Abstract
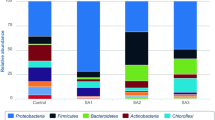
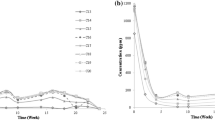
Petroleum hydrocarbons, mainly consisting of n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are considered as priority pollutants and biohazards in the environment, eventually affecting the ecosystem and human health. Though many previous studies have investigated the change of bacterial community and alkane degraders during the degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons, there is still lack of understanding on the impacts of soil alkane contamination level. In the present study, microcosms with different n-alkane contamination (1%, 3% and 5%) were set up and our results indicated a complete alkane degradation after 30 and 50 days in 1%- and 3%-alkane treatments, respectively. In all the treatments, alkanes with medium-chain length (C11-C14) were preferentially degraded by soil microbes, followed by C27-alkane in 3% and 5% treatments. Alkane contamination level slightly altered soil bacterial community, and the main change was the presence and abundance of dominant alkane degraders. Thermogemmatisporaceae, Gemmataceae and Thermodesulfovibrionaceae were highly related to the degradation of C14- and C27-alkanes in 5% treatment, but linked to alkanes with medium-chain (C11-C18) in 1% treatment and C21-alkane in 3% treatment, respectively. Additionally, we compared the abundance of three alkane-monooxygenase genes, e.g., alk_A, alk_P and alk_R. The abundance of alk_R gene was highest in soils, and alk_P gene was more correlated with alkane degradation efficiency, especially in 5% treatment. Our results suggested that alkane contamination level showed non-negligible effects on soil bacterial communities to some extents, and particularly shaped alkane degraders and degrading genes significantly. This study provides a better understanding on the response of alkane degraders and bacterial communities to soil alkane concentrations, which affects their biodegradation process.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acer O, Guven K, Bekler F M, Gul-Guven R (2016). Isolation and characterization of long-chain alkane-degrading Acinetobacter sp. BT1A from oil-contaminated soil in Diyarbakir, in the Southeast of Turkey. Bioremediation Journal, 20(1): 80–87
Alonso-Gutiérrez J, Figueras A, Albaigés J, Jiménez N, Viñas M, Solanas A M, Novoa B (2009). Bacterial communities from shoreline environments (costa da morte, northwestern Spain) affected by the prestige oil spill. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(11): 3407–3418
Amouric A, Quéméneur M, Grossi V, Liebgott P P, Auria R, Casalot L (2010). Identification of different alkane hydroxylase systems in Rhodococcus ruber strain SP2B, an hexane-degrading actinomycete. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 108(6): 1903–1916
Baek K H, Yoon B D, Cho D H, Kim B H, Oh H M, Kim H S (2009). Monitoring bacterial population dynamics using real-time PCR during the bioremediation of crude-oil-contaminated soil. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19(4): 339–345
Bamforth S M, Singleton I (2005). Bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Current knowledge and future directions. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 80(7): 723–736
Binazadeh M, Karimi I A, Li Z (2009). Fast biodegradation of long chain n-alkanes and crude oil at high concentrations with Rhodococcus sp. Moj-3449. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 45(3): 195–202
Callaghan AV, Davidova I A, Savage-Ashlock K, Parisi VA, Gieg L M, Suflita J M, Kukor J J, Wawrik B (2010). Diversity of benzyl- and alkylsuccinate synthase genes in hydrocarbon-impacted environments and enrichment cultures. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(19): 7287–7294
Campeão M E, Reis L, Leomil L, de Oliveira L, Otsuki K, Gardinali P, Pelz O, Valle R, Thompson F L, Thompson C C (2017). The deep-sea microbial community from the Amazonian Basin associated with oil degradation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 1019
Carls M G, Thedinga J F (2010). Exposure of pink salmon embryos to dissolved polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons delays development, prolonging vulnerability to mechanical damage. Marine Environmental Research, 69(5): 318–325
Chandra S, Sharma R, Singh K, Sharma A (2013). Application of bioremediation technology in the environment contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbon. Annals of Microbiology, 63(2): 417–431
Cheng L, Shi S, Li Q, Chen J, Zhang H, Lu Y (2014). Progressive degradation of crude oil n-alkanes coupled to methane production under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. PLoS One, 9(11): e113253
Coleman N V, Yau S, Wilson N L, Nolan L M, Migocki M D, Ly M A, Crossett B, Holmes A J (2011). Untangling the multiple monooxygenases of Mycobacterium chubuense strain NBB4, a versatile hydrocarbon degrader. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 3(3): 297–307
