Abstract
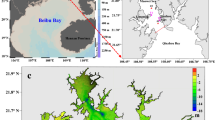
Laizhou Bay and its adjacent waters are of great importance to China’s marine oil and gas development. It is therefore crucial to estimate return-period values of marine environmental variables in this region to ensure the safety and success of maritime engineering and maritime exploration. In this study, we used numerical simulations to estimate extreme wave height, sea current velocity and sea-level height in western Laizhou Bay. The results show that the sea-level rise starts at the mouth of the bay, increases toward west/southwest, and reaches its maximum in the deepest basin of the bay. The 100-year return-period values of sea level rise can reach 3.4–4.0 m in the western bay. The elevation of the western part of the Qingdong Oil Field would remain above the sea surface during extreme low sea level, while the rest of the oil field would be 1.6–2.4 m below the sea surface. The return-period value of wave height is strongly affected by water depth; in fact, its spatial distribution is similar to the isobath’s. The 100-year return-period values of effective wave height can be 6 m or higher in the central bay and be more than 1 m in the shallow water near shore. The 100-year return-period values of current velocity is about 1.2–1.8 m s−1 in the Qingdong Oil Field. These results provide scientific basis for ensuring construction safety and reducing construction cost.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng, Z. Q., Zhou, L. M., Wu, L. Y., and Guo, P. F., 2007. Numerical computation of wave heights of multiyear return periods in the Bohai Sea. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, Z: 8–14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
HI, 2012. MIKE Spectral Wave Module. User Guide and Scientific Documentation, Release 2012, (D.H.I). Danish Hydraulic Institute, Denmark, 1–56.
Editorial Board for Marine Atlas, 1992. Marine Atlas of Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea: Hydrology. Ocean Press. Beijing, 524pp.
Editorial Committee for ‘Chinese Harbours and Embayments’, 1991. Chinese Harbours and Embayments(Part 3)—Northern and Eastern Shandong Peninsula. Ocean Press, Beijing, 487pp (in Chinese).
Fu, C. F., Fu, X., Wu, S. H., Yu, F. J., and Dong, J. X., 2014. Numerical simulation study on deepwater channel influenced by negative storm surge and its features in Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36 (3): 30–38.
Han, S. Z., Wang, H. L., and Guo, P. F., 2003.A study of extreme SWH estimation method by using satellite altimeter data. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 33 (5): 657–664 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ji, Q. L., Dong, S., Cao, S. J., and Tao, S. S., 2010. Coincidence risk of extreme storm surges in adjacent Bohai Bay and Laizhou Bay. Proceedings of the Twentieth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. Beijing, 883–887.
Li, M. J., Qi, P., and Hou, Y. J., 2009. Computation of highest water levels of multiyear return periods along the coast of Shandong. Marine Sciences, 33 (11): 78–81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lv, X. C., Yuan D. K., Ma, X. D., and Tao, J. H., 2014. Wave characteristics analysis in Bohai Sea based on ECMWF wind field. Ocean Engineering, 91 (15): 159–171.
Wang, B., 2005. The research on the distribution of extreme value of the marine environment variables in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. Master thesis. Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang, L. S., and Zhang, F. Q., 1989. The estimation of storm surge in the Yangjiaogou. Journal of Shandong Meteorology, 3: 16–18 (in Chinese).
Wang, Z. F., Wu, K. J., Zhou, L. M., and Wu, L. Y., 2012. Wave characteristics and extreme parameters in the Bohai Sea. China Ocean Engineering, 26 (2): 341–350.
Wolski, T., Wisniewski, B., Giza, A., Kowalewska-Kalkowska, H., Boman, H., Grabbi-Kaiv, S., Hammarklint, T., Holfort, J., and Lydeikaite, Ž., 2014. Extreme sea levels at selected stations on the Baltic Sea coast. Oceanologia, 56 (2): 259–290.
Wu, D. X., Gao, S. H., Wang, Y. M., and Chen, X. E., 2011. Atlas of Monthly Averaged Wind and Temperature of Bohai and Yellow Sea. China Ocean University Press, Qingdao, 150pp.
Xing, L., Xu, J. S., and Sun, P. K.,2013. Engineering geological environment for the access to the artificial island in the west coast of Laizhou Bay. Marine Geology Frontier, 29 (12): 45–50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin, B. S., He, Y. J., Hou, Y. J., Cheng, M. H., Su, J. Z., and Lin, X., 2002. A new method of return period wave height calculation. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 33 (1): 30–35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zu, Y. F., and Yu, Y. X., 2003. The numerical modeling of astronomy- storm tide in the Bohai Sea and a calculation method for extreme water levels of multiyear return periods. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 25 (4): 10–17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, H. W., 2014. Study of cementing technology in complex formation in Qingdong oil field. Technology and business, 1: 178–178 (in Chinese).
Zhao, B., Zhang, P., and Wang, J. Y., 2000. Numerical computations of return period set-up value induced by storm surge in Chengbei sea area in Bohai Sea. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 18 (3): 14–19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou, Y. L., Yang, F. J., and Sun, L. J., 2007. The analysis of the typhoon storm surge and the estimation of extreme value of the typhoon storm surge in the Laizhou Bay. Science & Technology Information, 27: 210–210 (in Chinese).
Zuo, J. C., Yang, Y. Q., Zhang, S. D., Mu, L., and Du, L., 2011. Numerical simulation of extreme water level of multiyear return period in the Bohai Sea. The International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers, Maui, Hawaii, 789–796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Qiao, L., Xu, J. et al. Estimation of extreme marine hydrodynamic variables in western Laizhou Bay. J. Ocean Univ. China 14, 425–432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2757-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2757-z