Abstract
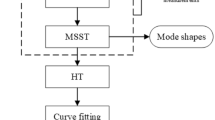
For modal parameter estimation of offshore structures, one has to deal with two challenges: 1) identify the interested frequencies, and 2) reduce the number of false modes. In this article, we propose an improved method of modal parameter estimation by reconstructing a new signal only with interested frequencies. The approach consists of three steps: 1) isolation and reconstruction of interested frequencies using FFT filtering, 2) smoothness of reconstructed signals, and 3) extraction of interested modal parameters in time domain. The theoretical improvement is that the frequency response function (FRF) of filtered signals is smoothed based on singular value decomposition technique. The elimination of false modes is realized by reconstructing a block data matrix of the eigensystem realization algorithm (ERA) using the filtered and smoothed signals. The advantage is that the efficiency of the identification process of modal parameters will be improved greatly without introducing any false modes. A five-DOF mass-spring system is chosen to illustrate the procedure and demonstrate the performance of the proposed scheme. Numerical results indicate that interested frequencies can be isolated successfully using FFT filtering, and unexpected peaks in auto spectral density can be removed effectively. In addition, interested modal parameters, such as frequencies and damping ratios, can be identified properly by reconstructing the Hankel matrix with a small dimension of ERA, even the original signal has measurement noises.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allemang, R. J., and Brown, D. L., 1998. A unified matrix polynomial approach to modal identification. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 211 (3): 301–322.
Braun, S., and Ram, Y. M., 1987. Time and frequency identification methods in over-determined systems. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 1 (3): 245–257.
Ewins, D. J., 2009. Modal Testing: Theory, Practice and Applications (2nd edition). Research Studies Press, Baldock, Hertfordshire, England, 576pp.
Hu, S.-L. J., Bao, X. X., and Li, H. J., 2010. Model order determination and noise removal for modal parameter estimation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 24 (6): 1605–1620.
Huang, J. N., and Pappa, R. S., 1985. An Eigensystem Realization Algorithm (ERA) for modal parameter identification and model reduction. Journal of Guidance Control and Dynamics, 8 (5): 620–627.
Jwo, D. J., and Chang, S. C., 2008. Application of optimization technique for GPS navigation Kalman filter adaptation. In: ICIC’8 Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing: Advanced Intelligent Computing Theories and Applications. Aspects of Theoretical and Methodological Issues, 227–234.
Kalman, R. E., 1960. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Transactions of the ASME. Series D. Journal of Basic Engineering, 82: 35–45.
Kalman, R. E., and Bucy, R. S., 1961. New results in linear filtering and prediction theory. Transactions of the ASME, Series D, Journal of Basic Engineering, 83: 95–107.
Li, H. J., Liu, F. S., and Hu, S.-L. J., 2008. Employing incomplete complex modes for model updating and damage detection of damped structures. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 51 (12): 2254–2268.
Liu, F. S., 2011. Direct mode-shape expansion of a spatially incomplete measured mode by a hybrid-vector modification. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 330 (18–19): 4633–4645.
Liu, F. S., and Li, H. J., 2012. Rapid direct mode shape expansion for offshore jacket structures using a hybrid vector. Ocean Engineering, 51 (1): 119–128.
Liu, F. S., and Li, H. J., 2013. A two-step mode shape expansion method for offshore jacket structures with physical meaningful modeling errors. Ocean Engineering, 63 (1): 26–34.
Liu, F. S., Chen, Z. S., and Li, W., 2012. Non-iterative mode shape expansion for three-dimensional structures based on coordinate decomposition. Journal of Vibroengineering, 14 (3): 984–993.
Pickrel, C. R., 1996. Estimating the rank of measured response data using SVD and principal response functions. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Structural Dynamics Modeling, Test Analysis and Correlation DTA/ NAFEMS, 89–100.
Sanliturk, K. Y., and Cakar, O., 2005. Noise elimination from measured frequency response functions. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 19: 615–631.
Skingle, W. T., and Urgueira, A., 1997. Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis. Research Studies Press, Taunton, Somerset, England, 488pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Qin, J., Li, H. et al. An improved lower order method of modal parameter estimation for offshore structures using reconstructed signals. J. Ocean Univ. China 14, 969–974 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2438-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-015-2438-y