Abstract
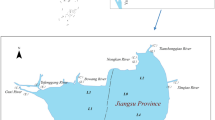
Several studies have documented that during ‘green tide’ events, comprising green macroalgae blooms in aquatic ecosystems, dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) levels remain relatively steady despite the absorption of a large amount of DIP. In this study, surface sediment samples and a sediment core were extracted using a modified sequential extraction scheme, and water and surface sediment samples were analyzed in April 2017 to better understand phosphorus (P) cycling and replenishment in Subei shoal. We used a simple model on equilibrium of adsorption-desorption to present the buffering capacity of phosphate. The total P (TP) in the surface sediments ranged from 12.2 to 28.4 µmol g−1 (average 15.5 µmol g−1) and was dominated by inorganic P. TP, exchangeable P, reactive and reductive Fe/Al bound P, and authigenic apatite P significantly decreased northward and eastward from Subei shoal, contrary to the detrital P and organic P results. Dissolved and particulate inorganic P in the water samples ranged from 0.01 to 0.54 µmol L−1 (average 0.19 µmol L−1) and 0.9 to 19.6 µmol g−1 (average 4.9 µmol g−1), respectively. The applied model showed that suspended particulate matter is an important regulator of DIP behavior. Thus, modification of SPM can alter the DIP buffering capacity. The calculated buffering capacity in the surface layer of the sea water was > 60 within Subei shoal and always > 10 along the path of floating Ulva prolifera, providing a reasonable explanation for the steady concentration of DIP and its replenishment during the blooming of this green macroalgae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, S. L., Brunner, S. L., Klump, J. V., Houghton, E. M., and Miller, T. R., 2018. Spatial analysis of toxic or otherwise bioactive cyanobacterial peptides in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 44(5): 924–933.
Bian, C., Jiang, W., Quan, Q., Wang, T., Greatbatch, R. J., and Li, W., 2013. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011. Journal of Marine Systems, 121–122: 24–35.
Cao, W., 2006. A study on the speciation of phosphorus in the sediments of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China, Qingdao.
Cao, X. Y., Wang, H., Lu, M., Ge, C. F., Zhou, L. M., and Yang, G. P., 2019. Evaluation study for phosphorus mobilisation-release behaviour on different marine sediments: Focus on phosphate sorption characteristics. Environmental Chemistry, 16: 179–186.
Compton, J., Mallinson, D., Glenn, C. R., Filippelli, G., Föllmi, K., Shields, G., et al., 2000. Variation in the global phosphorus cycle. SEPM Special Publications, 66: 21–33.
Dai, J. C., Song, J. M., Li, X. G., Zheng, G. X., and Yuan, H. M., 2006. Phosphorus and its environmental marker function in Jiaozhou Bay sediments. Environmental Science, 27: 1953–1962.
Ding, Y. M., 2014. Impacts of Ulva (Enteromorpha) prolifera in the green tide on the Yellow Sea ecological environment — Implications from migration and transformation of biogenic elements. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China, Qingdao.
Duan, H., Ma, R., Xu, X., Kong, F., Zhang, S., Kong, W., et al., 2009. Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(10): 3522–3528.
Einstein, H. A., and Krone, R. B., 1962. Experiments to determine modes of cohesive sediment transport in salt water. Journal of Geophysical Research, 67(4): 1451–1461.
Froelich, P. N., 1988. Kinetic control of dissolved phosphate in natural rivers and estuaries: A primer on the phosphate buffering mechanism. Limnology and Oceanography, 33: 649–668.
Guo, W., Zhao, L., and Li, X., 2016. The interannual variation of green tide in the Yellow Sea. Haiyang Xuebao, 38(12): 36–45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang, J., Wu, L., Gao, S., and Li, J., 2014. Analysis on the interannual distribution variation of green tide in Yellow Sea. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 23: 572–578.
Li, M. G., 2011. Advances in the research and development of the radial sandbanks. Journal of the Waterways and Harbors Division, 32(4): 229–243.
Lin, P., and Guo, L., 2016. Dynamic changes in the abundance and chemical speciation of dissolved and particulate phosphorus across the river-lake interface in southwest Lake Michigan. Limnology and Oceanography, 61(2): 771–789.
Monbet, P., Brunskill, G. J., Zagorskis, I., and Pfitzner, J., 2007. Phosphorus speciation in the sediment and mass balance for the central region of the Great Barrier Reef continental shelf (Australia). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71: 2762–2779.
Murphy, J., and Riley, J. P., 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural water. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27: 31–36.
Nguyen, L. M., 2000. Phosphate incorporation and transformation in surface sediments of a sewage-impacted wetland as influenced by sediment sites, sediment pH and added phosphate concentration. Ecological Engineering, 14: 139–155.
