Abstract
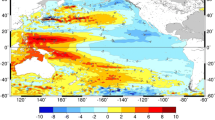
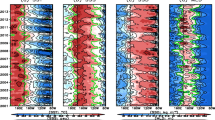
The Sea Level Anomaly-Torque (SLAT, relative to a reference location in the Pacific Ocean), which means the total torque of the gravity forces of sea waters with depths equal to the Sea Level Anomaly (SLA) in the tropical Pacific Ocean, is defined in this study. The time series of the SLAT from merged altimeter data (1993–2003) had a great meridional variation during the 1997–1998 El Niño event. By using historical upper layer temperature data (1955–2003) for the tropical Pacific Ocean, the temperature-based SLAT is also calculated and the meridional variation can be found in the historical El Niño events (1955–2003), which suggests that the meridional shifts of the sea level anomaly are also intrinsic oscillating modes of the El Niño cycles like the zonal shifts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan R. J., N. Nicholls, P. D. Jones, and I. J. Butterworth, 1991. A further extension of the Tahiti-Darwin SOI, early SOI results and Darwin pressure. J. Climate, 4: 743–749.
Cassou C, and C. Perigaud, 2000. ENSO simulated by intermediate coupled models and evaluated with observations over 1970–98. Part II: role of the off-equatorial ocean and meridional winds. J. Climate, 13: 1635–1663.
Chen J. N., G. T. Song, J. T. Chu, and L. Y. Xu, 2003a. Anomalous sea temperature of westward transferring north equatorial current and ENSO. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 22(4): 10–17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen J. N., G. T. Song, J. T. Chu, and L. Y. Xu, 2003b. Oceanic temperature anomalous signal pathway in the equatorial Pacific. Advances in Water Science, 14(2): 152–157 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ducet N., P. Y. Le Traon, and G. Reverdin, 2000. Global high resolution mapping of ocean circulation from TOPEX/Poseidon and ERS-1/2. J. Geophys. Res., 105: 19477–19498.
Fedorov A. V., and S. G. Philander, 2000. Is El Niño changing? Science, 288: 1997–2002.
Harrison, D. E., and N. K. Larkin, 1996. The COADS sea level pressure signal: A near-global El Niño composite and time series view, 1946–1993. J. Climate, 9: 3025–3055.
Jin, F. F., 1997a. An equatorial ocean recharge paradigm for ENSO, Part I: Conceptual model. J. Atmos. Sci., 54: 811–829.
Jin, F. F., 1997b. An equatorial ocean recharge paradigm for ENSO, Part II: A stripped-down coupled model. J. Atmos. Sci., 54: 830–847.
Kug, J. S., I. S. Kang, and S. I. An, 2003. Symmetric and antisymmetric mass exchanges between the equatorial and off equatorial Pacific associated with ENSO. J. Geophys. Res., 108(C8): 3284, doi: 10.1029/2002JC001671.
Können G. P., P. D. Jones, M. H. Kaltofen, and R. J. Allan, 1998. Pre-1866 extensions of the Southern Oscillation Index using early Indonesian and Tahitian meteorological readings. J. Climate, 11: 2325–2339.
Meinen C. S., 2005. Meridional extent and interannual variability of the Pacific ocean tropical-subtropical warm water exchange. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 35(3): 323–335
Meinen C. S., and M. J. McPhaden, 2000. Observations of warm water volume changes in the equatorial Pacific and their relationship to El Niño and La Niña. J. Climate., 13: 3551–3559.
Meinen C. S., and M. J. McPhaden, 2001. Interannual variability in warm water volume transports in the equatorial pacific during 1993–1999. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 31: 1324–1345.
McPhaden M. J., 1999. Genesis and evolution of the 1997–98 El Niño. Science, 283: 950–954.
Miller L., and R. Cheney, 1990. Large-scale meridional transport in the tropical Pacific Ocean during the 1986–1987 El Niño from Geosat. J. Geophys. Res., 95: 17905–17919.
Perigaud C., F. Melin, and C. Cassou, 2000. ENSO simulated by intermediate models and evaluated with observations over 1970–1998, part I, role of the off-equatorial variability, J. Climate., 13: 1605–1634.
Rebert J. P., J. R. Donguy, G. Eldin, and K. Wyrtki, 1985. Relationship between sea level, thermocline depth, heat content, and dynamic height in the tropical Pacific Ocean, J. Geophy. Res., 90: 11719–11725.
Reynolds R. W., and T. M. Smith, 1994, Improved global sea surface temperature analysis using optimum interpolation. J. Climate, 7: 929–948.
Reynolds R. W., and T. M. Smith, 1995. A high resolution global sea surface temperature climatology. J. Climate, 8: 1571–1583.
Trenberth K. E., 1997. The definition of El Niño. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 78: 2771–2777.
Trenberth K. E. and D. P. Stepaniak, 2001. Indices of El Niño evolution. J. Climate, 14: 1697–1701.
Wang B., R. Wu, and R. Lukas, 1999. Roles of the western North Pacific wind variation in thermocline adjustment and ENSO phase transition. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan. 77: 1–16.
Woodruff, S. D., R. J. Slutz, R. L. Jenne, and P. M. Steurer, 1987. A comprehensive ocean-atmosphere data set. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 68: 1239–1250.
Yan X. H., C. R. Ho, Q. A. Zheng., and V. Klemas, 1992. Temperature and size variabilities of the Western Pacific Warm Pool. Science, 258: 1643–1645.
Yu J. Y., and C. R. Mechoso, 2001. Coupled atmosphere-ocean GCM study of the ENSO cycle. J. Climate, 14: 2329–2350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, M., Qu, L. Meridional variation of the 1955–2003 sea level anomalies in the tropical Pacific Ocean associated with El Niño events. J Ocean Univ. China 6, 332–338 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-007-0332-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-007-0332-y