Abstract
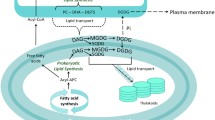
Marine microalga Isochrysis galbana is an important feed species with a high nutritional value. Different from other unicellular algae, its cell contains two chloroplasts which are the major sites for lipid synthesis. Here, we optimized a chloroplast isolation approach suitable for the isolation of I. galbana chloroplasts and determined the purity and integrity of the isolated chloroplasts through microscopic observations and enzyme activity assay. The chloroplast lipids were analyzed with a ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-Q Exactive Orbitrap-mass spectrometry. This newly developed isolation approach is simple and reliable to isolate chloroplasts with high integrity and purity. The average yield of intact chloroplasts was 15.3%±0.1%. Glycolipids and acylglycerols were the main chloroplast lipids. Glycolipids accounted for 56.6% of chloroplast lipid. Digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) and sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol (SQDG) were the main glyceroglycolipids. The fatty acyl R1/R2 were mostly 18:4/16:1, 18:3/16:1 and 18:4/18:5 in DGDGs, 14:0/18:4, 18:4/18:5, 18:4/18:4 and 18:3/18:4 in MGDGs and 16:0/14:0, 16:0/18:3, and 18:4/18:3 in SQDGs. In addition, diacylglycerol (DAG) was the most abundant acylglycerols; the content of 22:6/18:4-DAG was the highest. There was a little amount of glycosphingolipid (GSL) in chloroplast. Digalactosylmonoglyceride (DGMG), monogalactosylmonoglyceride (MGMG), sulfoquinovosylmonoacylglycerol (SQMG), monoglyceride (MAG), phospholipids (PLs), ceramide (Cer) and betaine lipids were nearly undetectable in chloroplast. The fatty acid proportions of DGDGs, MGDGs, SQDGs, DAGs, triglycerides (TAGs) and GSLs were either higher or lower than or similar to those of whole-cell. Collectively, our isolation approach is applicable to many aspects of chloroplast biology, and may offer a reference for the isolation of chloroplasts from other marine microalgae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhattab, M., Kermanshahi-Pour, A., and Brooks, M. S. L., 2018. Microalgae disruption techniques for product recovery: Influence of cell wall composition. Journal of Applied Phycology, 31(1): 61–88, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1560-9.
Andreyev, A. Y., Fahy, E., Guan, Z. Q., Kelly, S., Li, X., McDonald, J. G., et al., 2010. Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR-4-activated macrophages. Journal of Lipid Research, 51(9): 2785–2797, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M008748.
Anna, E. T., Petrie, J. R., Pushkar, S., Thomas, V., and Singh, S. P., 2015. Expression of mouse MGAT in Arabidopsis results in increased lipid accumulation in seeds. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6: 1180, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01180.
Arnon, D. I., 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiology, 24(1): 1–15, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1.
Aronsson, H., and Jarvis, P., 2002. A simple method for isolating import-competent Arabidopsis chloroplasts. FEBS Letters, 529(2–3): 215–220, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03342-2.
Bendif, E. M., Probert, I., Carmichael, M., Romac, S., Hagino, K., and De Vargas, C., 2014. Genetic delineation between and within the widespread coccolithophore morpho-species Emiliania huxleyi and Gephyrocapsa oceanica (Haptophyta). Journal of Phycology, 50: 140–148, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12147.
Bligh, E. G., and Dyer, W. J., 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 37(8): 911–917, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099.
Chen, M., Markham, J. E., Dietrich, C. R., Jaworski, J. G., and Cahoon, E. B., 2008. Sphingolipid long-chain base hydroxylation is important for growth and regulation of sphingolipid content and composition in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 20(7): 1862–1878, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.057851.
Choudhury, M. D., and Chakrabarti, P., 1980. Cellular and chloroplast lipid composition of the leaves of Mimosa pudica. Phytochemistry, 19(4): 519–523, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(80)87006-3.
