Abstract
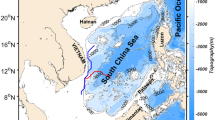
Relative roles of Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in driving summer upwelling in the South China Sea (SCS) are examined using QuikSCAT scatterometer wind data. The major upwelling regions in the SCS are the coastal regions east and southeast of Vietnam (UESEV), east and southeast of Hainan Island (UESEH), and southeast of Guangdong province (USEG). It is shown that the Ekman transport due to alongshore winds and Ekman pumping due to offshore wind stress curl play different roles in the three upwelling systems. In UESEV, Ekman pumping and Ekman transport are equally important in generating upwelling. The Ekman transport increases linearly from 0.49 Sv in May to 1.23 Sv in August, while the Ekman pumping increases from 0.36 to 1.22 Sv during the same period. In UESEH, the mean estimates of Ekman transport and Ekman pumping are 0.14 and 0.07 Sv, respectively, indicating that 33% of the total wind-driven upwelling is due to Ekman pumping. In USEG, the mean Ekman transport is 0.041 Sv with the peak occurring in July, while Ekman pumping is much smaller (0.003 on average), indicating that the upwelling in this area is primarily driven by Ekman transport. In the summers of 2003 and 2007 following El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events, both Ekman transport and Ekman pumping decrease in UESEV due to the abnormally weak southwest monsoon. During the same events, however, Ekman transport is slightly enhanced and Ekman pumping is weakened in UESEH and USEG.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. S., 1973. Upwelling and coastal jets in a continuously stratified ocean. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 3(3): 245–257.
Bombar, D., Dippner, J. W., Doan, H. N., Ngoc, L. N., Liskow, I., Loick-Wilde, N., and Voss, M., 2010. Sources of new nitrogen in the Vietnamese upwelling region of the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C6), DOI: 10.1029/2008JC005154.
Brink, K. H., Jones, B. H., Van Leer, J. C., Mooers, C. N. K., Stuart, D. W., Stevenson, M. R., Dugdale, R. C., and Heburn, G. W., 1981. Physical and biological structure and variability in an upwelling center off Peru near 15°C during March, 1977. In: Coastal Upwelling, Coastal and Estuarine Sciences, Vol. 1. Richards, F. A., ed., AGU, Washington, D. C., 473–495, DOI: 10.1029/CO001p0473.
Cai, S. Q., Long, X. M., Wu, R. H., and Wang, S. G., 2008. Geographical and monthly variability of the first baroclinic Rossby radius of deformation in the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 74(1–2): 711–720.
Cai, W. J., and Lennon, G. W., 1988. Upwelling in the Taiwan Strait in response to wind stress, ocean circulation and topography. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 26(1): 15–31.
Dippner, J. W., Nguyen, K. V., Hein, H., Ohde, T., and Loick, N., 2007. Monsoon-induced upwelling off the Vietnamese coast. Ocean Dynamics, 57(1): 46–62.
Du, Y., Xie, S. P., Huang, G., and Hu, K. M., 2009. Role of air-sea interaction in the long persistence of El Niño-induced North Indian Ocean warming. Journal of Climate, 22: 2023–2038.
Freilich, M. H., and Dunbar, R. S., 1999. The accuracy of the NSCAT 1 vector winds: Comparisons with National Data Buoy Center buoys. Journal of Geophys Research, 104(C5): 11231–11246.
Gan, Z. J., and Cai, S. Q., 2001. Geographical and seasonal variability of Rossby radii in South China Sea. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20(1): 1–9.
Gargett, A. E., 1991. Physical Processes and the Maintenance of Nutrient-Rich Euphotic Zones. Limnology and Oceanography, 36(8): 1527–1545.
Ho, C. R., Zheng, Q. A., Song, Y. S., Kuo, N. J., and Hu, J. H., 2000. Seasonal variability of sea surface height in the South China Sea observed with TOPEX/Poseidon altimeter data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(C6): 13981–13990.
