Abstract
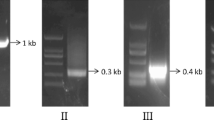
A putative tetrasporophyte-specific gene, designated as SSH466 (GenBank accession No. DQ019223), was one of the genes identified in this work using suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) method in Gracilaria lemaneiformis. The full length of the gene was obtained using SMART RACE strategy. Sequence analysis revealed that the gene had 1 019 nucleotides, including an open reading frame of 498 nucleotides encoding 166 amino acid residues, 158 nucleotides of 5′ untranslated region and 363 nucleotides of 3′ non-coding region. Protein motif and secondary structure prediction showed that there existed a transmembrane domain with a unique β-sheet. Thus, SSH466 protein might be a cross-membrane protein. Sequence homology search in the public GenBank databases did not reveal any significant match with SSH466. Virtual Northern blot analysis confirmed that it was a tetrasporophyte-specific gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahn, S. C., M. S. Bae, Y. B. Park, S. I. Oh, J. U. Jeung, J. M. Bae, et al., 2001. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel low temperature-induced gene, blti2, from barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1532: 134–137.
Brun, F., M. Gonneau, M. Laloue, and F. Nogue, 2003. Identification of Physcomitrella patens genes specific of bud and gametophore formation. Plant Sci., 165: 1267–1274.
Caturla, M., C. Chaparro, K. Schroeyers, and M. Holsters, 2002. Suppression subtractive hybridization to enrich low-abundance and submergence-enhanced transcripts of adventitious root primordia of Sesbania rostrata. Plant Sci., 162: 915–921.
Cramer, R. A., and C. B. Lawrence, 2004. Identification of Alternaria brassicicola genes expressed in planta during pathogenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Fungal Genet. Biol., 41: 115–128.
De la Vega, E., B. M. Degnan, M. R. Hall, and K. J. Wilson, 2007. Differential expression of immune-related genes and transposable elements in black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) exposed to a range of environmental stressors. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 23: 1072–1088.
Diatchenko, L., Y. C. Lau, A. P. Campbell, A. Chenchik, F. Moqadam, B. Huang, et al., 1996. Suppression subtractive hybridization: a method for generating differentially regulated or tissue-specific cDNA probes and libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93: 6025–6030.
Endege, W. O., K. E. Steinmann, L. A. Boardman, S. N. Thibodeau, and R. Schlegel, 1999. Representative cDNA libraries and their utility in gene expression profiling. Biotechniques, 26: 542–550.
Liu, Q. Y., J. P. van der Meer, and M. E. Reith, 1994. Isolation and characterization of phase-specific complementary DNAs from sporophytes and gametophytes of Porphyra purpurea (Rhodophyta) using subtracted complementary DNA libraries. J. Phycol., 30: 513–520.
Shary, S., and S. Guha-Mukherjee, 2004. Isolation and expression studies of differentiation-specific genes in tobacco dihaploids using PCR-based subtractive hybridization method. Plant Sci., 166: 317–322.
Shim, W. B., and L. D. Dunkle, 2002. Identification of genes expressed during cercosporin biosynthesis in Cercospora zeae-maydis. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 61: 237–248.
Singh, M, B. L. Burson, and S. A. Finlayson, 2007. Isolation of candidate genes for apomictic development in buffelgrass (Pennisetum ciliare). Plant Mol. Biol., 64: 673–682.
Sun, X., G. P. Yang, Y. X. Mao, X. C. Zhang, Z. H. Sui, and S Qing, 2002. Analysis of expressed sequence tags of a marine algae, Gracilaria/Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Progr. Nat. Sci., 12: 518–523.
Ye, N. H., H. X. Wang, and Q. C. Wang, 2006. Formation and early development of tetraspores of Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Gracilaria, Gracilariaceae) under laboratory conditions. Aquaculture, 254: 219–226.
Zhu, Y., T. J. Johnson, A. A. Myers, and M. R. Kanost, 2003. Identification by subtractive suppression hybridization of bacteria induced genes expressed in Manduca sexta fat body. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 33: 541–559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Zhang, X. Identification of a putative tetrasporophyte-specific gene in Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Gracilariales, Rhodophyte). J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 299–303 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0299-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0299-3