Abstract
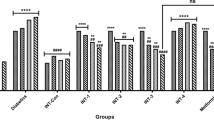
Sea cucumber and cordyceps sinensis are used as both food and traditional medicines in Asia. This study was carried out in order to investigate the hpyerglycemic effect of a mixture of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicas) and cordyceps sinensis (Cordyceps militaris) (SCC) in diabetic rat and explore the mechanism underlining such an effect. The diabetic model rat was induced with intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ). The diabetic model rats were randomly divided into control group (0.9% NaCl), low dose group (300 mg SCC·(kg body weight)−1) and high dose group (1200 mg SCC (kg body weight)−1). Sodium chloride and SCC were intragastrically administered once a day for 35 d. Changes in fasting serum glucose and serum insulin content, oral glucose tolerance and liver and muscle glycogen content were routinely evaluated. Pancreas tissue and β-cells of islets were observed under both optical and transmission electronic microscope, respectively. The abundance of glucose metabolism-relating genes in gastrocnemius and epididymal adipose tissue was determined with either reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) or western blotting. Results showed that SCC significantly decreased fasting serum glucose content, improved glucose tolerance and increased serum insulin and glycogen content; repaired STZ-injured β-cells of diabetic rat, and increased the expression of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI(3)K), protein kinase B (PKB) and glucose transporter 4 (Glut4) encoding protein in both gastrocnemius and adipose tissue, and Glut4 encoding gene in peripheral tissue. Our findings demonstrated that SCC exerted an anti-hyperglycemic effect by repairing β-cells and promoting insulin-mediated signal transduction pathway in insulin-sensitive gastrocnemius and adipose tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti, K. G., and Zimmet, P. Z., 1998. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine, 15: 539–553.
Berwick, D. C., Dell, G. C., Welsh, G. I., Heesom, K. J., Hers, I., Fletcher, L. M., Cooke, F. T., and Tavaré, J. M., 2004. Protein kinase B phosphorylation of PIKfyve regulates the trafficking of GLUT4 vesicles. Journal of Cell Science, 117: 5985–5993.
Bordbar, S., Anwar, F., and Saari, N., 2011. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods-A review. Marine Drugs, 9(10): 1761–1805.
Chang, W., Lim, S., Song, H., Song, B. W., Kim, H. J., Cha, M. J., Sung, J. M., Kim, T. W., and Hwang, K. C., 2008. Cordy cepin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. European Journal of Pharmacology, 597: 64–69.
Chopra, M., Galbraith, S., and Darnton-Hill, I., 2002. A global response to a global problem: The epidemic of overnutrition. Bull World Health Organ, 80: 952–958.
Fan, H. Z., 2001. The research and development of sea cucumber and its compositions in medical function. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 4: 37–44.
Furuta, M., Yano, Y., Gabazza, E. C., Araki-Sasaki, R., Tanaka, T., Katsuki, A., Hori, Y., Nakatani, K., Sumida, Y., and Adachi, Y., 2002. Troglitazone improves Glut4 expression in adipose tissue in an animal model of obese type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 56: 159–171.
Guo, J. Y., Li, C. Y., Wang, J., Liu, Y. M., and Zhang, J. H., 2011. Vanadium-enriched Cordyceps sinensis, a contemporary treatment approach to both diabetes and depression in rats. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 10: 1093–1099.
Hu, X. O., Wang, Y. M., and Wang, J. F., 2010. Dietary saponins of sea cucumber alleviate orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats via PPAR-α and SREBP-1c signaling. Lipids in Health and Disease, 9: 25–32.
Jiang, Z. Y., Zhou, Q. L., Coleman, K. A., Chouinard, M., Boese, Q., and Czech, M. P., 2003. Insulin signaling through Akt/protein kinase B analyzed by small interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(13): 7569–7574.
Jung, C. H., Seog, H. M., Choi, I. W., Choi, H. D., and Cho, H. Y., 2005. Effect of wild ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) leaves on lipid peroxidation levels and antioxidant enzyme activities in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Journal of Ethno-pharmacology, 98: 245–250.
Kim, H. O., and Yun, J. W., 2005. A comparative study on the production of exopolysaccharides between two entomopathogenic fungi Cordyceps militaris and Cordyceps sinensis in submerged mycelila cultures. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 99(4): 728–738.
Liu, Z. Y., Oliveira, A. C., and Su, Y. C., 2010. Purification and characterization of pepsin-solubilized collagen from skin and connective tissue of giant red sea cucumber (Parastichopus californicus). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(2): 1270–1274.
