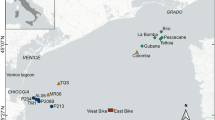
Abstract
The construction of artificial reefs has unparallelly developed for a few decades in China. Artificial reefs can be used to manage and conserve commercially exploited fish and crustacea. However, their suitability as ecological niche is poorly characterized. Therefore, in this study, we detected the seasonal variation of community biodiversity and the corresponding driving environmental factors. We also explored the relationships between dominant species and environmental factors to identify appropriate ecological niche areas. Different statistical analysis methods were used to assess species distribution within an artificial reef area in Xixiakou during nine sampling events in four seasons between 2017 and 2018. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) and cluster analysis results indicated that the components of community can be divided into two clusters. Complexity of community, which is exhibited by species number, biodiversity, and catch per unit effort (CPUE), was significantly higher in summer than in other seasons. Generalized additive model (GAMs) results revealed the significant effects of temperature and chlorophyll a on the community structure. Sebastes schlegelii, Hexagrammos otakii, Conger myriaster and Charybdis japonica were the dominant species in four seasons. GAMs results indicated that temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), pH and chlorophyll a affect the CPUE of dominant species significantly. The distinct suitable ecological niche for each dominant species was found in this study. For example, Charybdis japonica preferred to live in the area with 20.7–22.1 °C, dissolved oxygen 7.07–7.15 mg L−1 and salinity 31.8–31.9. The results of this study are beneficial to resource conservation and fishery management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batáry, P., Matthiesen, T., and Tscharntke, T., 2010. Landscape-moderated importance of hedges in conserving farmland bird diversity of organic vs. conventional croplands and grasslands. Biological Conservation, 143(9): 2020–2027, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2010.05.005.
Bohnsack, J. A., 1989. Are high densities of fishes at artificial reefs the result of habitat limitation or behavioral preference? Bulletin of Marine Science, 44(2): 631–645.
Bortone, S. A., and Nelson, B. D., 1995. Food habits and forage limits of artificial reef fishes in the northern Gulf of Mexico. ECOSET’95, International Conference on Ecological System Enhancement Technology for Aquatic Environments. Japan International Marine Science and Technology Federation, Tokyo, Japan, 215–218.
Chiba, S., and Saino, T., 2002. Interdecadal change in the upper water column environment and spring diatom community structure in the Japan Sea: An early summer hypothesis. Marine Ecology Progress, 231(1): 23–35, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps231023.
Dong, T. W., Huang, L. Y., Tang, Y. L., Sheng, H. X., and Liu, C. D., 2015. Preliminary evaluation of artificial reef around Rizhao Qiansan Island on the enhancement of fishery resources. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 45(8): 38–45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Falcão, M., Santos, M. N., Drago, T., Serpa, D., and Monteiro, C., 2009. Effect of artificial reefs (southern Portugal) on sediment-water transport of nutrients: Importance of the hydrodynamic regime. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 83(4): 451–459, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2009.04.028.
Farré, M., Tuset, V. M., Maynou, F., Recasens, L., and Lombarte, A., 2013. Geometric morphology as an alternative for measuring the diversity of fish assemblages. Ecological Indicators, 29: 159–166, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.12.005.
Ge, S. S., Zhao, W. X., Song, J. J., Yu, D. D., Liu, Y., Wang, Q. X., and Zhou, J., 2019. Study on trophic niches of Sebastes schlegelii and Hexagrammos otakii in the artificial reef area of Xiaoheishan Island. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(18): 6923–6931 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guisan, A., and Zimmermann, N. E., 2000. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecological Modelling, 135(2): 147–186, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00354-9.
Guy, C. S., and Willis, D. W., 1991. Seasonal variation in catch rate and body condition for four fish species in a South Dakota natural lake. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 6(3): 281–292, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02705060.1991.9665305.
Hastie, T., and Tibshirani, R., 1987. Generalized additive model: Some applications. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 82(398): 371–386, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7070-7_8.
Hawkins, J. P., Roberts, C. M., Gell, F. R., and Dytham, C., 2007. Effects of trap fishing on reef fish communities. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 17(2): 111–132, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.784.
Hixon, M. A., and Beets, J. P., 1989. Shelter characteristics and caribbean fish assemblages: Experiments with artificial reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science, 44(2): 666–680.
Ji, D., Bian, X., Song, N., and Gao, T., 2014. Feeding ecology of Hexagrammos otakii in Lidao Rongcheng. Journal of Fisheries of China, 38(9): 1399–1409 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jin, J., Liu, S. M., Ren, J. L., Liu, C. G., Zhang, J., and Zhang, G. L., 2013. Nutrient dynamics and coupling with phytoplankton species composition during the spring blooms in the Yellow Sea. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 97: 16–32, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.05.002.
