Abstract
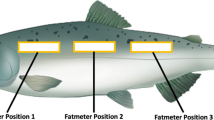
Comparing fat content with physiological status can throw light on the reproduction and feeding behavior of the fish. The biological data of 586 bigeye tuna were collected from the longline fishery in the waters of Western Central Indian Ocean from November, 2012 to March, 2013. The spatial or temporal distribution of the fat content, and the relationships of fat content with gender, round weight, gonadal maturity and fork length were analyzed. A generalized additive model (GAM) was used to analyze the relationships between fat content and fork length (FL), gonadosomatic index (GSI), condition factor (K), and somatic index (SI). Results showed that: 1) the fat content of bigeye tuna was in the range of 3.1%–27.1% with the average 12.8%; 2) there were no significant geographical differences of average fat content (P > 0.05) among 1° squares in general; 3) there were no significant differences (P > 0.05) of the fat content for different genders, months, or gonad maturity stages; 4) there was an extremely significant correlation (P = 0.000) between fat content and FL and GSI. There was no significant correlation (P = 0.051) between fat content and K. There was a significant correlation (P = 0.003) between fat content and SI. The results of this study suggest that the fat content of the matured fish was relatively stable. The survey area was in a spawning region, and the survey period was the spawning season for bigeye tuna.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard, F. X., 1981. Le thon Germon (Thunnus alalunga Bonnaterre 1788) de l’Océan Atlantique. De la Dynamique des Populations à la Strategie Demographique. Université de Paris, Paris, 7–21 (in French).
Black, K. D., and Pickering, A. D., 1998. Biology of Farmed Fish. Sheffield Academic Press, Sheffield, 1–14.
Chen, X. Z., Yang, S. L., Zhang, Y., Fan, W., and Wu, Y. M., 2013. Vertical distribution of bigeye tuna Thunnus obesus in the tropical Indian Ocean. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 20 (3): 660–671.
Dygert, P. H., 1990. Seasonal changes in energy content and proximate composition associated with somatic growth and reproduction in a representative age-class of female English sole. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 119: 791–801.
Encina, L., and Granado-Lorencio, C., 1997. Seasonal changes in condition, nutrition, gonad maturation and energy content in barbel, Barbus sclateri, inhabiting a fluctuating river. Environment Biology of Fishes, 50: 75–84.
Evans, K., Langley, A., and Clear, N. P., 2008. Behaviour and habitat preferences of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) and their influence on longline fishery catches in the western Coral Sea. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 65: 2427–2443.
Eveson, J. P., Million, J., Sardenne, F., and Croizier, G. L., 2015. Estimating growth of tropical tunas in the Indian Ocean using tag-recapture data and otolith-based age estimates. Fisheries Research, 163: 58–68.
Flath, L. E., and Diana, J. S., 1985. Seasonal energy dynamics of the alewife in southeastern Lake Michigan. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 114: 328–337.
Goni, N., and Arrizabalaga, H., 2010. Seasonal and interannual variability of fat content of juvenile albacore (Thunnus alalunga) and bluefin (Thunnus thynnus) tunas during their feeding migration to the Bay of Biscay. Progress in Oceanography, 86 (1–2): 115–123.
Hida, T. S., 1973. Food of tunas and dolphins (pisces: Scombridae and Coryphaenidae) with emphasis on the distribution and biology of their prey Stolephorus buccaneeri (Engraulidae). Fish Bull, 71 (1): 135–145.
IOTC, 2014. Report of the Seventeenth Session of the IOTC Scientific Committee. Seychelles, IOTC-2014-SC17-R[E]: 357.
Kelso, J. R. M., 1973. Seasonal energy change in walleye and their diet in west blue lake, Manitoba. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 102: 363–368.
Laure, P., Pierre, P., and Sebastiaan, A. L. M. K., 2009. Modeling fish growth and reproduction in the context of the Dynamic Energy Budget theory to predict environmental impact on anchovy spawning duration. Journal of Sea Research, 62 (2–3): 93–105.
Li, P., Chen, J. T., and Zhu, G. P., 2010. Biological characteristics of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) in southern and central Indian Ocean. Marine and Coastal Fisheries, 32 (3): 283–289.
Masahiko, M., and Yasuaki, T., 1997. Vertical distribution and optimum temperature of bigeye tuna in the eastern tropical Indian Ocean based on regular and deep tuna longline catches. National Fish University, 46 (1): 13–20.
Schaefer, K. M., 2001. Reproductive biology of tunas. In: Tuna: Physiology, Ecology and Evolution. Fish Physiology, Vol. 19. Block, B. A., and Stevens, E. D., eds., Academic Press, San Diego, 225–270.
Schaefer, K. M., and Fuller, D. W., 2010. Vertical movements, behavior, and habitat of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) in the equatorial eastern Pacific Ocean, ascertained from archival tag data. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 157: 2625–2642.
Shul’man, C. E., 1974. Life Cycles of Fish: Physiology and Biochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York, 8–19.
Solovieff, B. S., 1970. Distribution and biology of bigeye tuna in the Indian Ocean. Rybn Kbos, (3): 313.
Song, L. M., Chen, H., Hu, G. S., and Li, D. J., 2014. The fat content of albacore tuna in waters near Cook Islands. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 23 (3): 456–462 (in Chinese).
Song, L. M., Zhao, H. L., and Li, D. J., 2015. The relationship between age and muscle fat content of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) in the western central Indian Ocean. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 46 (4), DOI: 10.11693/hyhz20141000292.
State Oceanic Administration People’s Republic of China, 2007. Specification for Oceanographic Survey. Standard Press of China, Beijing, GB12763.6-2007.
Yang, S. L., Zhang, Y., Fan, W., and Dai, Y., 2012. Relationship between the temporal-spatial distribution of fish in bigeye tuna fishing grounds and the thermocline characteristics in thetropical Indian Ocean. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 19 (4): 679–689.
Ye, Z. J., Wang, Y. J., and Gao, T. X., 2003. Study on tuna longline fishery in the Eastern Indian Ocean: The Biology of Thunnus obesus Captured. Ocean University of Qingdao, 33 (3): 343–348 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, L., Shen, Z., Li, J. et al. The relationship between fat content and biological parameters of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obseus) in the Western Central Indian Ocean. J. Ocean Univ. China 15, 853–860 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-016-2974-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-016-2974-0