Abstract
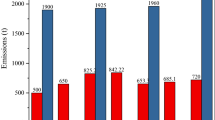
Mercury, as a global pollutant, has significant impacts on the environment and human health. The current state of atmospheric mercury emissions, pollution and control in China is comprehensively reviewed in this paper. With about 500–800 t of anthropogenic mercury emissions, China contributes 25%–40% to the global mercury emissions. The dominant mercury emission sources in China are coal combustion, non-ferrous metal smelting, cement production and iron and steel production. The mercury emissions from natural sources in China are equivalent to the anthropogenic mercury emissions. The atmospheric mercury concentration in China is about 2–10 times the background level of North Hemisphere. The mercury deposition fluxes in remote areas in China are usually in the range of 10–50 μg·m−2·yr−1. To reduce mercury emissions, legislations have been enacted for power plants, non-ferrous metal smelters and waste incinerators. Currently mercury contented in the flue gas is mainly removed through existing air pollution control devices for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particles. Dedicated mercury control technologies are required in the future to further mitigate the mercury emissions in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Global Mercury Assessment 2013: Sources, Emissions, Releases and Environmental Transport. Geneva, Switzerland: UNEP Chemicals Branch, 2013
Pirrone N, Mason R P. Hg Fate and Transport in the Global Atmosphere: Emissions, Measurements and Models. Geneva. Switzerland: Springer, 2009
Sprovieri F, Pirrone N, Ebinghaus R, Kock H, Dommergue A. A review of worldwide atmospheric mercury measurements. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(17): 8245–8265
Schroeder W H, Munthe J. Atmospheric mercury-An overview. Atmospheric Environment, 1998, 32(5): 809–822
Ci Z J, Zhang X S, Wang Z W. Enhancing atmospheric mercury research in China to improve the current understanding of the global mercury cycle: the need for urgent and closely coordinated efforts. Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 46(11): 5636–5642
Fu X W, Feng X B, Sommar J, Wang S F. A review of studies on atmospheric mercury in China. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 421–422: 73–81
Lindberg S E, Bullock R, Ebinghaus R, Engstrom D, Feng X B, Fitzgerald W, Pirrone N, Prestbo E, Seigneur C. A synthesis of progress and uncertainties in attributing the sources of mercury in deposition. Ambio, 2007, 36(1): 19–32
Lynam M M, Keeler G J. Automated speciated mercury measurements in Michigan. Environmental Science and Technology, 2005, 39(23): 9253–9262
Obrist D, Tas E, Peleg M, Matveev V, Faïn X, Asaf D, Luria M. Bromine-induced oxidation of mercury in the mid-latitude atmosphere. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 22(1): 22–26
Wu Y, Wang S X, Streets D G, Hao JM, Chan M, Jiang J K. Trends in anthropogenic mercury emissions in China from 1995 to 2003. Environmental Science and Technology, 2006, 40(17): 5312–5318
Streets D G, Hao JM, Wu Y, Jiang J K, Chan M, Tian H Z, Feng X B. Anthropogenic mercury emissions in China. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39(40): 7789–7806
Pacyna E G, Pacyna J M, Steenhuisen F, Wilson S. Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 22(40): 4048–4063
Pacyna E G, Pacyna J M, Sundseth K, Munthe J, Kindbom K, Wilson S, Steenhuisen F, Maxson P. Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020. Atmospheric Environment, 2010, 44(20): 2487–2499
Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP) and United Nations Environment Programme. (UNEP). Technical Background Report to the Global Atmospheric Mercury Assessment. Geneva, Switzerland: UNEP, 2008
Pirrone N, Chinirella S, Feng X B, Finkelman R B, Friedli H R, Leaner J, Mason R, Mukherjee A B, Stracher G B, Streets D G, Telmer K. Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(13): 5951–5964
Feng X B, Hong Y T. Estimation of mercury released to the air from coal combustion in China. Coal Mine Environment Protection, 1996, 10(3): 10–13
Wang Q C, Shen W G, Ma S W. The estimation of mercury emission fromcoal combustion in China. China Environmental Science, 1999, 19(4): 318–321
Jiang J K, Hao J M, Wu Y, Streets D G, Duan L, Tian H Z. Development of mercury emission inventory from coal combustion in China. Environmental Sciences, 2005, 26(2): 34–39
