Abstract
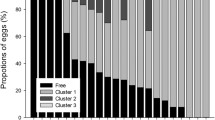
The buoyancy of Artemia resting eggs is a feature with both biological and economic importance. Since the buoyancy of resting eggs is dependent on the specific weight of the eggs or salinity of ambient water, we suppose that habitat salinity may exert a selection pressure on resting egg buoyancy, and thereby lower habitat salinity may result in better floating capacity of resting eggs and vice versa. In this study, we compared the floating capacity of resting eggs from 25 Artemia populations. The results showed that the floating capacity of resting eggs varied greatly among different populations. The minimum salinity to float some eggs varied from 0 to 180. The salinity at which all resting eggs floated varied from 80 to 320. The FS50 (salinity with 50% eggs floating) of Zhundong and Yuncheng population was not detectable (over 50% eggs floating in distilled water), that of Kyêbxang Co population was 4.3, while the maximum value found in Dabancheng population was 234.5. In terms of the ‘apparent specific weight’ of resting eggs, 18 populations exhibited a single-peak distribution pattern, while the other 7 populations showed a multiple-peak or non-peak distribution. Negative correlations were found between FS50 and chorion thickness, and between FS50 and the volume percentage of the chorion in eggs, supporting a previous standpoint that shell thickness was a determinative factor for the floating capacity of resting eggs. A positive correlation was determined between FS50 and habitat salinity. The hypothesis that habitat salinity may cause a directional selection on the buoyancy of resting eggs seems to be true.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abatzopoulos, T. J., Baxevanis, A. D., Triantaphyllidis, G. V., Criel, G., Pador, E. L., Van Stappen, G., et al., 2006. Quality evaluation of Artemia urmiana Günther (Urmia Lake, Iran) with special emphasis on its particular cyst characteristics (International study on Artemia LXIX). Aquaculture, 254(1): 442–454.
Abatzopoulos, T. J., Kastritsis, C. D., and Triantaphyllidis, C. D., 1986. A study of karyotypes and heterochromatic associations in Artemia, with special reference to two N. Greek populations. Genetica, 71(1): 3–10.
Abatzopoulos, T. J., Zhang, B., and Sorgeloos, P., 1998. Artemia tibetiana: Preliminary characterization of a new Artemia species found in Tibet (People’s Republic of China). International study on Artemia. LIX. International Journal of Salt Lake Research, 7(1): 41–44.
Arashkevich, E. G., Sapozhnikov, P. V., Soloviov, K. A., Kudyshkin, T. V., and Zavialov, P. O., 2009. Artemia parthenogenetica (Branchiopoda: Anostraca) from the Large Aral Sea: Abundance, distribution, population structure and cyst production. Journal of Marine Systems, 76(3): 359–366.
Asem, A., and Sun, S. C., 2014. Biometric characterization of Chinese parthenogenetic Artemia (Crustacea: Anostraca) cysts, focusing on its relationship with ploidy and habitat altitude. North-Western Journal of Zoology, 10(1): 149–157.
Asem, A., Eimanifar, A., and Sun, S. C., 2016. Genetic variation and evolutionary origins of parthenogenetic Artemia (Crustacea: Anostraca) with different ploidies. Zoologica Scripta, 45(4): 421–436.
Asem, A., Eimanifar, A., Rastegar-Pouyani, N., Hontoria, F., De Vos, S., Van Stappen, G., et al., 2020. An overview on the nomenclatural and phylogenetic problems of native Asian brine shrimps of the genus Artemia Leach, 1819 (Crustacea, Anostraca). ZooKeys, 902(2): 1–15.
Baitchorov, V M., and Nagorskaja, L. L., 1999. The reproductive characteristics of Artemia in habitats of different salinity. International Journal of Salt Lake Research, 8(4): 287–291.
Chang, M. S., Asem, A., and Sun, S. C., 2017. The incidence of rare males in seven parthenogenetic Artemia (Crustacea: Anostraca) populations. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 41: 138–143.
Clegg, J. S., and Conte, F. P., 1980. A review of the cellular and developmental biology of Artemia. In: The Brine Shrimp Artemia, Volume 2, Physiology, Biochemistry, Molecular Biology. Persoone, G., et al., eds., Universa Press, Wetteren, 211–254.
Drinkwater, L. E., and Crowe, J. H., 1991. Hydration state, metabolism, and hatching of Mono Lake Artemia resting eggs. Biological Bulletin, 180(3): 432–439.
Eimanifar, A., Rezvani, S., and Carapetian, J., 2006. Genetic differentiation of Artemia urmiana from various ecological populations of Urmia Lake assessed by PCR amplified RFLP analysis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 333(2): 275–285.
Gilbert, J. J., 2017. Resting-egg hatching and early population development in rotifers: A review and a hypothesis for differences between shallow and deep waters. Hydrobiologia, 796(1): 235–243.
