Abstract
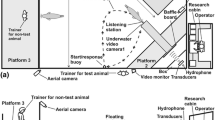
Attracting released hatchery-reared fish to designated areas during the growth process is vital to realize the objectives of sea ranching. Based on the bottom artificial reefs and surface kelp culture facilities in the Xiangshan Bay sea ranch, we proposed systematic techniques related to acoustic conditioning of the black seabream (Sparus macrocephalus). Experiments conducted in 12 m × 10 m × 1.6 m ponds on Xixuan Island showed that black seabream was positively sensitive to 500–600 Hz periodic signals. Conditioned responses were apparent after 8 d. Two to three days were required for recovery of the memory of a conditioned response after a 20-day interval. According to the practical application requirements in the open sea, unattended acoustic conditioning equipment was developed. The ranching equipment was used in 12 m × 12 m × 2.5 m cages, and the behavior of black seabream juveniles was successfully guided after 7 days. Of the 16000 released fish, 82.5% of them were conditioned with a flexible grading net. To avoid inducing a stress response, the juveniles were released into the sea ranch in situ from the net cage. The acoustic conditioning equipments were moved into the open sea and the aggregation phenomenon of the released fish was observed when the sound was played. After 6 months of investigation and based on Sr+ marking, only one acoustically conditioned fish was found outside the 3.5-km2 sea ranch area, thereby reached the goal of guiding activity. The practical effect in the Xiangshan Bay sea ranch showed the validity of the acoustic conditioning system, which may contribute to improve the operation of the sea ranches in the East China Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhandiwad, A. A., Whitchurch, E. A., Colleye, O., Zeddies, D. G., and Sisneros, J. A., 2017. Seasonal plasticity of auditory saccular sensitivity in ‘sneaker’ type II male plainfin midshipmanfish, Porichthys notatus. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 203 (3): 411–422.
Brotto, D. S., Krohling, W., and Zalmon, I. R., 2006. Fish community modeling agents on an artificial reef on the northern coast of Rio de Janeiro–Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 54 (4): 205–212.
Burkepile, D. E., and Hay, M. E., 2008. Herbivore species richness and feeding complementarity affect community structure and function on a coral reef. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105 (42): 16201–16206.
Cheng, M. H., and Xu, R. Y., 1989. Initial acoustic taming experiment on Sparus macrocephalus. Marine Sciences, 3: 65–67.
Egner, S. A., and Mann, D. A., 2005. Auditory sensitivity of sergeant major damselfish, Abudefduf saxatilis from post-settlement juvenile to adult. Marine Ecology Progress, 285 (1): 213–222.
Fabi, G., and Sala, A., 2002. An assessment of biomass and diel activity of fish at an artificial reef (Adriatic Sea) using a stationary hydroacoustic technique. Ices Journal of Marine Science, 59 (2): 411–420.
Han, Z. Q., Li, Y. Z., Chen, G. B., and Gao, T. X., 2008. Population genetic structure of coral reef species Plectorhinchus flavomaculatus in South China Sea. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7 (11): 1774–1781.
Hunter, W. R., and Sayer, M. D. J., 2009. The comparative effects of habitat complexity on faunal assemblages of northern temperate artificial and natural reefs. Ices Journal of Marine Science, 66 (4): 691–698.
Hwang, B. K., and Jang, H. Y., 2014. Spatial characteristics of fish distribution lured by artificial reefs in Jeju marine ranching area. Bulletin of the Korean Society of Fisheries Technology, 50 (1): 31–38.
Jiang, Z. Y., Zhang, G. S., and Liang, Z. L., 2008. Acoustic taming on Chrysophrys major by rectangular continuant of 300 Hz. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 15 (1): 86–90.
Kotrschal, A., and Taborsky, B., 2010. Environmental change enhances cognitive abilities in fish. PLoS Biology, 8 (4): 1–7.
Lee, Y. W., 2015. Visual census and hydro-acoustic survey of demersal fish aggregations in Ulju small scale marine ranching area (MRA), Korea. Bulletin of the Korean Society of Fisheries Technology, 51 (1): 16–25.
Leis, J. M., Carson-Ewart, B. M., Hay, A. C., and Cato, D. H., 2003. Coral-reef sounds enable nocturnal navigation by some reef-fish larvae in some places and at some times. Journal of Fish Biology, 63 (3): 724–737.
