Abstract
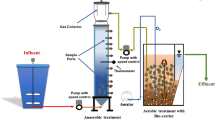
In this study, sponges were used to immobilize domesticated sludge microbes in a limited space, forming an immobilized biosystem capable of algae and microcystins removal. The removal effects on algae, microcystins and UV260 of this biosystem and the mechanism of algae removal were studied. The results showed that active sludge from sewage treatment plants was able to remove algae from a eutrophic lake’s water after 7 d of domestication. The removal efficiency for algae, organic matter and microcystins increased when the domesticated sludge was immobilized on sponges. When the hydraulic retention time (HRT) was 5h, the removal rates of algae, microcystins and UV260 were 90%, 94.17% and 84%, respectively. The immobilized biosystem consisted mostly of bacteria, the Ciliata and Sarcodina protozoans and the Rotifer metazoans. Algal decomposition by zoogloea bacteria and preying by microcreatures were the two main modes of algal removal, which occurred in two steps: first, absorption by the zoogloea; second, decomposition by the zoogloea bacteria and the predacity of the microcreatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouacha N., I. Maatouk, G. Vincent, and Y. Levi, 2002. A colorimetric and uorometric microplate assay for the detection of microcystins-LR in drinking water without preconcentration. Food Chem. Toxicol., 40: 1677–1683.
Bruchet, A., F. Bernazau, I. Baudin, and P. Pieronne, 1998. Algae toxins in surface water, analysis and treatment. Wat. Supply, 16: 611–623.
Carmichael, W. W., 1992. Cyanobacterial secondary meta-bolites-the cyanotoxins. J. Appl. Bacteriol., 72: 445–459.
Curt, F., 1998. Which policies can stop large scale eutrophication? Wat. Sci. Tech., 37(3): 193–200.
Cousins, I. T., D. J. Bealing, H. A. James, and A. Sutton, 1996. Biodegradation of MCYST-LR by indigenous mixed bacterial populations. Wat. Res., 30(2): 481–485.
Frederic, E., M. Konstanze, and W. Jean-louis, 2000. Risk of cyanobacterial toxins in Riga waters. Wat. Res., 34 (11): 2979–2988.
Hu, W. R., P. Q. Liu, and H. Y. Pei, 2003. Characteristics and mechanism analysis of O3 and ClO2 as algicides on inactivating algae. Chin. Sci. Bull., 48(9): 429–433.
Jeanine, D. P., and K. E. James, 1998. Effect of ozone on disinfection by-product formation of algae. Wat. Sci. Tech., 37(2): 49–55.
Kaya, K., and M. M. Watanabe, 1994. Chemistry and toxicology of cyclic heptapeptide toxins, the microcystins from cyanobacteria. Microbiol. Cult. Coll., 10: 5–33.
Leaf, S. S., and R. Chatterjee, 1999. Developing a strategy on eutrophication. Wat. Sci. Tech., 39(12): 307–314.
Oudra, B., M. Loudiki, B. Sbiyyaa, R. Martins, V. Vasconcelos, et al., 2001. Isolation, characterization and quantification of microcystins (heptapeptides hepatotoxins) in Microcystis aeruginosa dominated bloom of Lalla Takerkoust Lake-Reservoir (Morocco). Toxicon, 39: 1375–1381.
Rositano, J., G. Newcombe, B. Nicholson, and P. Sztajnbok, 2001. Ozonation of NOM and algae toxins in four treated water. Wat. Res., 35(1): 23–32.
Shi, W., S. H. Jing, and H. G. Zhu, 2003. Study on sanitation criterion of algae in source water in China. Sanitation Res., 32(2): 97–100.
Wang, S. F., 2000. Removal methods of algae in lake and reservoir. Tech. Prev. Cure Pollu., 13(1): 23–25.
Wellker, M., and C. Steinberg, 1999. Indirect photolysis of cyanotoxins: one possible mechanism for their low persistence. Wat. Res., 33(5): 1159–1164.
Wellker, M., and C. Steinberg, 2000. Rates of humic substance photosensitized degradation of microcystins-LR in natural water. Environ. Sci. Technol., 34(16): 3415–3419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, H., Hu, W. Study on algae removal by immobilized biosystem on sponge. J Ocean Univ. China 5, 327–332 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-006-0024-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-006-0024-z