Jing, H., Liu, H., Suzuki, K., Sohrin, R., and Nishioka, J., 2010. Community compositions of bacteria and archaea in the Sea of Okhotsk during summer. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 61(2): 191–204, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01450.
Kaifu, K., Miller, M. J., Aoyama, J., Washitani, I., and Tsukamoto, K., 2013. Evidence of niche segregation between freshwater eels and conger eels in Kojima Bay, Japan. Fisheries Science, 79(4): 593–603, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-013-0628-3.
Kilfoyle, A. K., Freeman, J., Jordan, L. K., Quinn, T. P., and Spieler, R. E., 2013. Fish assemblages on a mitigation boulder reef and neighboring hardbottom. Ocean & Coastal Management, 75: 53–62, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2013.02.001.
Kim, J. H., and Kang, J. C., 2016. The immune responses in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii for the stress by the exposure to the dietary lead (II). Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 46: 211–216, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.07.022.
Lara, E. N., and González, E. A., 1998. The relationship between reef fish community structure and environmental variables in the southern Mexican Caribbean. Journal of Fish Biology, 53: 209–221, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1998.tb01028.x.
Lawesson, J. E., 2010. Effects of species partition on explanatory variables in direct gradient analysis: A case study from Senegal. Journal of Vegetation Science, 8(3): 409–414, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/3237332.
Leitao, F., Santos, M. N., Erzini, K., and Monteiro, C. C., 2008. Fish assemblages and rapid colonization after enlargement of an artificial reef off the Algarve coast (southern Portugal). Marine Ecology, 29(4): 435–448, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0485.2008.00253.x.
Li, S. F., Yan, L. P., Li, C. S., and Hu, F., 2004. The analysis of fish composition pattern in the northern East China Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China, 28(04): 384–392 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lima, J. S., Zalmon, I. R., and Love, M., 2019. Overview and trends of ecological and socioeconomic research on artificial reefs. Marine Environmental Research, 145: 81–96, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.01.010.
Liu, C. D., Guo, X. F., Tang, Y. L., Sheng, H. X., and Huang, L. Y., 2015. Phytoplankton community composition and its relationship with environmental factors in the artificial reef area around the Qiansan islets, Haizhou Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 22(3): 545–555 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lorenzen, K., Leber, K. M., and Blankenship, H. L., 2010. Responsible approach to marine stock enhancement: An update. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 18(2): 189–210, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10641262.2010.491564.
Lowry, M. B., Glasby, T. M., Boys, C. A., Folpp, H., Suthers, I., and Gregson, M., 2014. Response of fish communities to the deployment of estuarine artificial reefs for fisheries enhancement. Fisheries Management and Ecology, 21(1): 42–56, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/fme.12048.
Lv, Z. B., Li, F., Wang, B., Xu, B. Q., Wei, Z. H., Zhang, H. J., and Zhang, P. C., 2011. Community structure of fish resources in spring and autumn in the Yellow Sea of Shandong. Journal of Fisheries of China, 35(5): 692–699 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Magurran, A. E., 1988. Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, 181pp.
Makarenkov, V., and Legendre, P., 2002. Nonlinear redundancy analysis and canonical correspondence analysis based on polynomial regression. Ecology, 83(4): 1146–1161, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[1146:NRAACC]2.0.CO;2.
Manage, A., 2008. Community-level analysis of anthropogenic impacts on rocky shore communities in Sri Lanka. Nature Proceedings, 2008: 1–1, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.2317.1.
Mcardle, B. H., and Anderson, M. J., 2001. Fitting multivariate models to community data: A comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology, 82(1): 290–297, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2001)082[0290:FMMTCD]2.0.CO;2.
Möhlmann, T. W., Wennergren, U., Talle, M., Favia, G., Damiani, C., Bracchetti, L., and Koenraadt, C. J., 2017. Community analysis of the abundance and diversity of mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae) in three European countries at different latitudes. Parasites & Vectors, 10(1): 510, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2481-1.
Pinkas, L., Oliphant, M. S., and Iverson, I. L., 1971. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in California waters. Fish Bulletin, 152: 1–105.
Ransom, J., 1974. Biostatistical analysis J. H. Zar. American Biology Teacher, 36(5): 316–316.
Rice, J., 2000. Evaluating fishery impacts using metrics of community structure. Ices Journal of Marine Science, 57(3): 682–688, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.2000.0735.
Robichaud, D., Hunte, W., and Chapman, M. R., 2000. Factors affecting the catchability of reef fishes in Antillean fish traps. Bulletin of Marine Science, 67(2): 831–844.
Smith rJr., K. L., Kaufmann, R. S., Edelman, J. L., and Baldwin, R. J., 1992. Abyssopelagic fauna in the central North Pacific: Comparison of acoustic detection and trawl and baited trap collections to 5800 m. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 39(3–4): 659–685, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0198-0149(92)90094-A.