Tian H Z, Wang Y, Xue Z G, Cheng K, Qu Y P, Chai F H, Hao JM. Trend and characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Hg, As, and Se from coal combustion in China, 1980–2007. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(23): 11905–11919
Zhang L. Emission characteristics and synergistic control strategies of atmospheric mercury from coal combustion in China. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2012
Wang S X, Liu M, Jiang J K, Hao JM, Wu Y, Streets D G. Estimate the mercury emissions from non-coal sources in China. Environmental Sciences, 2006, 27(12): 2401–2406
Hylander L D, Herbert R B. Global emission and production of mercury during the pyrometallurgical extraction of nonferrous sulfide ores. Environmental Science and Technology, 2008, 42(16): 5971–5977
Li G H, Feng X B, Li Z G, Qiu G L, Shang L H, Liang P, Wang D Y, Yang Y K. Mercury emission to atmosphere from primary Zn production in China. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(20): 4607–4612
Yin R S, Feng X B, Li Z G, Zhang Q, Bi XW, Li G H, Liu J L, Zhu J J, Wang J X. Metallogeny and environmental impact of Hg in Zn deposits in China. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(1): 151–160
Wu Q R, Wang S X, Zhang L, Song J X, Yang H, Meng Y. Update of mercury emissions from China’s primary zinc, lead and copper smelters, 2000–2010. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(22): 11153–11163
Guan D B, Liu Z, Geng Y, Lindner S, Hubacek K. The gigatonne gap in China’s carbon dioxide inventories. Nature Climate Change, 2012, 2: 672–675
Wang Q, Shen W, Ma Z. Estimation of mercury emission from coal combustion in China. Environmental Science and Technology, 2000, 34(13): 2711–2713
Zhang MQ, Zhu Y C, Deng RW. Evaluation of mercury emissions to the atmosphere from coal combustion, China. Ambio, 2002, 31(6): 482–484
Huang W, Yang Y. Mercury in coal in China. Coal Geology of China, 2002, 14(5): 37–40
Zhang J, Ren D, Xu D, Zhao F. Mercury in coal and its effect on environment. Advances in Environmental Science, 1999, 7(3): 100–104
United States Geological Survey (USGS). Mercury Content in Coal Mines in China. 2004
Ren D, Zhao F, Dai S, Zhang J, Luo K. Geochemistry of Trace Elements in Coal. Beijing: Science Press, 2006
Zheng L, Liu G, Chou C L. The distribution, occurrence and environmental effect of mercury in Chinese coals. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 384(1–3): 374–383
Tian H Z, Wang Y, Xue Z G, Qu Y P, Chai F H, Hao J M. Atmospheric emissions estimation of Hg, As, and Se from coal-fired power plants in China, 2007. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(16): 3078–3081
Tian H Z, Wang Y, Cheng K, Qu Y P, Hao JM, Xue Z G, Chai F H. Control strategies of atmospheric mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants in China. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 2012, 62(5): 576–586
Tian H Z, Lu L, Hao JM, Gao J J, Cheng K, Liu K Y, Qiu P P, Zhu C Y. A review of key hazardous trace elements in Chinese coals: Abundance, occurrence, behavior during coal combustion and their environmental impacts. Energy and Fuels, 2013, 27(2): 601–614
Zhang L, Wang S X, Meng Y, Hao J M. Influence of mercury and chlorine content of coal on mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants in China. Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 46(11): 6385–6392
Chen L, Duan Y, Zhuo Y, Yang L, Zhang L, Yang X, Yao Q, Jiang Y, Xu X. Mercury transformation across particulate control devices in six power plants of China: The co-effect of chlorine and ash composition. Fuel, 2007, 86(4): 603–610
Zhou J. Emissions and Control of Mercury from Coal-Fired Utility Boilers in China. China Workshop on Mercury Control from Coal Combustion, Beijing, 2005
Zhou J, Wang G, Luo Z, Cen K. An experimental study of mercury emissions from a 600 MW pulverized coal-fired boiler. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2006, 21(6): 569–572
Zhou J, Zhang L, Luo Z, Hu C. Study on mercury emission and its control for boiler of 300 MW unit. Thermal Power Generation, 2008, 37(4): 22–27
Wang Y, Duan Y, Yang L, Jiang Y. An analysis of the factors exercising an influence on the morphological transformation of mercury in the flue gas of a 600 MW coal-fired power plant. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2008, 23(4): 399–403
Yang X, Duan Y, Jiang Y, Yang L. Research on mercury form distribution in flue gas and fly ash of coal-fired boiler. Coal Science and Technology, 2007, 35(12): 55–58
