Abstract
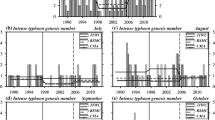
Using the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis dataset from 1959–2004, the location and strength of the ITCZ (Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone), as well as their relations with typhoons in the northwestern Pacific were studied. It was found that the pentad location and strength of the ITCZ had close relations with the typhoon frequency. Higher latitude location or strengthened ITCZ were found to be favorable for the occurrence of typhoons over the Northwestern Pacific. An index was defined for ascertaining the location of the ITCZ. It was found that the index defined with the maximum value of pentad and monthly meridional shear of zonal wind speed could better describe the location of ITCZ than another index defined with the maximum value of convergence. Correlation analysis between the index of ITCZ and the maximum cloud cover in the tropics showed that there were close relations between the ITCZ determined by the index and the maximum tropical cloud belt. The strength index of an ITCZ was defined as the zonal wind speed difference at latitudes south and north of the ITCZ. It was found that there are close relations between the ITCZ intensity and typhoon occurrence in the South China Sea [10°N–20°N, 100°E–120°E] and regions east of the Philippines and near the Mariana Islands [5°N–20°N, 127.5°E–150°E].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L. S., and Z. Y. Meng, 2001. An overview on tropical cyclone research progress in China during the past ten years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci., 25(3): 420–432.
Chen, L. S., H. B. Luo, Y. H. Duan, and H. Yu, 2004. An overview of tropical cyclone and tropical meteorology research progress. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 21(3): 505–514.
Chen, M., Y. G. Zheng, and Z. Y. Tao, 1999. An analysis on tropical cyclones’ climatic feature in the western north Pacific for 1949–1996. J. Trop. Meteorol., 15(1): 10–16.
Elsberry, R. L., 1995. Global perspectives on tropical cyclone. WMO. TD-NO.693, Chapter 4, 106–197.
Liang, B. Q., 1995. Course of Synoptic Meteorology. Meteorology Press. Chapter 7, 329.
Philander, S. G. H., 1990. El Nino, La Nina and Southern Oscillation. Academic Press, San Diego, Calif., 293pp.
Yang, C. F., X. L. Jiao, and C. Peng, 2003. The tropical belt of convergence and the climate of South China Sea. Mar. Sci. Bull., 22(6): 83–87.
Zhang, Q. Y., and J. B. Peng, 2003. The interannual and interdecadal variations of East Asian summer circulation and its impact on the landing typhoon frequency over China during summer. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci., 27(1): 97–106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, D., Sun, J. & Li, Y. Analysis of the anomalous strength and location of the ITCZ affecting the formation of northern Pacific typhoons. J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 124–130 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0124-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0124-z