Čopič, A., Antoine-Bally, S., Giménez-Andrés, M., Garay, C. L. T., Antonny, B., Manni, M. M., et al., 2018. A giant amphipathic helix from a perilipin that is adapted for coating lipid droplets. Nature Communications, 9(1): 1332, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03717-8.
Eltgroth, M. L., Watwood, R. L., and Wolfe, G. V., 2005. Production and cellular localization of neutral long-chain lipids in the Haptophyte algae Isochrysis galbana and Emiliania huxleyi. Journal of Phycology, 41(5): 1000–1009, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00128.x.
Ferro, M., Salvi, D., Brugière, S., Miras, S., Kowalski, S., Louwagie, M., et al., 2003. Proteomics of the chloroplast envelope membranes from Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2(5): 325–345, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M300030-MCP200.
Fitzpatrick, L. M., and Keegstra, K., 2001. A method of isolating a high yield of Arabidopsis chloroplasts capable of efficient import of precursor proteins. Plant Journal, 27(1): 59–65, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0960-7412.2001.01061.x.
Gaude, N., Brehelin, C., Tischendorf, G., Kessler, F., and Dormann, P., 2007. Nitrogen deficiency in Arabidopsis affects galactolipid composition and gene expression and results in accumulation of fatty acid phytyl esters. Plant Journal, 49(4): 729–739, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02992.x.
Gnouma, A., Sadovskaya, I., Souissi, A., Sebai, K., Medhioub, A., Grard, T., et al., 2017. Changes in fatty acids profile, monosaccharide profile and protein content during batch growth of Isochrysis galbana (T.iso). Aquaculture Research, 48(9): 4982–4990, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13316.
Granafei, S., Losito, I., Palmisano, F., and Cataldi, T. R. I., 2017. Unambiguous regiochemical assignment of sulfoquinovosyl mono- and diacylglycerols in parsley and spinach leaves by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization sequential mass spectrometry assisted by regioselective enzymatic hydrolysis. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 31(18): 1499–1509, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.7928.
Guschina, I. A., and Harwood, J. L., 2006. Lipids and lipid metabolism in eukaryotic algae. Progress in Lipid Research, 45(2): 160–186, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2006.01.001.
Hölzl, G., and Dörmann, P., 2019. Chloroplast lipids and their biosynthesis. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 70: 51–81, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physchem-042018-052300.
Hori, T., and Green, J. C., 1985. The ultrastructure of mitosis in Isochrysis galbana parke (Prymnesiophyceae). Protoplasma, 125(1): 140–151, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297359.
Huang, L. L., Xu, J. L., Zong, C. H., Zhu, S., Ye, M. W., Zhou, C. X., et al., 2017. Effect of high temperature on the lipid composition of Isochrysis galbana Parke in logarithmic phase. Aquaculture International, 25(1): 327–339, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-0031-z.
Huang, Q., Lei, H., Dong, M., Tang, H., and Wang, Y., 2019. Quantitative analysis of 10 classes of phospholipids by ultrahighperformance liquid chromatography tandem triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. Analyst, 144(13): 3980–3987, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an00676a.
Huerlimann, R., and Heimann, K., 2013. Comprehensive guide to acetyl-carboxylases in algae. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 33(1): 49–65, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2012.668671.
Jarvis, P., Dormann, P., Peto, C. A., Lutes, J., Benning, C., and Chory, J., 2000. Galactolipid deficiency and abnormal chloroplast development in the Arabidopsis MGD synthase 1 mutant. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(14): 8175–8179, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.100132197.
Kalisch, B., Dörmann, P., and Hólzl, G., 2016. DGDG and glycolipids in plants and algae. Subcell Biochem, 86: 51–83, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25979-6_3.
Kelly, A. A., Froehlich, J. E., and Dormann, P., 2003. Disruption of the two digalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase genes DGD1 and DGD2 in Arabidopsis reveals the existence of an additional enzyme of galactolipid synthesis. Plant Cell, 15(11): 2694–2706, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.016675.