Lo, H. C., Hsu, T. H., Tu, S. T., and Lin, K. C., 2006. Antihyperglycemic activity of natural and fermented Cordyceps sinensis in rats with diabetes induced by nicotinamide and streptozotocin. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, 34: 819–832.
Long, T. T., Wang, J. F., Zhao, Q., Zhang, X., Li, X. L., Xue, C. H., and Li, Z. J., 2012. Protective effect and mechanism of Apostichopus japonicus on kidney of diabetic rats. Food Science, 33(1): 252–256.
Manning, B. D., and Newgard, C. B., 2007. PKB/PKB signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell, 129: 1261–1274.
Mohammad, S., Taha, A., Bamezai, R. N., and Baquer, N. Z., 2006. Modulation of glucose transporter (GLUT4) by vanadate and Trigonella in alloxan-diabetic rats. Life Sciences, 78: 820–824.
Okada, T., Kawano, Y., and Hazeki, O., 1994. Essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in insulin-induced glucose transport and antilipolysis in rat adipocytes: Studies with a selective inhibitor wortmannin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269: 3568–3573.
Panda, A. K., and Swain, K. C., 2011. Traditional uses and medicinal potential of Cordyceps sinensis of Sikkim. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 2: 9–13.
Park, S. E., Yoo, H. S., Jin, C. Y., Hong, S. H., Lee, Y. W., Kim, B. W., Lee, S. H., Kim, W. J., Cho, C. K., and Choi, Y. H., 2009. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity in human lung carcinoma cells by the water extract of Cordyceps militaris. Food Chemistry Toxicology, 47(7): 1667–1675.
Ramkumar, K. M., Vanitha, P., Uma, C., Suganya, N., Bhakkiyalakshmi, E., and Sujatha, J., 2011. Antidiabetic activity of alcoholic stem extract of Gymnema montanum in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 49: 3390–3394.
Su, H. C., Hung, L. M., and Chen, J. K., 2006. Resveratrol a red wine antioxidant, possesses an insulin-like effect in strepto-zotocin-induced diabetic rats. American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology and Metabolism, 290(6): E1339–E1346.
Tomlinson, K. C., Gardiner, S. M., Hebden, R. A., and Bennett, T., 1992. Functional consequences of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus, with particular reference to the cardiovascular system. Pharmacological Reviews, 44: 103–150.
Tremblay, F., Lavigne, C., Jacques, H., and Marette, A., 2003. Dietary cod protein restores insulin-induced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PKB and Glut4 translocation to the T-tubules in gastrocnemius of high-fat-fed obese rats. Diabetes, 52: 29–37.
Wang, J. F., Fu, J., Xu, L. L., Yang, Y. C., Wang, Y. M., and Xue, C. H., 2011. Involvement of the PI3K/Akt pathway in the hypoglycemic effects of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicas in diabetic rats. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 28(2): 172–177.
Wang, P. H., Tsai, M. J., Hsu, C. Y., Wang, C. Y., Hsu, H. K., and Weng, C. F., 2008. Toona sinenis Roem (Meliaceae) leaf extract alleviates hyperglycemia via altering adipose glucose transporter 4. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 46: 2554–2560.
Watson, R. T., and Pessin, J. E., 2001. Subcellular compartmentalization and trafficking of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter, GLUT4. Exp. Cell Research, 27(1): 75–83.
Won, S. Y., and Park, E. H., 2005. Anti-inflammatory and related pharmacological activities of cultured mycelia and fruiting bodies of Cordyceps militaris. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 96: 555–561.
Xu, J., Wang, Y. M., Feng, T. Y., Zhang, B., Sugawara, T., and Xue, C. H., 2011. Isolation and anti-fatty liver activity of a novel cerebroside from the sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 75(8): 1466–1471.
Xu, L. L., Wang, J. F., Tang, X., Wang, Y. M., Fu, J., and Xue, C. H., 2011. Hypoglycemia effect and the mechanism of Cordyceps militaris. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 27(9): 1331–1332.
Yu, R. M., Yin, Y., Yang, W., Ma, W. L., Yang, L., Chen, X. J., Zhang, Z., Ye, B., and Song, L. Y., 2009. Structural elucidation and biological activity of a novel polysaccharide by alkaline extraction from cultured Cordyceps militaris. Carbohydrate Polymers, 75: 166–171.
Zhang, Y., Song, S., Song, D., Liang, H., Wang, W., and Ji, A., 2010. Proliferative effects on neural stem/progenitor cells of a sulfated polysaccharide purified from the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicas. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengeering, 109(1): 67–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Wang, J., Li, Z. et al. Hpyerglycemic effect of a mixture of sea cucumber and cordyceps sinensis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. J. Ocean Univ. China 13, 271–277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-014-2073-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-014-2073-z