Abstract
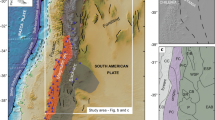
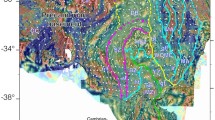
The Papua New Guinea-Solomon (PN-SL) arc is one of the regions with active crustal motions and strong geological actions. Thus, its complex subduction system makes it an ideal laboratory for studying the initiation mechanism of plate subduction. However, the PN-SL subduction system has not yet been sufficiently studied, and its density structure has yet to be revealed. In this paper, we used the free-air gravity data, Parker-Oldenburg density surface inversion method, and the genetic algorithm density inversion method to obtain the density structure of an approximately 1000-km-long northwest-southeast line crossing the PN-SL subduction system under the constraints of the CRUST1.0 global crustal model, onshore seismic data, and the LLNL-G3Dv3 global P-wave velocity model. The density structure shows that density differences between the plates on the two sides of the trench could play a significant role in plate subduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chadwick, J., Perfit, M., McInnes, B., Kamenov, G., Plank, T., Jonasson, I., et al., 2009. Arc lavas on both sides of a trench: Slab window effects at the Solomon Islands triple junction, SW Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 279(3–4): 293–302, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.01.001.
Cooper, P. A., and Taylor, B., 1985. Polarity reversal in the Solomon Islands arc. Nature, 314(6010): 428–430, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/314428a0.
Cordell, L., and Henderson, R. G., 1968. Iterative three-dimensional solution of gravity anomaly data using a digital computer. Geophysics, 33(4): 596–601, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1439955.
Finlayson, D. M., Cull, J. P., Wiebenga, W. A., Furumoto, A. S., and Webb, J. P., 1972. New Britain — New Ireland crustal seismic refraction investigations 1967 and 1969. Geophysical Journal International, 29(3): 245–253, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1972.tb06157.x.
Fullea, J., Fernandez, M., and Zeyen, H., 2008. FA2BOURG — A FORTRAN 90 code to compute Bouguer gravity anomalies from gridded free air anomalies: Application to the Atlantic-Mediterrannean transition zone. Computers & Geosciences, 34(12): 1665–1681, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2008.02.018.
Galewsky, J., and Silver, E. A., 1997. Tectonic controls on facies transitions in an oblique collision: The western Solomon Sea, Papua New Guinea. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 109(10): 1266–1278.
Gerard, A., and Debeglia, N., 1975. Automatic three-dimensional modeling for the interpretation of gravity or magnetic anomalies. Geophysics, 40(6): 1014–1034, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1440578.
Hall, R., and Spakman, W., 2002. Subducted slabs beneath the eastern Indonesia-Tonga region: Insights from tomography. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 201(2): 321–336, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00705-7.
Hanyu, T., Tejada, M. L. G., Shimizu, K., Ishizuka, O., Fujii, T., Kimura, J. I., et al., 2017. Collision-induced post-plateau volcanism: Evidence from a seamount on Ontong Java Plateau. Lithos, 294: 87–96, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2017.09.029.
Hinze, W. J., Von Frese, R. R., and Saad, A. H., 2013. Gravity and Magnetic Exploration: Principles, Practices, and Applications. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, 525pp.
Holm, R. J., and Richards, S. W., 2013. A re-evaluation of arc-continent collision and along-arc variation in the Bismarck Sea region, Papua New Guinea. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 60(5): 605–619, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2013.824505.
Honza, E., Davies, H. L., Keene, J. B., and Tiffin, D. L., 1987. Plate boundaries and evolution of the Solomon Sea region. Geo-Marine Letters, 7(3): 161–168, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02238046.
Inoue, H., Coffin, M. F., Nakamura, Y., Mochizuki, K., and Kroenke, L. W., 2008. Intrabasement reflections of the Ontong Java Plateau: Implications for plateau construction: Ontong Java Plateau construction. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(4): Q04014, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GC001780.
Laske, G., Masters, G., Ma, Z., and Pasyanos, M., 2013. Update on CRUST1.0 — A 1-degree global model of Earth’s crust. Geophysical Research Abstracts. Vienna, 2658.