Klein, U., Chen, C., Gibbs, M., and Platt-Aloia, K. A., 1983. Cellular fractionation of Chlamydomonas reinhardii with emphasis on the isolation of the chloroplast. Plant Physiology, 72(2): 481–487, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.72.2.481.
Kobayashi, K., Endo, K., and Wada, H., 2016. Role of lipids in chloroplast biogenesis. Subcellular Biochemistry, 86: 21–49, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25979-6_5.
Kobayashi, K., Kondo, M., Fukuda, H., Nishimura, M., and Ohta, H., 2007. Galactolipid synthesis in chloroplast inner envelope is essential for proper thylakoid biogenesis, photosynthesis, and embryogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(43): 17216–17221, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704680104.
LaBrant, E., Barnes, A. C., and Roston, R. L., 2018. Lipid transport required to make lipids of photosynthetic membranes. Photosynthesis Research, 138(3): 345–360, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-018-0545-5.
Li, S., Xu, J., Chen, J., Chen, J., Zhou, C. X., and Yan, X. J., 2014. Characterization of the triacylglycerol profile in marine diatoms by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Applied Phycology, 26(3): 1389–1398, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0159-4.
Lim, T. K., 2014. Mimosa pudica. Springer Netherlands, Germany, 821–835.
Liu, B., and Benning, C., 2013. Lipid metabolism in microalgae distinguishes itself. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 24(2): 300–309, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2012.08.008.
Liu, W., Pearce, C. M., Alabi, A. O., and Gurney-Smith, H., 2009. Effects of microalgal diets on the growth and survival of larvae and post-larvae of the basket cockle, Clinocardium nuttallii. Aquaculture, 293(3): 248–254, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.04.032.
Lynch, D. V., and Dunn, T. M., 2004. An introduction to plant sphingolipids and a review of recent advances in understanding their metabolism and function. New Phytologist, 161: 677–702, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2003.00992.x.
Mason, C. B., Bricker, T. M., and Moroney, J. V., 2006. A rapid method for chloroplast isolation from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nature Protocols, 1(5): 2227–2230, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.348.
Moellering, E. R., Miller, R., and Benning, C., 2009. Molecular genetics of lipid metabolism in the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In: Lipids in Photosynthesis. Wada, H., and Murata, N., eds., Springer Netherlands, Germany, 139–155.
Mosmann, T., 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal of Immunological Methods, 65(1): 55–63, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4.
Naumann, I., Darsow, K. H., Walter, C., Lange, H. A., and Buchholz, R., 2007. Identification of sulfoglycolipids from the alga Porphyridium purpureum by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 21(19): 3185–3192, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.3190.
Pernet, F., and Tremblay, R., 2004. Effect of varying levels of dietary essential fatty acid during early ontogeny of the sea scallop Placopecten magellanicus. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 310(1): 73–86, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2004.04.001.
Piro, A., Serra, I. A., Spadafora, A., Cardilio, M., Bianco, L., Perrotta, G., et al., 2015. Purification of intact chloroplasts from marine plant Posidonia oceanica suitable for organelle proteomics. Proteomics, 15(23–24): 4159–4174, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201500246.
Rausch, T., 1981. The estimation of micro-algal protein content and its meaning to the evaluation of algal biomass I comparison of methods for extracting protein. Hydrobiologia, 78(3): 237–251, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00008520.
Reyes, C. D. L., Ortega, M. J., Rodríguez-Luna, A., Talero, E., and Zubia, E., 2016. Molecular characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of galactosylglycerides and galactosylceramides from the microalga Isochrysis galbana. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 64(46): 8783–8794, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03931.
Roche, S. A., and Leblond, J. D., 2010. Betaine lipids in chlorarachniophytes. Phycological Research, 58(4): 298–305, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1835.2010.00590.x.