Lavens, P., and Sorgeloos, P., 1987. The cryptobiotic state of Artemia resting eggs, its diapause deactivation and hatching: A review. In: Artemia Research and Its Applications, Volume 2, Metabolism and Development, Enzymes Related to Nucleotide and Metabolism, Genome Structure and Expression. Decleir, W., et al., eds., Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, 27–64.
Lenz, P. H., 1980. Ecology of an alkali-adapted variety of Artemia from Mono Lake, California, USA. In: The Brine Shrimp Artemia, Volume 3, Ecology, Culturing, Use in Aquaculture. Persoone, G., et al., eds., Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, 79–96.
Leonova, G. A., Bobrov, V. A., Bogush, A. A., Bychinskii, V. A., and Anoshin, G. N., 2007. Geochemical characteristics of the modern state of salt lakes in Altai Krai. Geochemistry International, 45(10): 1025–1039.
Li, W. H., 1988. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of Altun Mountain Nature Reserve. Xinjiang Environmental Protection, 1988(1): 13–16 (in Chinese).
Liang, K. Y., 1987. The salt lake and its geological and hydrogeological conditions in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Research, 1987(1): 3–10 (in Chinese).
Litvinenko, L. I., Litvinenko, A. I., and Boiko, E. G., 2016. Brine Shrimp Artemia in Western Siberia Lakes. Siberian Publishing Company ‘Nauka’, Novosibirsk, 295pp.
Liu, C. S., and Wang, H. Y., 1995. The bait analysis on Artemia sinica in saltlake at Shanxi Yuncheng. Journal of Shanxi Teacher’s University, 9(1): 36–38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J. Y., Zheng, M. P., and Luo, J., 1998. Study of Artemia in Lagkor Co, Tibet, I: Biological feature. Journal of Lake Sciences, 10(002): 92–96 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, S. S., Liu, X. F., Jia, Q. X., Kong, F. J., Zheng, M. P., and Lü, G. J., 2014. Assessment of spatial distribution and cysts resources of Artemia in late autumn in Dangxiong Co salt lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(1): 26–33.
Ma, L., and Wang, W., 2003. Comparison of the biological characteristics of two Artemia populations from Aqikekule Lake and Gahai Lake. Marine Sciences, 27(11): 34–37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma, Z. Z., 1995. Preliminary studies on algae in salt pans and saline lakes of northern China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 26(3): 317–322 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Makkaveev, P. N., and Stunzhas, P. A., 2017. Salinity measurements in hyperhaline brines: A case study of the present Aral Sea. Oceanology, 57(6): 892–898.
Mirabdullayev, I. M., Joldasova, I. M., Mustafaeva, Z. A., Kazakhbaev, S., Lyubimova, S. A., and Tashmukhamedov, B. A., 2004. Succession of the ecosystems of the Aral Sea during its transition from oligohaline to polyhaline water body. Journal of Marine Systems, 47(1): 101–107.
Mura, G., and Nagorskaya, L., 2005. Notes on the distribution of the genus Artemia in the former USSR countries. Journal of Biological Research, 4: 139–150.
Nambu, Z., Tanaka, S, and Nambu, F., 2004. Influence of photoperiod and temperature on reproductive mode in the brine shrimp, Artemia franciscana. Journal of Experimental Zoology, Part A. Comparative Experimental Biology, 301A(6): 542–546.
Pan, Z. Q., Sun, J. H., Li, M. R., and Bian, B. Z., 1991. The biometrics of Artemia parthenogenetica from different localities in Shandong and Xinjiang. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1991(2): 62–69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Proctor, V. W., 1964. Viability of crustacean eggs recovered from ducks. Ecology, 45(3): 656–658.
Ren, M. L., Guo, Y., Wang, J. L., Su, R., Li, H., and Ren, B., 1996. Survey of Artemia Ecology and Resources in Inland Salt Lakes in Northwest China. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press, Harbin, 260pp (in Chinese).
Sainz-Escudero, L., López-Estrada, E. K., Rodríguez-Flores, P. C., and García-París, M., 2021. Settling taxonomic and nomenclatural problems in brine shrimps, Artemia (Crustacea: Branchiopoda: Anostraca), by integrating mitogenomics, marker discordances and nomenclature rules. PeerJ, 9: e10865.
Sang, J., 2018. Analysis of bacterial diversity in Yuncheng Salt Lake and polyphasic taxonomy of four novel halophilic bacteria. Master thesis. Shandong University (Weihai) (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sorgeloos, P., 1997. Determination and identification of biological characteristics of Artemia urmiana for application in aquaculture. In: The Lake Urmiah Cooperation Project. Sorgeloos, P., ed., Laboratory of Aquaculture and Artemia Reference Center, Belgium, 1–50.
Sura, S. A., and Belovsky, G. E., 2016. Impacts of harvesting on brine shrimp (Artemia franciscana) in Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Ecological Applications, 26(2): 407–414.