Li, Z. G., Ye, Z. J., and Wang, R., 2015. Spatial and seasonal patterns of ichthyoplankton assemblages in Haizhou Bay and its adjacent waters of China. Journal of Ocean University of China, 14 (5): 1041–1052.
Melendez, M. T. F., Kang, K. M., and Shin, H. O., 2015. Preliminary study about behavior characteristics of red and black rockfish around artificial reefs and natural habitats by using biotelemetry techniques. Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 10 (3): 132–145.
Noguchi, M., 1996. Marine ranching of Japanese flounder by acoustic training. Bulletin of National Research Institute of Aquaculture, 2 (Suppl.): 119–121.
Pickering, H., 1999. Marine ranching: A legal perspective. Ocean Development and International Law, 30 (2): 161–190.
Pursche, A. R., Suthers, I. M., and Taylor, M. D., 2014. The effect of targeted stocking on behavior and space utilization of a released finfish. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 71 (5): 1100–1106.
Sala, A., Fabi, G., and Manoukian, S., 2008. Vertical diel dynamic of fish assemblage associated with an artificial reef (northern Adriatic Sea). Scientia Marina, 71 (2): 54–61.
Simpson, S. D., Jeffs, A., Montgomery, J. C., McCauley, R. D., and Meekan, M. G., 2008. Nocturnal relocation of adult and juvenile coral reef fishes in response to reef noise. Coral Reefs, 27 (1): 97–104.
Simpson, S. D., Meekan, M. G., Montgomery, J. C., McCauley, R. D., and Jeffs, A., 2005. Homeward sound. Science, 308 (5719): 221–221.
Teodosio, M. A., Paris, C. B., Wolanski, E., and Morais, P., 2016. Biophysical processes leading to the ingress of temperate fish larvae into estuarine nursery areas: A review. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 183: 187–202.
Tlusty, M. F., Andrew, J., Baldwin, K., and Bradley, T. M., 2008. Acoustic conditioning for recall/recapture of escaped Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout. Aquaculture, 274 (1): 57–64.
Tolimieri, N., Jeffs, A., and Montgomery, J. C., 2000. Ambient sound as a cue for navigation by the pelagic larvae of reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress, 207 (1): 219–224.
Wahlberg, M., and Westerberg, H., 2005. Hearing in fish and their reactions to sounds from offshore wind farms. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 288 (1): 295–309.
Wu, H. L., Huo, Y. Z., Han, F., Liu, Y. Y., and He, P. M., 2015. Bioremediation using Gracilaria chouae co-cultured with Sparus macrocephalus to manage the nitrogen and phosphorous balance in an IMTA system in Xiangshan Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 91 (1): 272–279.
Zhang, G. S., Tian, T., Xu, C. C., Jiang, Z. Y., and Yu, S. L., 2004. Increase in feed conversion efficiency in Sparus macrocephalus by acoustic behaviors control. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 19 (3): 204–207 (in Chinese).
Zion, B., and Barki, A., 2012. Ranching fish using acoustic conditioning: Has it reached a dead end? Aquacultures, 344-349 (2): 3–11.
Zion, B., Barki, A., Grinshpon, J., Rosenfeld, L., and Karplus, I., 2011a. Retention of acoustic conditioning in St Peter’s fish, Sarotherodon galilaeus. Journal of Fish Biology, 78 (3): 838–847.
Zion, B., Karplus, I., and Barki, A., 2014. Effect of duration and timing of acoustic signal transmission on ranched fish recapture. Journal of Applied Aquaculture, 26 (1): 11–21.
Zion, B., Karplus, I., Grinshpon, J., Rosenfeld, L., and Barki, A., 2011b. Periodic reinforcement of acoustically conditioned behavior in St. Peter’s fish, Sarotherodon galilaeus, for ranching purposes. Aquaculture, 315 (3-4): 394–399.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201303047) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51309150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Rahman, H.A., Jiang, Y. et al. Acoustic Conditioning System Development and Conditioning Experiments on Black Seabreams in the Xiangshan Bay Sea Ranch. J. Ocean Univ. China 17, 667–674 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-018-3479-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-018-3479-9