Rolland, N., Curien, G., Finazzi, G., Kuntz, M., Maréchal, E., Matringe, M., et al., 2012. The biosynthetic capacities of the plastids and integration between cytoplasmic and chloroplast processes. Annual Review of Genetics, 46: 233–264, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132544.
Seigneurin-Berny, D., Salvi, D., Dorne, A. J., Joyard, J., and Rolland, N., 2008. Percoll-purified and photosynthetically active chloroplasts from Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 46(11): 951–955, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.06.009.
Silitonga, A. S., Masjuki, H. H., Ong, H. C., Mahlia, T. M. I., and Kusumo, F., 2017. Optimization of extraction of lipid from Isochrysis galbana microalgae species for biodiesel synthesis. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 39: 1167–1175, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2017.1310957.
Simionato, D., Block, M. A., La Rocca, N., Jouhet, J., Marechal, E., Finazzi, G., et al., 2013. The response of Nannochloropsis gaditana to nitrogen starvation includes de novo biosynthesis of triacylglycerols, a decrease of chloroplast galactolipids, and reorganization of the photosynthetic apparatus. Eukaryot Cell, 12(5): 665–676, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.00363-12.
Spurr, A. R., 1969. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. Journal of Ultrastructure Research, 26(1): 31–43, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5320(69)90033-1.
Sun, J., Qiu, C., Qian, W., Wang, Y., Sun, L., Li, Y., et al., 2019. Ammonium triggered the response mechanism of lysine crotonylome in tea plants. BMC Genomics, 20(1): 340, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5716-z.
Wikfors, G. H., Ferris, G. E., and Smith, B. C., 1992. The relationship between gross biochemical composition of cultured algal foods and growth of the hard clam, Mercenaria mercenaria (L.). Aquaculture, 108(1): 135–154, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(92)90324-E.
Wilfling, F., Wang, H., Haas, J. T., Krahmer, N., Gould, T. J., Uchida, A., et al., 2013. Triacylglycerol synthesis enzymes mediate lipid droplet growth by relocalizing from the ER to lipid droplets. Developmental Cell, 24(4): 384–399, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.01.013.
Xu, C. C., Fan, J. L., and Shanklin, J., 2020. Metabolic and functional connections between cytoplasmic and chloroplast triacylglycerol storage. Progress in Lipid Research, 80: 101069, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101069.
Xu, J. L., Chen, D. Y., Yan, X. J., Chen, J. J., and Zhou, C. X., 2010. Global characterization of the photosynthetic glycerolipids from a marine diatom Stephanodiscus sp. by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 663(1): 60–68, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.01.026.
Yan, X. J., Li, H. Y., Xu, J. L., and Zhou, C. X., 2010. Analysis of phospholipids in microalga Nitzschia closterium by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 28(1): 106–112, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-010-9263-3.
Yang, M., Jiang, J. P., Xie, X., Chu, Y. D., Fan, Y., Cao, X. P., et al., 2017. Chloroplasts isolation from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under nitrogen stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8: 1503, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01503.
Yoshida, H., Saiki, M., Yoshida, N., Tomiyama, Y., and Mizushina, Y., 2009. Fatty acid distribution in triacylglycerols and phospholipids of broad beans (Vicia faba). Food Chemistry, 112(4): 924–928, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.003.
Yu, F. Y., Liu, B. H., Chou, H. N., and Chu, F. S., 2002. Development of a sensitive ELISA for the determination of microcystins in algae. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(15): 4176–4182, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0202483.
Zakim, D., and Herman, R. H., 1969. Regulation of fatty acid synthesis. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 22(2): 109–136, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/22.2.200.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ningbo Science and Technology Research Projects (No. 2019B10006), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFD0900400), the Zhejiang Major Science Project (No. 2019C02057), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA, the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (No. 2019A610416), the Ningbo Science and Technology Research Projects (No. 2019C10023), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31801724).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Y., Li, Y., Xu, J. et al. Isolation of Chloroplasts from Marine Microalga Isochrysis galbana Parke for Their Lipid Composition Analysis. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 225–235 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4834-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4834-4