Stephens Jr., J., and Pondella, D., 2002. Larval productivity of a mature artificial reef: The ichthyoplankton of King Harbor, California, 1974–1997. Ices Journal of Marine Science (Suppl), 59: S51–S58, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.2002.1189.
Stevenson, D. K., and Stuart-Sharkey, P., 1980. Performance of wire fish traps on the western coast of Puerto Rico. Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute. Miami, Florida, 173–193.
Sumaila, U. R., Cheung, W. W., Lam, V. W., Pauly, D., and Herrick, S., 2011. Climate change impacts on the biophysics and economics of world fisheries. Nature Climate Change, 1(9): 449–456, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1301.
Tang, W. Y., Tang, Y. L., Sheng, H. X., and Wan, R., 2018. Ecosystem health assessment of artificial reef area in Xigang, Weihai. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 48(3): 55–64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang, Y. L., Sun, X. M., Sheng, H. X., Wang, X. M., and Wan, R., 2016. Community structure of catch and its relationship with environmental factors in Xiaoshidao artificial reef zones of Weihai City. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 46(5): 25–34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ter Braak, C. J. F., and Smilauer, P., 2002. Canoco reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: Software for canonical community ordination (Version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, New York, USA.
Tokuhiro, K., Abe, Y., Matsuno, K., Onodera, J., Fujiwara, A., Harada, N., Hirawake, T., and Yamaguchi, A., 2019. Seasonal phenology of four dominant copepods in the Pacific sector of the Arctic Ocean: Insights from statistical analyses of sediment trap data. Polar Science, 19: 94–111, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polar.2018.08.006.
Valdes, M. A., 2008. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) as a basis for a plant functional group classification and a Bayesian belief network formulation for California oak woodlands. PhD thesis. University of California.
Vazquez Archdale, M., Anraku, K., Yamamoto, T., and Higashitani, N., 2003. Behavior of the Japanese rock crab ‘Ishigani’ Charybdis japonica towards two collapsible baited pots: Evaluation of capture effectiveness. Fisheries Science, 69(4): 785–791, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1444-2906.2003.00687.x.
Vicente, M., Falcão, M., Santos, M. N., Caetano, M., Serpa, D., Vale, C., and Monteiro, C., 2008. Environmental assessment of two artificial reef systems off southern Portugal (Faro and Olhão): A question of location. Continental Shelf Research, 28(6): 839–847, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2007.12.009.
Wang, F., Zhang, S., and Lin, J., 2013. Study of chlorophyll a distribution in marine ranching planning area of Xiangshan Bay. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 22(2): 266–273.
Wells, R. D., Boswell, K. M., Cowan Jr., J. H., and Patterson III, W. F., 2008. Size selectivity of sampling gears targeting red snapper in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fisheries Research, 89(3): 294–299, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2007.10.010.
Wu, Z. X., Zhang, L., Zhang, X. M., Zhang, P. D., and Li, W. T., 2012. Nekton community structure and its relationship with main environmental variables in Lidao artificial reef zones of Rongcheng. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(21): 6737–6746 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu, Z., Tweedley, J. R., Loneragan, N. R., and Zhang, X., 2019. Artificial reefs can mimic natural habitats for fish and macro-invertebrates in temperate coastal waters of the Yellow Sea. Ecological Engineering, 139: 105579, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.08.009.
Zhang, Y., Xu, Q., Xu, Q., Alós, J., Zhang, H., and Yang, H., 2018. Dietary composition and trophic niche partitioning of spotty-bellied greenlings Hexagrammos agrammus, fat greenlings H. otakii, Korean rockfish Sebastes schlegelii, and Japanese seaperch Lateolabrax japonicus in the Yellow Sea revealed by stomach content analysis and stable isotope analysis. Marine and Coastal Fisheries, 10(2): 255–268, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mcf2.10019.
Zhao, J., Liu, H., Yuan, Z. Z., Liu, X., Wang, H. W., Jiang, Y. S., Li, X. D., Liu, H. Y., Zheng, Y., and Yao, J. G., 2012. Selective feeding on three bivalves and feeding rhythm in Asian swimming crab Charybdis japonica. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 27(3): 226–230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zimmerman, J. K., and Palo, R. T., 2011. Reliability of catch per unit effort (CPUE) for evaluation of reintroduction programs—A comparison of the mark-recapture method with standardized trapping. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 401: 07, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2011016.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the Project of Marine and Fishery Technology Innovation of Shandong (No. 2017 HYCX007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Yang, W., Liu, C. et al. Relationships Between Community Structure and Environmental Factors in Xixiakou Artificial Reef Area. J. Ocean Univ. China 19, 883–894 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-020-4298-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-020-4298-3