Abstract
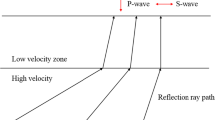
Compared to towed streamers, ocean-bottom seismometers (OBS) obtain both S-wave data and richer wavefield information. In this paper, the induced polarization method is used to conduct wavefield separation on OBS data obtained from the Shenhu area in the South China Sea. A comparison of the changes in P- and S-waves, and a comprehensive analysis of geological factors within the area, enable analysis and description of the occurrence of natural gas hydrate in the study area. Results show an increase in P-wave velocity when natural gas hydrate exists in the formation, whereas the S-wave velocity remains almost constant, as S-waves can only propagate through the rock skeleton. Therefore, the bottom-simulating reflection (BSR) response of the P-wave is better than that of the S-wave in the frequency analysis profile. In a wide-angle section, the refractive wave of the hydrate layer is evident when using P-wave components but identification is difficult with S-wave components. This velocity model illustrates the sensitivity of P- and S-wave components to gas hydrate. The use of this polarization method and results of analysis provide technical and theoretical support for research on hydrate deposits and other geological features in the Shenhu area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azik, I. P., and Terry, W., 1994, Applications of seismic polarization analysis. Geophysics, 59 (1): 119–130.
Fu, S. Y., and Lu, J. A., 2010. The characteristics and origin of gas hydrate in shenhu area, South China Sea. Marine Geology Letters, 26 (9): 6–10.
Katzman, R., Holbrook, W. S., and Paull, C. K., 1994. Combined vertical-incidence and wide-angle seismic study of a gas hydrate zone, Black Ridge. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 99 (B9): 17975–17995.
Mienert, J., Bünz, S., and Guidard, S., 2005. Ocean bottom seismometer investigations in the Omen Lange area offshore mid-norwat provided evidence for shallow gas layers in subsurface sediments. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 22 (1–2): 287–297.
Ruan, A. G., Chu, F. Y., and Meng, B. Z., 2007. Seismology study methods on ocean bottom nature gas hydrate and the usage of OBS. Natural Gas Geoscience, 27 (4): 46–48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sha, Z. B., Zhang, M., and Zhang, G. X., 2016. Using 4C OBS to reveal the distribution and velocity attributes of gas hydrates at the northern continental slope of South China Sea. Applied Geophysics, 12 (4): 555–563.
Song, H. B., Matsubayashi, O., and Kuramoto, S., 2003. Full waveform inversion of gas hydrate-related bottom simulation reflections. Journal of Geophysics, 46 (1): 42–46 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, W. W., Xie, C. L., Zhao, Q. X., and Hao, X. Z., 2015. Application of seismic shear wave detection in marine natural gas hydrate exploaration. Journal of Ocean Technology, 34 (2): 111–117 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu, S. G., Wang, X. J., Chen, R. X., and Wang, Z. J., 2015. Introduction of Nature Gas Hydrate Geological. Science Press, Beijing, 38–53.
Xia, C. L., 2009. A Study on pivotal data processing procedure of ocean bottom seismograph. Master thesis. China University of Geoscience, Beijing, 27–64.
Xia, C. L., Liu, X. W., Xia, M. L., and Liu, E. H., 2008. Application of ocean bottom seismic in exploration of gas hydrate. Progress of Exploration Geophysics, 31 (4): 259–264 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng, X. J., Wu, Z. L., and Hao, X. Z., 2010. 3-D seismic and OBS joint acquisition technology for gas hydrate investigation. Ocean Technology, 29 (1): 124–130.
Zhang, L., Zhao, M. H., and Qiu, X. L., 2014. Research progress of P-waves and S-waves speed structure. China Earth Science Joint Academic Annual Meeting, Beijing, 1596–1597.
Acknowledgements
The study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41304096, 41176077, 412303 18), the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2016ZX05024-001-002), the National Hightech R&D Program of China (863 Program) (Nos. 2013 AA092501, 2017YFC0307401), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 201762 019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, L., Liu, X., Zhang, J. et al. Sensitivity analysis of P-waves and S-waves to gas hydrate in the Shenhu area using OBS. J. Ocean Univ. China 17, 139–146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-018-3587-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-018-3587-6