Das N, Chandran P (2011). Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: An overview. Biotechnology Research International, 2011: 941810
Deng S, Ke T, Li L, Cai S, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Guo L, Chen L, Zhang D (2018). Impacts of environmental factors on the whole microbial communities in the rhizosphere of a metal-tolerant plant: Elsholtzia haichowensis Sun. Environmental Pollution, 237: 1088–1097
Ehrlich H L, Newman D K, Kappler A (2015) Ehrlich’s Geomicrobiology. Boca Raton: CRC Press
Ekperusi O A, Aigbodion, F I (2015) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons from crude oil-contaminated soil with the earthworm: Hyperiodrilus africanus. 3 Biotech, 5(6), 957–965
Elumalai P, Parthipan P, Karthikeyan O P, Rajasekar A (2017) Enzymemediated biodegradation of long-chain n-alkanes (C32 and C40) by thermophilic bacteria. 3 Biotech, 7, 116–126
Feng K, Zhang Z, Cai W, Liu W, Xu M, Yin H, Wang A, He Z, Deng Y (2017). Biodiversity and species competition regulate the resilience of microbial biofilm community. Molecular Ecology, 26(21): 6170–6182
Feng L, Wang W, Cheng J, Ren Y, Zhao G, Gao C, Tang Y, Liu X, Han W, Peng X, Liu R, Wang L (2007). Genome and proteome of longchain alkane degrading Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 isolated from a deep-subsurface oil reservoir. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104 (13): 5602–5607
Genovese M, Crisafi F, Denaro R, Cappello S, Russo D, Calogero R, Santisi S, Catalfamo M, Modica A, Smedile F, Genovese L, Golyshin P N, Giuliano L, Yakimov M M (2014). Effective bioremediation strategy for rapid in situ cleanup of anoxic marine sediments in mesocosm oil spill simulation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5: 162
Haritash A K, Kaushik C P (2009). Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1-3): 1–15
Hasanuzzaman M, Ueno A, Ito H, Ito Y, Yamamoto Y, Yumoto I, Okuyama H (2007). Degradation of long-chain n-alkanes (C-36 and C-40) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain WatG. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 59(1): 40–43
Hasinger M, Scherr K E, Lundaa T, Bräuer L, Zach C, Loibner A P (2012). Changes in iso- and n-alkane distribution during biodegradation of crude oil under nitrate and sulphate reducing conditions. Journal of Biotechnology, 157(4): 490–498
Hassanshahian M, Ahmadinejad M, Tebyanian H, Kariminik A (2013). Isolation and characterization of alkane degrading bacteria from petroleum reservoir waste water in Iran (Kerman and Tehran provenances). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 73(1): 300–305
Hassanshahian M, Zeynalipour M S, Musa F H (2014). Isolation and characterization of crude oil degrading bacteria from the Persian Gulf (Khorramshahr provenance). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 82(1-2): 39–44
Herlemann D P R, Labrenz M, Jürgens K, Bertilsson S, Waniek J J, Andersson A F (2011). Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME Journal, 5(10): 1571–1579
Jia J L, Zong S, Hu L, Shi S H, Zhai X B,Wang B B, Li G H, Zhang D Y (2017). The dynamic change of microbial communities in crude oilcontaminated soils from oil fields in China. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 26(2): 171–183
Jiang B, Li G, Xing Y, Zhang D, Jia J, Cui Z, Luan X, Tang H (2017). A whole-cell bioreporter assay for quantitative genotoxicity evaluation of environmental samples. Chemosphere, 184: 384–392
Jiménez N, Viñas M, Bayona J M, Albaiges J, Solanas A M (2007). The Prestige oil spill: Bacterial community dynamics during a field biostimulation assay. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77 (4): 935–945
Jiménez N, Viñas M, Guiu-Aragonés C, Bayona J M, Albaigés J, Solanas A M (2011). Polyphasic approach for assessing changes in an autochthonous marine bacterial community in the presence of Prestige fuel oil and its biodegradation potential. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 91(3): 823–834
Jurelevicius D, Alvarez V M, Peixoto R, Rosado A S, Seldin L (2013). The use of a combination of alkB primers to better characterize the distribution of alkane-degrading bacteria. PLoS One, 8(6): e66565
Kilbane J J 2nd (2006). Microbial biocatalyst developments to upgrade fossil fuels. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 17(3): 305–314
King C E, King G M (2014). Description of Thermogemmatispora carboxidivorans sp. nov., a carbon-monoxide-oxidizing member of the class Ktedonobacteria isolated from a geothermally heated biofilm, and analysis of carbon monoxide oxidation by members of the class Ktedonobacteria. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64(Pt 4): 1244–1251
Kulichevskaya I S, Ivanova A A, Baulina O I, RijpstraW I C, Sinninghe Damsté J S, Dedysh S N (2017). Fimbriiglobus ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gemmata-like planctomycete from Sphagnum peat bog and the proposal of Gemmataceae fam. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 67(2): 218–224
