Abstract
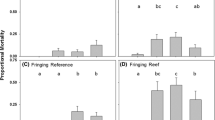
The release technique, affecting the survival rate of fish species released for stock enhancement, plays a vital role in the effectiveness of the enhancement. In order to improve the probability of released fish settling down to bottom, a new cage-based release technique was designed and tested via a water tank with artificial reef models. Two coral reef fish species, Sebastes schlegelii and Paralichthys olivaceus were assessed using this technique. Fish behavior and distribution in water tank were recorded and compared with the traditional release release techniques. Results showed that in the case of cage-based release technique: 1) when the release process is just finished, the distribution index (DI) of juveniles S. schlegelii and P. olivaceus were 97.8% and 98.9% at reef area, 40% and 71.1% at release point, respectively, which was higher than those using two alternative techniques; 2) its impact duration was less than that in the other two conditions, where the DI within 4 hours was higher after releasing, especially for S. schiegelii. These findings indicated that the new cage-based technique could release the fish into the specified location, and has a potential to mitigate the stress reaction of fish caused by releasing process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R. M., Metaxas, A., and Snelgrove, P. V. R., 2018. Applying movement ecology to marine animals with complex life cycles. Annual Review of Marine Science, 10: 19–42.
Aprahamian, M. W., Smith, K. M., Mcginnity, P., Mckelvey, S., and Taylor, J., 2003. Restocking of salmonids-Opportunities and limitations. Fisheries Research (Amsterdam), 62: 0–227.
Blaxter, J. H. S., 2000. The enhancement of marine fish stocks. Advances in Marine Biology, 38: 1–54.
Brennan, N. P., Darcy, M. C., and Leber, K. M., 2006. Predator-free enclosures improve post-release survival of stocked common snook. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 335: 302–311.
Dance, S. K., Lane, I., and Bell, J. D., 2003. Variation in short-term survival of cultured sandfish (Holothuria scabra) released in mangrove-seagrass and coral reef flat habitats in Solomon Islands. Aquaculture, 220: 495–505.
Demirci, A., and Bayraktar O., 2019. Barotrauma treatment performance of fish release devices and its effects on fishing operations. Ege Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 36: 2.
Feng, J. R., Liu, L. M., and Jiang, H. B., 2014. Histological observation of germ cell development and discovery of spermatophores in ovoviviparous black rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli, Hilgendorf) in reproductive season. Journal of Ocean University of China, 13: 830–836.
Garlock, T. M., and Lorenzen, K., 2017. Marine angler characteristics and attitudes toward stock enhancement in Florida. Fisheries Research, 186: 439–445.
Gitschlag, G., and Renaud, M., 1994. Field experiments on survival rates of caged and released red snapper. North American Journal of Fisheries Management, 14: 6.
Hair, C., 2016. Optimising methods for community-based sea cucumber ranching: Experimental releases of cultured juvenile Holothuria scabra into seagrass meadows in Papua New Guinea. Aquaculture Reports, 3: 198–208.
Hannah, R. W., Rankin, P. S., and Blume, M. T. O., 2012. Use of a novel cage system to measure post-recompression survival of Northeast Pacific rockfish. Marine and Coastal Fisheries, 4: 46–56.
Jayasinghe, J. D. H. E., Bathige, S. D. N. K., Nam, B. H., Noh, J. K., and Lee, J., 2016. Comprehensive characterization of three glutathione s-transferase family proteins from black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology and Pharmacology, 189: 31–43.
Jiang, Z., Guo, Z., Zhu, L., and Liang, Z., 2019. Structural design principle and research progress of artificial reef. Journal of Fisheries of China, 43: 1881–1889 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Kitada, S., 2018. Economic, ecological and genetic impacts of marine stock enhancement and sea ranching: A systematic review. Fish and Fisheries, 19: 511–532.
Layman, C. A., Allgeier, J. E., and Montana, C. G., 2016. Mechanistic evidence of enhanced production on artificial reefs: A case study in a Bahamian seagrass ecosystem. Ecological Engineering, 95: 574–579.
Li, Y. S., and Qiu, X. L., 2008. Development and measures on stock enhancement of Korean fishery. China Fisheries, 8: 28–29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liang, J., 2013. Main factors affecting stock enhancement effect of marine fishery resources and its countermeasures. Chinese Fisheries Economics, 31: 122–134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, H., Lu, H., Zhang, P., Li, W., and Zhang, X., 2018. Attraction effect of artificial reef model and macroalgae on juvenile Sebastes schlegelii and Hexagrammos otakii. Journal of Fisheries of China, 42: 48–59 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, X. L., 2007. Studies on the stress response of fish. Journal of Hydroecology, 27: 1–3 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mclean, M., Roseman, E. F., Pritt, J. J., Kennedy, G., and Manny, B. A., 2015. Artificial reefs and reef restoration in the Laurentian great lakes. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 41: 1–8.
Rhodes, R., Whitehead, J., Smith, T., and Denson, M., 2018. A benefit-cost analysis of a red drum stock enhancement program in South Carolina. Journal of Benefit-Cost Analysis, 9: 323–341.
Rougier, A., Ateweberhan, M., and Harris, A., 2013. Strategies for improving survivorship of hatchery-reared juvenile Holothuria scabra in community-managed sea cucumber farms. SPC Beche-de-mer Information Bulletin, 33: 14–22.
Salayo, N. D., Azuma, T., and Castel, R. J. G., 2020. Stock enhancement of abalone, Haliotis asinina, in multi-use buffer zone of Sagay Marine Reserve in the Philippines. Aquaculture, 523: 735128.
Sánchez-Lamadrid, A., 2004. Effectiveness of releasing gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) for stock enhancement in the bay of Cadiz. Aquaculture, 231: 135–148.
Simon, T., Pinheiro, H. T., and Joyeux, J. C., 2011. Target fishes on artificial reefs: Evidences of impacts over nearby natural environments. Science of the Total Environment, 409: 4579–4584.
Tanaka, M., 2000. Diminution of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus juveniles released on artificial reefs. Bulletin of Ishikawa Prefecture Fisheries Research Center, 18: 1013–1019.
Taylor, A. L., 2016. Sea ranching release techniques for cultured sea cucumber Holothuria scabra (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea) juveniles within the high-energy marine environments of northern Australia. Aquaculture, 465: 109–116.
Williams, L. J., Herbig, J. L., and Szedlmayer, S. T., 2015. A cage release method to improve fish tagging studies. Fisheries Research, 172: 125–129.
Wu, J., Zhang, S., Sun, M., and Chen, Y., 2004. Experiment on the distribution of different artificial reef models for Paralichthys olivaceus. Marine Fisheries, 26: 271–276 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yamashita, Y., Nagahora, S., Yamada, H., and Kitagawa, D., 1994. Effects of release size on survival and growth of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in coastal waters off Iwate prefecture, northeastern Japan. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 105: 269–276.
Zhou, Y., Cai, W., Chen, P., Lu, G., and Jia, X., 2011. Attraction effect of various artificial reef models on Sparus microcephalus. Journal of Fisheries of China, 35: 700–718 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41501560, 41606110), the Young Orient Scholars Programme of Shanghai (No. QD2017038), and the Shanghai Special Research Fund for Training College’s Young Teachers (No. ZZSHOU 18025). The authors would like to thank the assistance of the staffs in marine ranching laboratory in Ocean University of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., He, Y., Guo, Z. et al. Improvement on the Effectiveness of Marine Stock Enhancement in the Artificial Reef Area by a New Cage-Based Release Technique. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 992–998 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4816-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4816-y