Abstract
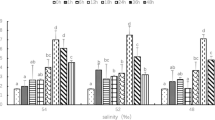
The effects of salinity on hemolymph osmotic pressure, Na+ concentration and Na+-K+-ATPase activity of gill of Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis were studied. The results showed that hemolymph osmotic pressure and Na+ concentration increased significantly (P<0.05), and the Na+-K+-ATPase activity of gills decreased significantly (P<0.05) when salinity increased from 0 to 16. The hemolymph osmotic pressure and Na+ concentration in each treatment group rose remarkably at 0.125 d or 0.25 d, while the Na+-K+-ATPase activity of gill reduced gradually with increased experiment time in 3 d. Then the three parameters remained at a constant level after 0.25 d, 0.125 d and 3 d, respectively, and higher hemolymph osmotic pressure, higher Na+ concentration and lower Na+-K+-ATPase activity of gill occurred at higher salinity. The effect of salinity change on protein concentration of hemolymph was indistinct (P>0.05); However, the protein concentration decreased gradually with the increase of salinity from 0.25 d to 1 d, and then tended to be stable from day 1 to day 15.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barra, J. A., A. Péqueux, and W. Humbert, 1983. A morphological study on gills of a crab acclimated to freshwater. Tissue and Cell, 15: 583–596.
Bianchini, A., A. Péqueux, and R. Gilles, 1988. Effects of TAP and DPC on the transepithelial potential difference of isolated perfused gills of the fresh water acclimated crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 90A: 315–319.
Bradford, M. M., 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem., 72: 248–254.
Castiho, P. C., I. A. Martins, and A. Bianchini, 2001. Gill Na+/K+-ATPase and osmoregulation in the estuarine crab, Chasmagnathus granulata Dana, 1851 (Decapoda, Grapsidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 256: 215–227.
Castille, F. L, and A. L. Lawrence, 1981. The effect of salinity on the osmotic, Na, and chloride concentrations in the hemolymph of euryhaline shrimp of the genus Penaeus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 68A: 75–80.
Chen, J. C., and P. G. Chia, 1997. Osmotic and ionic concentrations of Scylla serrata (Forskål) subjected to different salinity levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 117A: 239–244.
Dalla Via, G. J., 1986b. Salinity responses of the juvenile shrimp Penaeus japonicus. II. Free amino acids. Aquaculture, 55: 307–316
Dalla Via, G. J., 1989. The effect of salinity on free amino acids in the prawn Palaemon elegans (Rathke). Arch. Hydrobiol., 115: 125–135.
Freire, C. A., J. C. McNamara, J. C. Rosa, and L. J. Greene, 1995. Neuroendocrine control of osmotic regulation in the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii (Wiegmann) (Crustacea, Decapoda); Free amino acid concentrations in the hemolymph. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 100: 83–91.
Gilles, R., A. Péqueux, and A. Bianchini, 1988. Physiological aspects of NaCl movements in gills of the euryhaline crab, Eriocheir sinensis, acclimated to fresh water. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 90A: 201–207.
Huong, D. T. T., W. J. Yang, A. Okuno, and M. N. Wilder, 2001. Changes in free amino acids in the hemolymph of giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii exposed to varying salinities: relationship to osmoregulatory ability. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 128A: 317–326.
Kamemoto, F. L., 1991. Neuroendocrinology of osmoregulation in crabs. Zool. Sci. 8: 827–833.
Lignon, J. M., and A. Péqueux, 1988. Transbranchial and transcuticular potentials in the gill filaments of the crayfish Astacus leptodectytus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 90A: 820–829.
Lima, A. G., J. C. McNamara, and W. R. Terra, 1997. Regulation of hemolymph osmolytes and gill Na+/K+-ATPase activities during acclimation to saline media in the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii (Wiegmann, 1836) (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 215: 81–91.
Lin, S. C., C. H. Liou, and J. H. T. Cheng, 2000. The role of the antennal glands in ion and body volume regulation of cannulater Penaeus monodon reared in various salinity conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 127A: 121–129.