Li H, BoufadelMC (2010). Long-term persistence of oil from the Exxon Valdez spill in two-layer beaches. Nature Geoscience, 3(2): 96–99
Liu C, Wang W, Wu Y, Zhou Z, Lai Q, Shao Z (2011). Multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in a marine alkane degrader, Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5. Environmental Microbiology, 13(5): 1168–1178
Liu Q, Tang J, Liu X, Song B, Zhen M, Ashbolt N J (2017). Response of microbial community and catabolic genes to simulated petroleum hydrocarbon spills in soils/sediments from different geographic locations. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 123(4): 875–885
Liu X, Chen Y, Zhang X, Jiang X, Wu S, Shen J, Sun X, Li J, Lu L, Wang L (2015). Aerobic granulation strategy for bioaugmentation of a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) treating high strength pyridine wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 295: 153–160
Lo Piccolo L, De Pasquale C, Fodale R, Puglia A M, Quatrini P (2011). Involvement of an alkane hydroxylase system of Gordonia sp. strain SoCg in degradation of solid n-alkanes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(4): 1204–1213
Lu Z, Zeng F, Xue N, Li F (2012). Occurrence and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in organo-mineral particles of alluvial sandy soil profiles at a petroleum-contaminated site. Science of the Total Environment, 433: 50–57
Lueders T (2017). The ecology of anaerobic degraders of BTEX hydrocarbons in aquifers. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 93(1): 1–13
Magoc T, Salzberg S L (2011). FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 27(21): 2957–2963
Masy T, Demaneche S, Tromme O, Thonart P, Jacques P, Hiligsmann S, Vogel TM (2016). Hydrocarbon biostimulation and bioaugmentation in organic carbon and clay-rich soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 99: 66–74
Mehdi H, Giti E (2008). Investigation of alkane biodegradation using the microtiter plate method and correlation between biofilm formation, biosurfactant production and crude oil biodegradation. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 62(2): 170–178
Ni N, Song Y, Shi R, Liu Z, Bian Y, Wang F, Yang X, Gu C, Jiang X (2017). Biochar reduces the bioaccumulation of PAHs from soil to carrot (Daucus carota L.) in the rhizosphere: A mechanism study. Science of the Total Environment, 601-602: 1015–1023
Pacwa-Plociniczak M, Plaza G A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2016). Monitoring the changes in a bacterial community in petroleumpolluted soil bioaugmented with hydrocarbon-degrading strains. Applied Soil Ecology, 105: 76–85
Pagé A P, Yergeau É, Greer C W (2015). Salix purpurea stimulates the expression of specific bacterial xenobiotic degradation genes in a soil contaminated with hydrocarbons. PLoS One, 10(7): e0132062
Powell S M, Bowman J P, Ferguson S H, Snape I (2010). The importance of soil characteristics to the structure of alkane-degrading bacterial communities on sub-Antarctic Macquarie Island. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 42(11): 2012–2021
Powell S M, Ferguson S H, Bowman J P, Snape I (2006). Using real-time PCR to assess changes in the hydrocarbon-degrading microbial community in Antarctic soil during bioremediation. Microbial Ecology, 52(3): 523–532
Ravin, N V, Rakitin A L, Ivanova A A, Beletsky AV, Kulichevskaya I S, Mardanov A V, Dedysh S N (2018) Genome analysis of Fimbriiglobus ruber SP5T, a planctomycete with confirmed chitinolytic capability. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 84(7): e02645–17
Ribeiro H, Mucha A P, Almeida C M R, Bordalo A A (2013). Bacterial community response to petroleum contamination and nutrient addition in sediments from a temperate salt marsh. Science of the Total Environment, 458-460: 568–576
Sangwan P, Chen X, Hugenholtz P, Janssen P H (2004). Chthoniobacter flavus gen. nov., sp. nov., the first pure-culture representative of subdivision two, Spartobacteria classis nov., of the phylum Verrucomicrobia. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70 (10): 5875–5881
Scherr K E, Lundaa T, Klose V, Bochmann G, Loibner A P (2012). Changes in bacterial communities from anaerobic digesters during petroleum hydrocarbon degradation. Journal of Biotechnology, 157 (4): 564–572
Setti L, Lanzarini G, Pifferi P G, Spagna G (1993). Further research into the aerobic degradation of N-Alkanes in a heavy oil by a pure culture of a Pseudomonas sp. Chemosphere, 26(6): 1151–1157
Silva E J, Rocha e Silva N M, Rufino R D, Luna J M, Silva R O, Sarubbo L A (2014). Characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas cepacia CCT6659 in the presence of industrial wastes and its application in the biodegradation of hydrophobic compounds in soil. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 117: 36–41
