Abstract
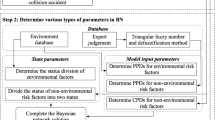
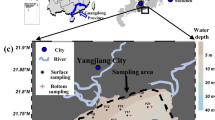
Marine environments have a considerable influence on the construction of the Chinese 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. Thus, an objective and quantitative risk assessment of marine environments has become a key problem that must be solved urgently. To deal with the uncertainty in marine environmental risks caused by complex factors and fuzzy mechanisms, a new assessment technique based on a weighted Bayesian network (BN) is proposed. Through risk factor analysis, node selection, structure construction, and parameter learning, we apply the proposed weighted BN-based assessment model for the risk assessment and zonation of marine environments along the Maritime Silk Road. Results show that the model effectively fuses multisource and uncertain environmental information and provides reasonable risk assessment results, thereby offering technical support for risk prevention and disaster mitigation along the Maritime Silk Road.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera, P. A., Fernández, A., and Reche, F., 2010. Hybrid Bayesian network classifiers: Application to species distribution models. Environmental Modelling & Software, 25 (12): 1630–1639.
Boutkhamouine, B., Roux, H., and Pérès, F., 2017. A Bayesian network approach for flash flood risk assessment. EGU General Assembly Conference. Vienna, 147–165.
Dubois, J. M., 2012. Remote sensing for hazard monitoring and disaster assessment: Marine and coastal applications in the Mediterranean region. Journal of Coastal Research, 9 (6): 62–67.
Fang, S. J., 2007. Marine Weapons and Equipment and Marine Battlefield Environment. China Ocean Press, Beijing, 126–134.
Feng, J., and Liu, Q., 2017. Pre-assessment for the loss caused by storm surge based on the SVM-BP neural network. Marine Environmental Science, 36 (4): 615–621.
Khatsü, P., and Westen, C., 2011. Urban multi-hazard risk analysis using GIS and remote sensing: A case study from Kohima Town, Nagaland, India. 26th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing. Enschede, 96–107.
Li, C. M., and Luo, X. L., 2006. Application of analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in disaster impact assessment model of tropical cyclone. Acta Tropical Meteorology, 22 (3): 223–228.
Li, M., and Liu, K. F., 2019. Causality-based attribute weighting via information flow and genetic algorithm for naive Bayes classifier. IEEE Access, 5 (7): 150630–150641.
Li, M., Hong, M., and Zhang, R., 2018a. Improved Bayesian network-based risk model and its application in disaster risk assessment. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 9 (2): 237–248.
Li, M., Zhang, R., and Hong, M., 2018b. Marine disaster assessment and management based on weighted Bayesian network. Ocean Development and Management, 35 (1): 52–59.
Li, M., Zhang, R., and Liu, K. F., 2020. A new ensemble learning algorithm combined with causal analysis for Bayesian network structural learning. Symmetry, 12 (12): 2054.
Li, X., Hong, M., and Wang, B., 2012. Disaster assessment and risk zoning concerning the South China Sea and Indian Ocean safety. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 6: 121–127.
Liu, Y. C., 2015. An adaptive multi-granularity concept extraction method -Gaussian cloud transformation. Computer Engineering and Applications, 51 (9): 1–8.
Pearl, J., 1995. From Bayesian networks to causal networks. In: Mathematical Models for Handling Partial Knowledge in Artificial Intelligence. Coletti, G, et al., eds., Plenum Press, New York, 206–302.
Qi, Q. H., and Cai, R. S., 2017. A Study on climate change and storm hazard risk of marine environment of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. Ocean Development and Management, 34 (5): 67–75.
Wang, S. C., Tang, H. Y., and Liu, X. H., 2007. Learning Bayesian networks in risk management. Control and Decision, 22 (5): 569–572.
Wen, S. Y., and Zhao, D. Z., 2007. Research on the weight of red tide disaster risk assessment index based on AHP method. Disaster Science, 22 (2): 9–14.
Wu, J., Zhu, X., and Zheng, S., 2013. Artificial immune system for attribute weighted Naive Bayes classification. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Singapore, 46–61.
Yang, L., and Li, Y., 2013. Design of comprehensive evaluation index system for marine disaster vulnerability. Journal of Marine Technology, 32 (3): 133–137.
Yang, L. Z., and Zhang, R., 2016. Risk assessment of the human environment of four major asean countries for the 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road. Marine Science Bulletin, 35 (6): 617–624.
Ye, T., Guo, W. P., and Shi, P. J., 2005. Risk analysis and integrated risk management of marine disaster systems in China since 1990. Journal of Natural Disasters, 14 (6): 65–70.
Zhang, E. Y., 2015. Port ship oil spill risk assessment based on fuzzy Bayesian network. Master thesis. Dalian Maritime University.
Zhang, R., 2012. Characteristics Diagnosis of Marine Environment and Risk Assessment of Maritime Military Activities. Beijing Normal University Press, Beijing, 312–336.
Zhang, S., Zhang, M., and Chi, G. T., 2010, The science and technology evaluation model based on entropy weight and empirical research during the 10th five-year of China. Chinese Journal of Management, 7 (1): 34–42.
Zhang, Y. Y., 2013. Air target threat assessment based on cloud model theory. Master thesis. PLA Information Engineering University.
Zhao, Q. L., and Xu, S. Y., 2007. Research progress of storm surge disaster risk assessment in coastal cities. Progress in Geographical Sciences, 26 (5): 32–40.
Zheng, C. W., and Li, X. Q., 2015. Marine environmental characteristics of the 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road: A statistical analysis of wind. Ocean Development and Management, 3 (8): 4–11.
Zheng, C. W., and Sun, W., 2016. 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road: Important routes, nodes and port characteristics. Ocean Development and Management, 33 (1): 4–13.
Zheng, C. W., Pan, J., and Li, J. X., 2013. Assessing the China sea wind energy and wave energy resources from 1988 to 2009. Ocean Engineering, 65: 39–48.
Zheng, C. W., Wang, Q., and Li, C. Y., 2017. An overview of medium- to long-term predictions of global wave energy resources. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 79: 1492–1502.
Zhou, X., and Jing, Z. L., 2004. Bilinear interpolation wavelet fusion method for remote sensing images. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 38 (4): 547–550.
Zhou, Z. H., 2016. Machine Learning. Tsinghua University Press. Beijing, 368–375.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Fundation (Nos. 41976188, 41775165), the Chinese National Natural Science Fundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20161464), and the Graduate Research and Innovation Project of Hunan Province (No. CX20200009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Zhang, R. & Liu, K. Risk Assessment of Marine Environments Along the South China Sea and North Indian Ocean on the Basis of a Weighted Bayesian Network. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 521–531 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4631-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4631-5