Duan Y, Cao Y, Kellie S, Liu K, Riley J T, Pan W. In-situ measurement and distribution of flue gas mercury for a utility PC boiler system. Journal of Southeast University, 2005, 21(1): 53–57
Wang Y, Duan Y, Yang L, Zhao C, Shen X, Zhang M, Zhuo Y, Chen C. Experimental study on mercury transformation and removal in coal-fired boiler flue gases. Fuel Processing Technology, 2009, 90(5): 643–651
Wu C, Duan Y, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Wang Q, Yang L. Characteristics of mercury emission and demercurization property of NID system of a 410 t/h pulverized coal fired boiler. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2008, 36(5): 540–544
Chen Y, Chai F, Xue Z, Liu T, Chen Y, Tian C. Study on mercury emission factors for coal-fired power plants. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(2): 49–52
Guo X, Zheng C, Jia X, Lin Z, Liu Y. Study on mercury speciation in pulverized coal-fired flue gas. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2004, 24(6): 185–188
Tang S. The mercury species and emissions from coal combustion flue gas and landfill gas in Guiyang. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2004
Goodarzi F. Speciation and mass-balance of mercury from pulverized coal fired power plants burning western Canadian subbituminous coals. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2004, 6(10): 792–798
He B, Cao Y, Romero C E, Bilirgen H, Sarunac N, Agarwal H, Pan W. Comparison and validation of OHM and SCEM measurements for a full-scale coal-fired power plant. Chemical Engineering Communications, 2007, 194(10–12): 1596–1607
Kellie S, Duan Y, Cao Y, Chu P, Mehta A, Carty R, Liu K, Pan W, Riley J T. Mercury emissions from a 100-MW wall-fired boiler as measured by semicontinuous mercury monitor and Ontario Hydro Method. Fuel Processing Technology, 2004, 85(6–7): 487–499
Lee S J, Seo Y C, Jang H N, Park K S, Baek J I, An H S, Song K C. Speciation and mass distribution of mercury in a bituminous coal-fired power plant. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(12): 2215–2224
Jun Lee S, Seo Y C, Jurng J, Hong J H, Park J W, Hyun J E, Gyu Lee T. Mercury emissions from selected stationary combustion sources in Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 325(1–3): 155–161
Otero-Rey J R, López-Vilariño J M, Moreda-Piñeiro J, Alonso-Rodríguez E, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, López-Mahía P, Prada-Rodríguez D. As, Hg, and Se flue gas sampling in a coal-fired power plant and their fate during coal combustion. Environmental Science and Technology, 2003, 37(22): 5262–5267
Shah P, Strezov V, Nelson P. Speciation of mercury in coal-fired power station flue gas. Energy and Fuels, 2010, 24(1): 205–212
Ito S, Yokoyama T, Asakura K. Emissions of mercury and other trace elements from coal-fired power plants in Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 368(1): 397–402
Meij R, te Winkel H. Mercury emissions from coal-fired power stations: The current state of the art in the Netherlands. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 368(1): 393–396
Shah P, Strezov V, Prince K, Nelson P F. Speciation of As, Cr, Se and Hg under coal fired power station conditions. Fuel, 2008, 87(10–11): 1859–1869
Yokoyama T, Asakura K, Matsuda H, Ito S, Noda N. Mercury emissions from a coal-fired power plant in Japan. Science of the Total Environment, 2000, 259(1–3): 97–103
Kim J H, Pudasainee D, Yoon Y S, Son S U, Seo Y C. Studies on speciation changes and mass distribution of mercury in a bituminous coal-fired power plant by combining field data and chemical equilibrium calculation. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(11): 5197–5203
Cheng C M, Hack P, Chu P, Chang Y N, Lin T Y, Ko C S, Chiang P H, He C C, Lai Y M, Pan W P. Partitioning of mercury, arsenic, selenium, boron, and chloride in a full-scale coal combustion process equipped with selective catalytic reduction, electrostatic precipitation, and flue gas desulfurization systems. Energy and Fuels, 2009, 23(10): 4805–4816
Information Collection Request (ICR). Results from onsite measurements in USA. Washington, D C: 2010
Wang S X, Zhang L, Li G H, Wu Y, Hao J M, Pirrone N, Sprovieri F, Ancora M P. Mercury emission and speciation of coal-fired power plants in China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(3): 1183–1192