Smits T H M, Witholt B, van Beilen J B (2003). Functional characterization of genes involved in alkane oxidation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek International Journal of General and Molecular Microbiology, 84(3): 193–200
Soman C, Li D,WanderMM, Kent A D (2017). Long-term fertilizer and crop-rotation treatments differentially affect soil bacterial community structure. Plant and Soil, 413(1–2): 145–159
Sun Y, Lu S, Zhao X, Ding A, Wang L (2017). Long-term oil pollution and in situ microbial response of groundwater in Northwest China. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72(4): 519–529
Throne-Holst M, Markussen S, Winnberg A, Ellingsen T E, Kotlar H K, Zotchev S B (2006). Utilization of n-alkanes by a newly isolated strain of Acinetobacter venetianus: The role of two alkB-type alkane hydroxylases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72(2): 353–360
Tomasek A, Staley C, Wang P, Kaiser T, Lurndahl N, Kozarek J L, Hondzo M, Sadowsky M J (2017). Increased denitrification rates associated with shifts in prokaryotic community composition caused by varying hydrologic connectivity. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 2304
Tourova T P, Sokolova D S, Semenova E M, Shumkova E S, Korshunova A V, Babich T L, Poltaraus A B, Nazina T N (2016). Detection of n-alkane biodegradation genes alkB and ladA in thermophilic hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria of the genera Aeribacillus and Geobacillus. Microbiology, 85(6): 693–707
Trevathan-Tackett S M, Seymour J R, Nielsen D A, Macreadie P I, Jeffries T C, Sanderman J, Baldock J, Howes J M, Steven A D L, Ralph P J (2017). Sediment anoxia limits microbial-driven seagrass carbon remineralization under warming conditions. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 93(6): fix033
Vasileiadis S, Puglisi E, Arena M, Cappa F, Cocconcelli P S, Trevisan M (2012). Soil bacterial diversity screening using single 16S rRNA gene V regions coupled with multi-million read generating sequencing technologies. PLoS One, 7(8): e42671
Wang X, Zhao X, Li H, Jia J, Liu Y, Ejenavi O, Ding A, Sun Y, Zhang D (2016). Separating and characterizing functional alkane degraders from crude-oil-contaminated sites via magnetic nanoparticlemediated isolation. Research in Microbiology, 167(9-10): 731–744
Wang Y, Nie M, Wan Y, Tian X, Nie H, Zi J, Ma X (2017). Functional characterization of two alkane hydroxylases in a versatile Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NY3. Annals of Microbiology, 67(7): 459–468
Wentzel A, Ellingsen T E, Kotlar H K, Zotchev S B, Throne-Holst M (2007). Bacterial metabolism of long-chain n-alkanes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 76(6): 1209–1221
Wu R R, Dang Z, Yi X Y, Yang C, Lu G N, Guo C L, Liu C Q (2011). The effects of nutrient amendment on biodegradation and cytochrome P450 activity of an n-alkane degrading strain of Burkholderia sp. GS3C. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2-3): 978–983
Zengler K, Heider J, Rossello-Mora R, Widdel F (1999). Phototrophic utilization of toluene under anoxic conditions by a new strain of Blastochloris sulfoviridis. Archives of Microbiology, 172(4): 204–212
Zhang D, Berry J P, Zhu D, Wang Y, Chen Y, Jiang B, Huang S, Langford H, Li G, Davison P A, Xu J, Aries E, Huang W E (2015). Magnetic nanoparticle-mediated isolation of functional bacteria in a complex microbial community. ISME Journal, 9(3): 603–614
Zhang D, Ding A, Cui S, Hu C, Thornton S F, Dou J, Sun Y, HuangWE (2013). Whole cell bioreporter application for rapid detection and evaluation of crude oil spill in seawater caused by Dalian oil tank explosion. Water Research, 47(3): 1191–1200
Zhang S, Yao H, Lu Y, Yu X,Wang J, Sun S, Liu M, Li D, Li Y F, Zhang D (2017). Uptake and translocation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and heavy metals by maize from soil irrigated with wastewater. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 12165
Zhao Q, Li R, Ji M, Ren Z J (2016). Organic content influences sediment microbial fuel cell performance and community structure. Bioresource Technology, 220: 549–556
Zhu L, Wang Y, Jiang L, Lai L, Ding J, Liu N, Li J, Xiao N, Zheng Y, Rimmington G M (2015). Effects of residual hydrocarbons on the reed community after 10 years of oil extraction and the effectiveness of different biological indicators for the long-term risk assessments. Ecological Indicators, 48: 235–243
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Scientific Foundation of China (No. 41672227).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Ding, A., Sun, Y. et al. Impacts of n-alkane concentration on soil bacterial community structure and alkane monooxygenase genes abundance during bioremediation processes. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 12, 3 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-018-1064-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-018-1064-5