Hu, J. Y., Kawamura, H., Hong, H. S., and Pan, W. R., 2003. A review of research on the upwelling in the Taiwan Strait. Bulletin of Marine Science, 73(3): 605–628.
Jing, Z. Y., Qi, Y. Q., and Du, Y., 2011. Upwelling in the continental shelf of northern South China Sea associated with 1997–1998 El Niño. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C2): C02033.
Jing, Z. Y., Qi, Y. Q., Hua, Z. L., and Zhang, H., 2009. Numerical study on the summer upwelling system in the northern continental shelf of the South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 29(2): 467–478.
Kuo, N. J., Zheng, Q. A., and Ho, C. R., 2000. Satellite observation of upwelling along the western coast of the South China Sea. Remote Sensing of Environment, 74(3): 463–470.
Lau, K. M., Wu, H. T., and Yang, S., 1998. Hydrologic processes associated with the first transition of the Asian summer monsoon: A pilot satellite study. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 79(9): 1871–1882.
Liu, W. T., and Xie, X., 1999. Spacebased observations of the seasonal changes of south Asian monsoons and oceanic responses. Geophysical Research Letters, 26(10): 1473–1476.
McPhaden, M. J., 1999. Genesis and evolution of the 1997–98 El Niño. Science, 283(5404): 950.
Naderi, F. M., Freilich, M. H., and Long, D. G., 1991. Spaceborne radar measurement of wind velocity over the ocean-An overview of the NSCAT scatterometer system. Proceedings of the IEEE, 79(6): 850–866.
Pickett, M. H., and Paduan, J. D., 2003. Ekman transport and pumping in the California Current based on the U.S. Navy’s high-resolution atmospheric model (COAMPS). Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(C10), 3327, DOI: 10.1029/2003 JC001902.
Shaw, P. T., and Chao, S. Y., 1994. Surface circulation in the South China Sea. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 41(11–12): 1663–1683.
Smith, R. L., 1968. Upwelling. In: Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review. Barnes, H., ed., George Allen and Unwin Ltd., Vol. 6, 11–46.
Smith, S. D., 1988. Coefficients for sea surface wind stress, heat flux, and wind profiles as a function of wind speed and temperature. Journal of Geophysical Research, 93(C12): 467–472.
Wang, B., Wu, R. G., and Li, T., 2003. Atmosphere-warm ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon variation. Journal of Climate, 16(8): 1195–1211.
Wang, C., and Weisberg, R. H., 2000. The 1997–98 El Niño evolution relative to previous El Niño events. Journal of Climate, 13(2): 488–501.
Wang, G. H., Wang, C. Z., and Huang, R. X., 2010. Interdecadal variability of the eastward current in the South China Sea associated with the summer Asian monsoon. Journal of Climate, 23(22): 6115–6123.
Wyrtki, K., 1961. Scientific results of marine investigations of the South China Sea and the Gulf of Thailand 1959–1961. NAGA Report, Vol. 2.
Xie, S. P., Hu, K. M., Hafner, J., Tokinaga, H., Du, Y., Huang, G., and Sampe, T., 2009. Indian Ocean capacitor effect on Indo-western Pacific climate during the summer following El Niño. Journal of Climate, 22(3): 730–747.
Xie, S. P., Xie, Q., Wang, D. X., and Liu, W. T., 2003. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(C8), 3261, DOI: 10.1029/2003JC001867.
Xu, H. M., Xie, S. P., Wang, Y. Q., Zhuang, W., and Wang, D. X., 2008. Orographic effects on South China Sea summer climate. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 100(1): 275–289.
Zhao, H., and Tang, D. L., 2007. Effect of 1998 El Niño on the distribution of phytoplankton in the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(C2), C02017, DOI: 10.1029/2006JC003536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Wang, H., Li, M. et al. Role of Ekman transport versus Ekman pumping in driving summer upwelling in the South China Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 12, 355–365 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-013-1904-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-013-1904-7