Song J X, Wang S X, Li G H. Spatial distribution of mercury content of zinc concentrates in China. Science Paper Online, 2010, 5(6): 472–475
Wang S X, Song J X, Li G H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Wan Q, Streets D G, Chin C K, Hao J M. Estimating mercury emissions from a zinc smelter in relation to China’s mercury control policies. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(10): 3347–3353
Zhang L, Wang S X, Wu Q R, Meng Y, Yang H, Wang F Y, Hao J M. Were mercury emission factors for Chinese non-ferrous metal smelters overestimated? Evidence from onsite measurements in six smelters. Environmental Pollution, 2012, 171: 109–117
Gunson A J, Veiga M M. Mercury and artisanal mining in China. Environmental Practice, 2004, 6(2): 109–120
Sikkema J K, Alleman J E, Ong S K, Wheelock T D. Mercury regulation, fate, transport, transformation, and abatement within cement manufacturing facilities: review. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(20): 4167–4178
Won J H, Lee T G. Estimation of total annual mercury emissions from cement manufacturing facilities in Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 62: 265–271
Mlakar T L, Horvat M, Vuk T, Stergaršek A, Kotnik J, Tratnik J, Fajon V. Mercury species, mass flows and processes in a cement plant. Fuel, 2010, 89(8): 1936–1945
Li W J. Characterization of atmospheric mercury emissions from coal-fired power plant and cement plant. Dissertation for the Master Degree. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2011
Zhang L. Research on mercury emission measurement and estimate from combustion resources. Dissertation for the Master Degree. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Toolkit for Identification and Quantification of Mercury Releases. 2005
Fukuda N, Takaoka M, Doumoto S, Oshita K, Morisawa S, Mizuno T. Mercury emission and behavior in primary ferrous metal production. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(22): 3685–3691
Tian H Z, Gao J J, Lu L, Zhao D, Cheng K, Qiu P P. Temporal trends and spatial variation characteristics of hazardous air pollutant emission inventory from municipal solid waste incineration in China. Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 46(18): 10364–10371
Mason R P, Fitzgerald W F, Morel F M M. The biogeochemical cycling of elemental mercury: Anthropogenic influences. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(15): 3191–3198
Feng X B, Yan H Y, Wang S F, Qiu G L, Tang S L, Shang L H, Dai Q J, Hou Y M. Seasonal variation of gaseous mercury exchange rate between air and water surface over Baihua reservoir, Guizhou, China. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(28): 4721–4732
Feng X B, Wang S F, Qiu G G, He T R, Li G H, Li Z G, Shang L H. Total gaseous mercury exchange between water and air during cloudy weather conditions over Hongfeng Reservoir, Guizhou, China. J Geophys Res-Atmos, 2008, 113(D15): D15309
Feng X B, Wang S F, Qiu G A, Hou Y M, Tang S L. Total gaseous mercury emissions from soil in Guiyang, Guizhou, China. J Geophys Res-Atmos, 2005, 110(D14): D14306
Shetty S K, Lin C J, Streets D G, Jang C. Model estimate of mercury emission from natural sources in East Asia. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(37): 8674–8685
Wu Y, Wang S X, Streets D G, Hao JM, Chan M, Jiang J K. Trends in anthropogenic mercury emissions in China from 1995 to 2003. Environmental Science and Technology, 2006, 40(17): 5312–5318
Pan L, Chai T F, Carmichael G R, Tang Y H, Streets D, Woo J H, Friedli H R, Radke L F. Top-down estimate of mercury emissions in China using four-dimensional variational data assimilation. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(13): 2804–2819
Strode S A, Jaegle L, Jaffe D A, Swartzendruber P C, Selin N E, Holmes C, Yantosca R M. Trans-Pacific transport of mercury. J Geophys Res-Atmos, 2008, 113(D15): D15305
Gbor P K, Wen D Y, Meng F, Yang F Q, Zhang B N, Sloan J J. Improved model for mercury emission, transport and deposition. Atmospheric Environment, 2006, 40(5): 973–983
Feng X B, Shang L H, Wang S F, Tang S L, Zheng W. Temporal variation of total gaseous mercury in the air of Guiyang, China. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2004, 109(D3): 3303
Fu X W, Feng X B, Qiu G L, Shang L H, Zhang H. Speicated atmospheric mercury and its potential source in Guiyang, China. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(25): 4205–4212
