Abstract
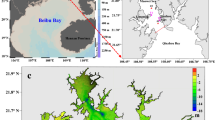
A hydro-dynamic model is established on basis of MIKE21FM to simulate the hydro-dynamic characteristics of Xinghua Bay and investigate the influence of reclamation project on the tidal elevation and tidal currents. Tidal elevation data was obtained at the six tide gauge stations around the Xinghua Bay, and another six current stations were established to observe the tidal current velocity and direction. Validation shows that the model-simulated tidal elevation and tidal currents agree well with observations made at different stations. Predictions are made according to the reclamation project proposed in the regional marine planning of Hanjiang Industrial Park around the port in Putian City. The variations of hydro-dynamic factors, such as tide, current velocity and direction and tidal influx are obtained, and the adverse effect of reclamation on marine environment is discussed. It is shown that the tidal level inside the Xinghua Bay during high tide decreases after the reclamation project is completed. The tidal currents during flooding tide generally decrease in the southeast of the reclamation region, with the maximum decreasing amplitude reaching 0.44 m s−1. On the other hand, the tidal currents during flooding tide increase around the southeast and southwest corners of the reclamation region. The tidal currents during ebb tide increase around the southeast and southwest corners of the reclamation region, with the maximum increasing amplitude attaining 0.18 m s−1. The results in this paper can give some guidance for the marine environment management and the effective utilization of land in Putian.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Begnudelli, L., and Sanders, B. F., 2006. Unstructured grid finite-volume algorithm for shallow-water flow and scalar transport with wetting and drying. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 132 (4): 371–384.
Dong, D., Li, Y., Chen, X., Chen, B., and Zhang, R., 2014. Impacts of hydradynamic environment caused by large-scale reclamation in Qinzhou Bay. Guangxi Science, 21 (4): 357–364 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Du, P., Lou, A., Zhang, X., and Kuang, L., 2008. Analyses and prediction of reclamation in forebay on hydro-dynamics in the Jiaozhou Bay. Coastal Engineering, 27 (1): 28–40.
Feng, J., 2011. Application of MIKE21FM numerical model in environmental impact assessment of ocean engineering. Master thesis. Ocean University of China.
Gao, G. D., Wang, X. H., and Bao, X. W., 2014. Land reclamation and its impact on tidal dynamics in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 151: 285–267.
Gao, J., and Zhou, L., 2009. Study on tide current of the Xinghua Bay. Coastal Engineering, 28 (4): 1–10.
Guo, P., Cai, M., and Yan, D., 2014. Application of MIKE21 water environmental mathematic model in the planning and design of artificial eco-lake. Yellow River, 36 (4): 56–58.
Guo, Y., Wang, Q., Chen, J., Gao, W., Song, W., and Den, K., 2012. Research on tidal current characteristics and numerical simulation of the Xinghua Bay and the surrounding waters. Marine Science Bulletin, 31 (3): 262–267.
Han, S., and Jia, N., 2012. ECOMSED-based three-dimensional numerical model for sediment transport in Xinghua Bay. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 42 (4): 1–6.
Healy, M. G., and Hickey, K. R., 2002. Historic land reclamation in the intertidal wetlands of the Shannon estuary, western Ireland. Journal of Costal Research, 36: 365–373.
Janssen, M., 1996. A shrinking North Sea: New plans for reclamation on the Dutch coast. North Sea Monitor, 14 (3): 7–8.
Jiao, J. J., 2000. Modification of regional groundwater regimes by land reclamation. Hong Kong Geologist, 6: 29–36.
Kang, J. W., 1999. Changes in tidal characteristics as a result of the construction of sea-dike/sea-walls in the Mokpo coastal zone in Korea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 48: 429–438.
Kondo, T., 1995. Technological advances in Japan coastal development-land reclamation and artificial islands. Marine Technology Society Journal, 29 (3): 42–49.
Koo, B. J., Shin, S. H., and Lee, S., 2008. Changes in benthic macrofauna of the Saemangeum tidal flat as result of a drastic tidal reduction. Ocean and Polar Research, 30: 373–545.
Lee, M. O., and Park, S. J., 2006. Influence of reclamation works on the marine environment in a semi-closed bay. Journal of Ocean University of China, 5 (3): 219–227.
Li, J., Yang, X., and Dong, Y., 2007. Progress on environmental effects of tidal flat reclamation. Progress in Geography, 26 (2): 42–51.
Li, M., Shi, Z., and Fan, W., 2004. Application of tidal mathematical model in study on deep-water navigational channels in Xinghua Bay. Port & Waterway Engineering, 366 (7): 59–62.
Li, P., Li, G. X., Qiao, L. L., Chen, X. N., Shi, J. H., Gao, F., Wang, N., and Yue, S. H., 2014. Modeling the tidal dynamic changes induced by the bridge in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Continental Shelf Research, 84: 43–53.
Lu, R., Yu, D., Yang J., and Gu, J., 2010. Cumulative effects of coastal reclamation on tidal current in Xiamen Bay. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 30 (2): 165–174.
Luo, Z., 1997. An analysis of Hong Kong reclamation and its effect. Journal of Geography, 52 (3): 220–227.
Manda, A., and Matsuoka, K., 2006. Changes in tidal currents in the Ariake Sound due to reclamation. Estuaries and Coasts, 29 (4): 645–652.
Peng, B. R., Hong, H. S., and Hong, J. M., 2005. Ecological damage appraisal of sea reclamation and its application to the establishment of usage charge standard for filled seas: Case study of Xiamen, China. Environmental Informatics Archives, 3: 153–165.
Song, Z., Wang, S., Cheng, H., Li, S., and Guo, X., 2014. North branch at Changjiang River estuary and its effects on hydrodynamic condition. Yangtze River, 45 (1): 11–15.
Suzuki, T., 2003. Economic and geographic backgrounds of land reclamation in Japanese ports. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 47: 226–229.
Wang, Y., Wang, C., and Song, Z., 2002. Impacts of Tieji Bay reclamation project on deep channel at Sansha Bay. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 30 (6): 99–103.
Xing, Y., and Shu, C. W., 2005. High order finite difference WENO schemes with the exact conservation property for the shallow water equations. Journal of Computational Physics, 208 (1): 206–227.
Xu, T., 2010. Calculation principle and application example of a two-dimensional flow model–MIKE21 HD. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy, 16 (8): 867–869.
Yu, X. M., Wang, C., Deng, X. H., and Zhang, X. B., 2004. Research on branch streamflow and sedimentmathematicalmodel. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 22 (3): 221–224.
Zhang, M., Chen, C., Suo A., and Lin, Y., 2012. International advance of sea areas reclamation impact on marine environment. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21 (8): 1509–1513.
Zhao, K., Qiao, L., Shi, J., He, S., Li, G., and Yin, P., 2014. Evolution of sedimentary dynamic environment in the western Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China in the last 30 years. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.12.011.
Chang J., Liang, Q., Yan, F., and Hao, W. L., 2013. Reduction of waste water in Erhai Lake based on MIKE21 hydrodynamic and water quality model. The Scientific World Journal, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/958506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Bao, X., Ding, Y. et al. The impact of large-scale reclamation on hydro-dynamic environment–A case study of Xinghua Bay. J. Ocean Univ. China 15, 583–592 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-016-2911-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-016-2911-2