Otten, T. G., Xu, H., Qin, B., Zhu, G., and Paerl, H. W., 2012. Spatiotemporal patterns and ecophysiology of toxigenic microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: Implications for water quality management. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(6): 3480–3488.
Petersen, G. W., and Corey, R. B., 1966. A modified Chang and Jackson procedure for routine fraction of inorganic soil phosphates. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 30: 563–565.
Prastka, K., Sanders, R., and Jickells, T., 1988. Has the role of estuaries as sources or sinks of dissolved inorganic phosphorus changed over time? Results of a Kd study. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 36: 718–728.
Qi, X. H., 2005. Studies on biogeochemistry of phosphorus in the coastal waters of China. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China, Qingdao.
Redfield, A. C., Ketchum, B. H., and Richards, F. A., 1963. The influence of organisms on the composition of the sea water. In: The Sea. Hill, M. N., ed., John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 12–17.
Ruban, V., López-Sánchez, J. F., Pardo, P., Rauret, G., Muntau, H., and Quevauviller, P., 1999. Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1: 51–56.
Ruttenberg, K. C., 1992. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography, 37: 1460–1482.
Santschi, P. H., 1995. Seasonality in nutrient concentrations in Galveston Bay. Marine Environmental Research, 40: 337–362.
Shi, X., Qi, M., Tang, H., and Han, X., 2015. Spatial and temporal nutrient variations in the Yellow Sea and their effects on Ulva prolifera blooms. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 163: 36–43.
Slomp, C. P., Epping, E. H. G., Helder, W., and Van Rassphorst, W., 1996. A key role for iron-bound phosphorus in authigenic apatite formation in North Atlantic continental platform sediments. Journal of Marine Research, 54: 1179–1205.
Song, G., 2014. The distribution of phosphorus forms and affecting factors in the sediments of the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China, Qingdao.
Su, J., Fan, W., and Wang, F., 2020. Correlation analysis of spatial distribution change and driving factors of laver cultivation in Haizhou Bay. China Agricultural Information, 32: 22–31.
Wang, A., Gao, S., Jia, J., and Pan, S., 2005. Impact of Spartina alterniflora on sedimentary and morphological evolution of tidal salt marshes of Jiangsu, China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 60: 61–70.
Wang, C., and Morrison, R. J., 2014. Phosphorus speciation and changes with depth in the sediment of Lake Illawarra, New South Wales, Australia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(8): 3529–3541.
Wang, X. H., Qiao, F. L., Lu, J., and Gong, F., 2011. The turbidity maxima of the northern Jiangsu shoal-water in the Yellow Sea, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 93: 202–211.
Wei, Q., Wang, B., Yao, Q., Fu, M., Sun, J., Xu, B., et al., 2018. Hydro-biogeochemical processes and their implications for Ulva prolifera blooms and expansion in the world’s largest green tide occurrence region (Yellow Sea, China). Science of the Total Environment, 645: 257–266.
Wei, Q. S., and Wang, B. D., 2012. Distributions of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the surface sediments and their ecological implications in the areas of cold water mass and off the western coast of the Southern Yellow Sea. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32: 1697–1707.
Withers, P. J. A., Jarvie, H. P., Hodgkinson, R. A., Palmer-Felgate, E. J., Bates, A., Neal, M., et al., 2009. Characterization of phosphorus sources in rural watersheds. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38: 1998–2011.
Zhang, H., Wang, G., Zhang, C., Su, R., Shi, X., and Wang, X., 2020. Characterization of the development stages and roles of nutrients and other environmental factors in green tides in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Harmful Algae, 98: 101893.
Zhang, X. X., Yan, C., Xu, P., Dai, Y., Yan, W., Ding, X., et al., 2013a. Historical evolution of tidal flat reclamation in the Jiangsu coastal areas. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68: 1549–1558.
Zhang, X. Y., Yang, Q., Sun, Y., and Huang, J. S., 2013b. The distribution of phosphorus forms and bioavailability in sediments from Huang Dong Hai continental shelf. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33: 3509–3519.
Zhu, W., Wang, N., Dong, X., Cong, X., Han, X., and Pan, X., 2020. Study on the influence of turbulence intensity and sediment concentration on the settling velocity in Haizhou Bay. Marine Science Bulletin, 39: 475–506.
Zhu, Y., 2009. Preliminary study on distribution characteristics and biogeochemistry of various phosphorus forms in the sediments of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. PhD thesis. Ocean University of China, Qingdao.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1901215), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFE0124700), the China National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2022YFC3106002), and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST (No. 2020r028). We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Zheng, P., Su, R. et al. Role of Resuspended Sediments as Sources of Dissolved Inorganic Phosphorus Along Different Dimensions in the Subei Shoal, South Yellow Sea, China. J. Ocean Univ. China 22, 161–170 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-023-5275-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-023-5275-4