Tachibana, A., Nomura, H., and Ishimaru, T., 2019. Impacts of long-term environmental variability on diapause phenology of coastal copepods in Tokyo Bay, Japan. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(1): S273–S283.
Triantaphyllidis, G. V., Abatzopoulos, T. J., and Sorgeloos, P., 1998. Review of the biogeography of the genus Artemia (Crustacea, Anostraca). Journal of Biogeography, 25(2): 213–226.
Van Stappen, G., 2002. Zoogeography. In: Artemia: Basic and Applied Biology. Abatzopoulos, T. J., et al., eds., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 171–224.
Van Stappen, G., Sui, L. Y., Hoa, V. N., Tamtin, M., Nyonje, B., De Medeiros Rocha, R., et al., 2020. Review on integrated production of the brine shrimp Artemia in solar salt ponds. Reviews in Aquaculture, 12(2): 1054–1071.
Van Stappen, G., Sui, L. Y., Xin, N. H., and Sorgeloos, P., 2003. Characterisation of high-altitude Artemia populations from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, PR China. Hydrobiologia, 500: 179–192.
Vanhaecke, P., Tackaert, W., and Sorgeloos, P., 1987. The biogeography of Artemia: An updated review. In: Artemia Research and Its Applications, Volume 1, Morphology, Genetics, Strain Characterization, Toxicology. Sorgeloos, P., et al., eds., Universa Press, Wetteren, 129–155.
Wang, S. F., and Sun, S. C., 2007. Comparative observations on the cyst shells of seven Artemia strains from China. Microscopy Research and Technique, 70(8): 663–670.
Wang, S. M., and Dou, H. S. (chief eds.), 1998. Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing, 580pp (in Chinese).
Wang, Z. C., Asem, A., Okazaki, R. K., and Sun, S. C., 2019. The critical stage for inducing oviparity and embryonic diapause in parthenogenetic Artemia (Crustacea: Anostraca): An experimental study. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 37(5): 1669–1677.
Wu, Q., Zheng, M. P., Nie, Z., and Bu, L. Z., 2012. Natural evaporation and crystallization regularity of Dangxiongcuo carbonate-type salt lake brine in Tibet. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 28(9): 1895–1903 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao, Y. K., Shirodkar, P. V., Liu, W. G., Wang, Y. H., and Jin, L., 1999. Study on boron isotope geochemistry of salt lakes in Qaidam Basin, Qinghai. Progress in Natural Science, 9(7): 38–44 (in Chinese).
Xu, M. Q., Cao, H., Jia, Q. X., Gao, Y. R., and Chen, S. G., 2002. Preliminary study of plankton community diversity of the Gahai Salt Lake in the Qaidam Basin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 10(1): 38–43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, G., Hou, L., and Cai, H. Y., 1996. Study on the karyotypes of four Artemia populations from salt lakes in China. Zoological Research, 17(4): 489–493 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin, X. C., Yin, H., Zhou, K. X., Zhang, D. C., and Shi, J. P., 2001. Development and utilization of salt algae (Dunaliella salina) and brine shrimp (Artemia spp.) in the plateau salt lake of China. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 9(1): 4–8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, R. S., Liu, F. Q., Zhao, X. X., and Zheng, J. Y., 1990. Studies on the chromosomal ploidy composition of the brine shrimp, Artemia spp. Acta Zoologica. Sinica, 36(4): 412–419 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, R. X., Liao, L., Yin, C. T., and Guli, N., 2013. Isolation, antibacterial activity and growth characters of halophilic microorganisms from Dabancheng Salt Lake, Xinjiang. Biotech World, 10(7): 2–3 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng, M. P., Liu, X. F., and Zhao, W., 2007. Tectonogeochemical and biological aspects of salt lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(12): 1698–1708 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng, M. P., Xiang, J., Wei, X. J., and Zheng, Y., 1989. Salt Lakes on Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Beijing Science and Technology Press, Beijing, 431pp (in Chinese).
Zheng, X. Y., Zhang, M. G., Xu, C., and Li, B. X., 2002. An Overview of Salt Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing, 415pp (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Science and Technology Project of Tibet Autonomous Region (Nos. XZ201703-GB-04, XZ202102YD0022C), and the Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2020C26008). We are grateful to Ms. Bakytgul Ospan, Mr. Jianbao Liu, Mr. Hongjun Zhang, Mr. Liwei Luan, Mr. Dian’an Zhang, Mr. Rongchang Tian and Mr. Pengfei Wang for providing samples of resting eggs and the collecting information of some samples. We thank Miss Ran Gao for her help in the experiment. We also thank Prof. Zengjun Du for clarifying the determination time of salinities reported by Sang (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Huang, Z., Guo, Y. et al. A Comparative Study on the Buoyancy of Resting Eggs from Different Artemia Populations, with Emphasis on Its Relationships with Habitat Salinity and Biometric Characters of Resting Eggs. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 1585–1596 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-5031-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-5031-1