Lucu, C., M. Devescovi, B. Skaramuca, and V. Kozul, 2000. Gill Na+, K+-ATPase in the spiny lobster Palinurus elephas and other marine osmoconformers-Adaptiveness of enzymes from osmoconformity to hyperregulation. J. Exp. Mar Biol. Ecol., 246: 163–178.
Lucu, C., and M. Devescovi, 1999. Osmoregulation and branchial Na+, K+-ATPase in the lobster Homarus gammarus acclimated to dilute seawater. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 234: 291–304.
Lucu, C., and G. Flik, 1999. Na+/K+-ATPase and Na+/Ca2+ exchange activities in gills of hyperregulating Carcinus maenas. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol., 276(2): R490–R499.
Lü, F., L. Q. Pan, and J. Y. Ren, 2004. A study on the characteristics of gill Na+/K+-ATPase of the Eriocheir sinensis. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol., 3: 48–53.
Mo, J. L., P. Devos, and G. Trausch, 1998. Dopamine as a modulator of ionic transport and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the gills of the Chinese crab (Eriocher sinensis). J. Crustac. Biol., 1: 442–448.
Morris, S., and T. Edwards, 1995. Control of osmoregulation via regulation of Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the amphibious purple shore crab, Leptograpsus variegatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 112C: 129–136.
Morris, S., 2001. Neuroendocrine regulation of osmoregulation and the evolution of air-breathing in decapod crustaceans. J. Exp. Biol., 204(5): 979–989.
Neufeld, G. J., C. W. Holliday, and J. B. Pritchard, 1980. Salinity adaptation of gill Na+, K+-ATPase in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. J. Exp. Zool., 211:215–224.
Onken, H., and S. Riestenpatt, 1998. NaCl absorption across split gill lamellae of hyperregulating crabs: Transport mechanisms and their regulation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 119A: 883–893.
Péqueux, A., and R. Gille, 1978. Osmoregulation of the euryhaline Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis. Ionic transport across isolated perfused gills as related to the salinity of the environment. In: Proceedings of the 12th European Marine Biology Symposium, Stirling Scotland. Physiology and Behaviour of Marine Organisms. Pergamon Press, Oxford, England, 105–111.
Péqueux, A., and R. Gilles, 1981. Na+ fluxes across isolated perfused gills of the Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis. J. Exp. Biol., 92: 173–186.
Péqueux, A., and R. Gilles, 1988. The transepithelial potential difference of isolated perfused gills of the Chinese crab, Eriocheir sinensis acclimated to fresh water. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 89A: 163–172.
Péqueux, A., 1995. Osmotic regulation in crustaceans. Review. J. Crust. Biol., 15(1): 1–60.
Riestenpatt, S., W. Zeiske, and H. Onken, 1994. Cyclic AMP stimulation of electrogenic uptake of Na+ and Cl− across the gill epithelium of the Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis. J. Exp. Zool., 188: 159–174.
Spaargaren, D. H., 1971. Aspects of osmotic regulation in the shrimp Crangon crangon and Crangon allmnni. Neth. J. Sea. Res., 5: 275–333.
Trausch, G., M. C. Forget, and P. Devos, 1989. Bioamines-stimulated phosphorylation and Na+/K+-ATPase in the gills of Chinese crabs, Eriocheir sinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 94B: 487–492
Whealty, M. G, and R. P. Hentry, 1987. Branchial and antennal Na+/K+-dependent ATPase and carbonie anhydrase activity during salinity acclimation of the euryhaline crayfish Pacifastacus leniuscndus. J. Exp. Biol., 133: 73–86.
Wilder, M. N., K. Ikuta, M. Atmomarsono, T. Hatta, and Komuro, 1998. Changes in osmotic and ionic concentrations in the hemolymph of Macrobrachium rosenbergii exposed to varying salinities and correlation to ionic and crystalline composition of the cuticle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 119A: 941–950.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Pan, L. & Fu, L. Effect of salinity on hemolymph osmotic pressure, sodium concentration and Na+-K+-ATPase activity of gill of Chinese crab, Eriocheir sinensis . J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 77–82 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0077-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0077-2