrum-based IE technique and two other multisensor IE techniques. The CPIE shows a performance advantage, especially in a noisy environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM (1998), Standard Test Method for Measuring the P-Wave Speed and the Thickness of Concrete Plates Using the Impact-Echo Method, ASTM C1383-98a, USA.
Baggens O and Ryden N (2015), “Systematic Errors in Impact-Echo Thickness Estimation Due to Near Field Effects,” NDT and E International, 69: 16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2014.09.003
Carino NJ (2001), “The Impact-Echo Method: An Overview,” 2001 Structures Congress and Exposition, Washington, D.C., USA.
Choi H and Azari H (2017), “Guided Wave Analysis of Air-Coupled Impact-Echo in Concrete Slab,” Computers and Concrete, 20(3): 257–262. https://doi.org/10.12989/cac.2017.20.3.257
Choi H, Shams S and Azari H (2017), “NDE Application of Air-Coupled Array for Thickness Measurement of Concrete Slab,” IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, D.C., USA, pp. 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/ULTSYM.2017.8092508
Dai XW, Zhu JY, Tsai YT and Haberman MR (2011), “Use of Parabolic Reflector to Amplify In-Air Signals Generated During Impact-Echo Testing,” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 130(4): EL167–EL172. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.3632106
Epp T and Cha YJ (2017), “Air-Coupled Impact-Echo Damage Detection in Reinforced Concrete Using Wavelet Transforms,” Smart Materials and Structures, 26(2): 025018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/26/2/025018
FHWA (2017), Deficient Bridges by Highway System - National Bridge Inventory - Bridge Inspection - Safety Inspection - Bridges and Structures - Federal Highway Administration, (n.d.). Retrieved August 15, 2022, from https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/bridge/nbi/no10/defbr17.cfm
Gibson A and Popovics JS (2005), “Lamb Wave Basis for Impact-Echo Method Analysis,” Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 131(4): 438–443. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9399(2005)131:4(438)
Gibson A, Ryden N and Popovics JS (2007), “Advances in Air-Coupled Lamb Wave Scanning,” Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems Proceedings, pp. 157–166. https://doi.org/10.4133/1.2924664
Groschup R and Grosse CU (2015), “MEMS Microphone Array Sensor for Air-Coupled Impact-Echo,” Sensors (Switzerland), 15(7): 14932–14945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150714932
Kee SH and Gucunski N (2016), “Interpretation of Flexural Vibration Modes from Impact-Echo Testing,” Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 22(3): 04016009. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)is.1943-555x.0000291
Larsen JL, McElderry J, Baxter JS, Guthrie WS and Mazzeo BA (2020), “Automated Sounding for Concrete Bridge Deck Inspection Through a MultiChannel, Continuously Moving Platform,” NDT and E International, 109: 102177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2019.102177
Mazzeo BA, Larsen JL, McElderry J and Guthrie WS (2017), “Rapid Multichannel Impact-Echo Scanning of Concrete Bridge Decks from a Continuously Moving Platform,” AIP Conference Proceedings, 1806(1): 080003. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4974628
Medina R and Garrido M (2007), “Improving Impact-Echo Method by Using Cross-Spectral Density,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, 304(3–5): 769–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2007.03.019
Oh T, Kee SH, Arndt RW, Popovics JS and Zhu JY (2013), “Comparison of NDT Methods for Assessment of a Concrete Bridge Deck,” Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 139(3): 305–314. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)em.1943-7889.0000441
Pessiki SP and Carino NJ (1988), “Setting Time and Strength to Concrete Using the Impact-Echo Method,” ACI Materials Journal, 85(5): 389–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0963-8695(97)89004-4
Ryden N (2016), “Enhanced Impact Echo Frequency Peak by Time Domain Summation of Signals with Different Source Receiver Spacing,” Smart Structures and Systems, 17(1): 59–72. https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2016.17.1.059
Sansalone M and Streett W (1997), Impact-Echo: Nondestructive Evaluation of Concrete and Masonry, Bullbrier Press, Ithaca, NY, USA.
Shin SW, Popovics JS and Oh T (2012), “Cost Effective Air-Coupled Impact-Echo Sensing for Rapid Detection of Delamination Damage in Concrete Structures,” Advances in Structural Engineering, 15(6): 887–895. https://doi.org/10.1260/1369-4332.15.6.887
Shokouhi P, Gucunski N and Maher A (2006), “Applicability and Limitations of Impact Echo in Bridge Deck Condition Monitoring,” 19th Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, SAGEEP 2006: Geophysical Applications for Environmental and Engineering Hazzards - Advances and Constraints, pp. 385–401. https://doi.org/10.4133/1.2923671
Sun HB, Zhu JY and Ham SY (2018), “Automated Acoustic Scanning System for Delamination Detection in Concrete Bridge Decks,” Journal of Bridge Engineering, 23(6). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)be.1943-5592.0001237
Zhang Y, Wei XM, Tsai YT, Zhu JY, Fetrat FA and Gucunski N (2012), “Multisensor Data Fusion for Impact-Echo Testing of Concrete Structures,” Smart Materials and Structures, 21(7): 075021. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/21/7/075021
Zhu JY and Popovics JS (2002), “Non-Contact Detection of Surface Waves in Concrete Using an Air-Coupled Sensor,” AIP Conference Proceedings, 615: 1261–1268. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1472940
Zhu JY and Popovics JS (2005), “Non-Contact Imaging for Surface-Opening Cracks in Concrete with AirCoupled Sensors,” Materials and Structures, 38(9): 801–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02481652
Zhu JY and Popovics JS (2007), “Imaging Concrete Structures Using Air-Coupled Impact-Echo,” Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 133(6): 628–640. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9399(2007)133:6(628)
Acknowledgement
The Higher Commission for Education Development in Iraq, HCED, and Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almallah, N., Gucunski, N. Enhanced air-coupled impact echo technique by phase analysis of signals from multiple sensors. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 23, 297–310 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-024-2236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-024-2236-x