Musgrave, R. J., 2013. Evidence for late Eocene emplacement of the Malaita Terrane, Solomon Islands: Implications for an even larger Ontong Java Nui oceanic plateau: Malaita Terrane and Ontong Java Nui. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 118(6): 2670–2686, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50153.
Petterson, M. G., Babbs, T., Neal, C. R., Mahoney, J. J., Saunders, A. D., Duncan, R. A., et al., 1999. Geological-tectonic framework of Solomon Islands, SW Pacific: Crustal accretion and growth within an intra-oceanic setting. Tectonophysics, 301(1–2): 35–60, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00214-5.
Santos, D. F., Silva, J. B. C., Martins, C. M., dos Santos, R. D. C. S., Ramos, L. C., and de Araújo, A. C. M., 2015. Efficient gravity inversion of discontinuous basement relief. Geophysics, 80(4): G95–G106, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2014-0513.1.
Schellart, W. P., Lister, G. S., and Toy, V. G., 2006. A late Cretaceous and Cenozoic reconstruction of the Southwest Pacific region: Tectonics controlled by subduction and slab rollback processes. Earth-Science Reviews, 76(3-4): 191–233, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.01.002.
Simmons, N. A., Myers, S. C., Johannesson, G., and Matzel, E., 2012. LLNL-G3Dv3: Global P wave tomography model for improved regional and teleseismic travel time prediction. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 117(B10): B10302, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JB009525.
Stotz, I. L., Iaffaldano, G., and Davies, D. R., 2017. Late Miocene Pacific Plate kinematic change explained with coupled global models of mantle and lithosphere dynamics. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(14): 7177–7186, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL073920.
Taylor, B., 1979. Bismarck Sea: Evolution of a back-arc basin. Geology, 7(4): 171, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1979)7<171:BSEOAB>2.0.CO;2.
Tozer, B., Sandwell, D. T., Smith, W. H. F., Olson, C., Beale, J. R., and Wessel, P., 2019. Global bathymetry and topography at 15 arc sec: SRTM15+. Earth and Space Science, 6(10): 1847–1864, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EA000658.
Wallace, L. M., Stevens, C., Silver, E., McCaffrey, R., Loratung, W., Hasiata, S., et al., 2004. GPS and seismological constraints on active tectonics and arc-continent collision in Papua New Guinea: Implications for mechanics of microplate rotations in a plate boundary zone. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 109(B5): B05404, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JB002481.
Weissel, J. K., Taylor, B., and Karner, G. D., 1982. The opening of the Woodlark Basin, subduction of the Woodlark spreading system, and the evolution of northern Melanesia since mid-Pliocene time. Tectonophysics, 87(1–4): 253–277, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(82)90229-3.
Wessel, P., and Kroenke, L. W., 2000. Ontong Java Plateau and late Neogene changes in Pacific Plate motion. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B12): 28255–28277, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JB900290.
Wessel, P., Luis, J., Uieda, L., Scharroo, R., Wobbe, F., Smith, W., et al., 2019. The generic mapping tools version 6. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 20(11): 5556–5564, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GC008515.
Yang, G., Li, Y., Tong, L., Wang, Z., Si, G., Lindagato, P., et al., 2022. Natural observations of subduction initiation: Implications for the geodynamic evolution of the paleo-Asian Ocean. Geosystems and Geoenvironment, 1(1): 100009, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geogeo.2021.10.004.
Yang, G., Shen, C., Wang, J., Xuan, S., Wu, G., and Tan, H., 2018. Isostatic anomaly characteristics and tectonism of the New Britain Trench and neighboring Papua New Guinea. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 9(5): 404–410, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geog.2018.04.006.
Zhang, Z., Li, S., Tian, J., Yang, P., Ding, D., Zang, Y., et al., 2018. Formation mechanism of the moniliform seamounts outside the West Melanesian Trench. Geological Journal, 53(4): 1604–1610, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.2979.
Zhu, L., and Kanamori, H., 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B2): 2969–2980, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JB900322.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91858215, 42076224).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Xing, J., Gong, W. et al. Density Structure of the Papua New Guinea-Solomon Arc Subduction System. J. Ocean Univ. China 22, 1269–1276 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-023-5425-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-023-5425-8