Abstract
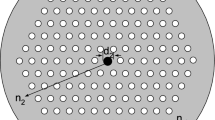
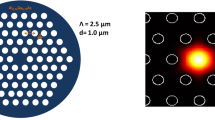
Based on the nonlinear and mode coupling effect in few-mode photonic crystal fiber (FM-PCF), an approach for supercontinuum (SC) generation in the mid-infrared (MIR) region is proposed. The propagation characteristics of Ge11.5As24Se64.5 FM-PCF have been analyzed and optimized by the full-vector finite element method. The two-mode generalized nonlinear Schrodinger equation (TM-GNLSE) is set up, and the SC generation has been analyzed by the split-step Fourier method. The SC from 1.80 µm to 11.32 µm is generated by pumping 3.0-cm-long fiber at the central wavelength of 3.0 µm, the peak power of 120 W, and the pulse duration of 250 fs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
STEINMEYER G, SKIBINA J S. Supercontinua: entering the mid-infrared[J]. Nature photonics, 2014, 8(11): 814–815.
KALRA S, VYAS S, TIWARI M, et al. Multi-material photonic crystal fiber in MIR region for broadband supercontinuum generation[M]//Optical and wireless technologies. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2018, 472: 199–209.
WEI W, PENG X, DAI S, et al. Visible to mid-infrared supercontinuum generated in novel GeS2−Ga2S3−CsI step-index fiber[J]. Journal of modern optics, 2019, 66(11): 1–7.
ZHU Y, ZHENG Z, GE X, et al. High-power, ultra-broadband supercontinuum source based upon 1/1.5 m dual-band pumping[J]. Chinese optics letters, 2021, 19(4): 041403–1–041403–6.
SAINI T S, KUMAR A, SINHA R K. Broadband mid-infrared supercontinuum spectra spanning 2–15 µm using As2Se3 chalcogenide glass triangular-core graded index photonic crystal fiber[J]. Journal of light wave technology, 2015, 33(18): 3914–3920.
CHENG T, NAGASAKA K, TUAN T H, et al. Mid-infrared supercontinuum generation spanning 2.0 to 15.1µm in a chalcogenide step-index fiber[J]. Optics letters, 2016, 41(9): 2117–2120.
WU B, ZHAO Z, WANG X, et al. Mid-infrared supercontinuum generation in a suspended-core tellurium-based chalcogenide fiber[J]. Optical materials express, 2018, 8(5): 1341–1348.
GAO W, AMRAOUI M E, LIAO M, et al. Mid-infrared supercontinuum generation in a suspended-core As2S3 chalcogenide microstructured optical fiber[J]. Optics express, 2013, 21(8): 9573–9583.
SHA B, SS A, MF A. Ultra-high birefringent, highly non-linear Ge20Sb15Se65 chalcogenide glass photonic crystal fiber with zero dispersion wavelength for mid-infrared applications[J]. Optik, 2020, 225: 1–27.
IRNIS K, OLE B. Multimode supercontinuum generation in chalcogenide glass fibres[J]. Optics express, 2016, 24(3): 2513–2526.
KHALIFA A B, SALEM A B, CHERIF R. Mid-infrared supercontinuum generation in multimode As2Se3 chalcogenide photonic crystal fiber[J]. Applied optics, 2017, 56(15): 4319–4324.
SWIDERSKI J, MICHALSKA M, MAZE G. Mid-IR supercontinuum generation in a ZBLAN fiber pumped by a gain-switched mode-locked Tm-doped fiber laser and amplifier system[J]. Optics express, 2013, 21(7): 7851–7857.
QIN G, XIN Y, KITO C, et al. Ultra-broadband supercontinuum generation from ultraviolet to 6.28 µm in a fluoride fiber[J]. Applied physics letters, 2009, 95(16): 584–588.
KUBAT I, PETERSEN C R, MØLLER U V, et al. Thulium pumped mid-infrared 0.9–9µm supercontinuum generation in concatenated fluoride and chalcogenide glass fibers[J]. Optics express, 2014, 22(4): 3959–3967.
SAFAEI A, BOLORIZADEH M A. Quantum mechanical treatment of the third order nonlinear term in NLS equation and the supercontinuum generation[C]//Photonic Fiber and Crystal Devices: Advances in Materials and Innovations in Device Applications X, August 28–September 1, 2016, San Diego, California, USA. Washington: SPIE, 2016: 995803.
CHAITANYA A, SINGH S T, AJEET K, et al. Ultra broad-band mid-IR supercontinuum generation in Ge11.5As24Se64.5 based chalcogenide graded-index photonic crystal fiber: design and analysis[J]. Applied optics, 2016, 55(36): 10138–10145.
FRANCESCO P, PETER H. Description of ultrashort pulse propagation in multimode optical fibers[J]. Journal of the optical society of America B, 2008, 25(10): 1645–1654.
FANG Y T, LIANG Z C. Unusual transmission through usual one-dimensional photonic crystal in the presence of evanescent wave[J]. Optics communications, 2010, 283(10): 2102–2108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Statements and Declarations
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61571237), and the Postgraduate Research and Innovation Program Project of Jiangsu (No.KYCX20_0795).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, W., Zhang, T. & Xu, C. Numerical research on mid-infrared supercontinuum generation in Ge11.5As24Se64.5 few-mode photonic crystal fibers. Optoelectron. Lett. 18, 0233–0237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-022-1121-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-022-1121-y