Fang F M, Wang Q C, Li J F. Urban environmental mercury in Changchun, a metropolitan city in Northeastern China: source, cycle, and fate. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 330(1–3): 159–170
Wang Z W, Chen Z S, Duan N, Zhang X S. Gaseous elemental mercury concentration in atmosphere at urban and remote sites in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2007, 19(2): 176–180
Yang Y K, Chen H, Wang D Y. Spatial and temporal distribution of gaseous elemental mercury in Chongqing, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 156(1–4): 479–489
Friedli H R, Arellano A F Jr, Geng F, Cai C, Pan L. Measurements of atmospheric mercury in Shanghai during September 2009. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 11(8): 3781–3788
Nguyen D L, Kim J Y, Shim S G, Zhang X S. Ground and shipboard measurements of atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury over the Yellow Sea region during 2007–2008. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(1): 253–260
Zhu J, Wang T, Talbot R, Mao H, Hall C B, Yang X, Fu C, Zhuang B, Li S, Han Y, Huang X. Characteristics of atmospheric Total Gaseous Mercury (TGM) observed in urban Nanjing, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(24): 12103–12118
Fu X W, Feng X B, Zhu W Z, Wang S F, Lu J L. Total gaseous mercury concentrations in ambient air in the eastern slope of Mt. Gongga, South-Eastern fringe of the Tibetan plateau, China. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(5): 970–979
Fu X W, Feng X B, Zhu W Z, Zheng W, Wang S F, Lu J Y. Total particulate and reactive gaseous mercury in ambient air on the eastern slope of the Mt. Gongga area, China. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23(3): 408–418
Wan Q, Feng X B, Lu J, Zheng W, Song X J, Han S J, Xu H. Atmospheric mercury in Changbai Mountain area, northeastern China I. The seasonal distribution pattern of total gaseous mercury and its potential sources. Environmental Research, 2009, 109(3): 201–206
Wan Q, Feng X B, Lu J, Zheng W, Song X J, Li P, Han S J, Xu H. Atmospheric mercury in Changbai Mountain area, northeastern China II. The distribution of reactive gaseous mercury and particulate mercury and mercury deposition fluxes. Environmental Research, 2009, 109(6): 721–727
Fu X W, Feng X B, Shang L H, Wang S F, Zhang H. Two years of measurements of atmospheric total gaseous mercury (TGM) at a remote site in Mt. Changbai area, Northeastern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(9): 4215–4226
Fu X W, Feng X B, Dong Z Q, Yin R S, Wang J X, Yang Z R, Zhang H. Atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) concentrations and mercury depositions at a high-altitude mountain peak in south China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(5): 2425–2437
Fu XW, Feng X B, Zhang G, Xu WH, Li X D, Yao H, Liang P, Li J, Sommar J, Yin R S, Liu N. Mercury in the marine boundary layer and seawater of the South China Sea: Concentrations, sea/air flux, and implication for land outflow. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(D6): 6303
Fu XW, Feng X B, Liang P, Deliger, Zhang H, Ji J, Liu P. Deliger, Zhang H, Ji J, Liu P. Temporal trend and sources of speciated atmospheric mercury at Waliguan GAW station, Northwestern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(4): 1951–1964
Ci Z J, Zhang X S, Wang Z W, Niu Z C. Atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) over a coastal/rural site downwind of East China: Temporal variation and long-range transport. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(15): 2480–2487
Ci Z J, Zhang X S, Wang Z W, Niu Z C, Diao X Y, Wang S W. Distribution and air-sea exchange of mercury (Hg) in the Yellow Sea. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 11(6): 2881–2892
Li Z, Xia C H, Wang X M, Xia Y R, Xie Z Q. Total gaseous mercury in Pearl River Delta region, China during 2008 winter period. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(4): 834–838
Zhang H. Concentrations of speciated atmospheric mercury a highaltitude background station in the Shangri-La area of Tibetan Plateau, China. In: Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant, Halifax, Canada, 2011
Zhang L, Wang S X, Wang L, Hao J M. Atmospheric mercury concentration and chemical speciation at a rural site in Beijing, China: implication of mercury emission sources. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13: 10505–10516
Dou H Y. Characteristics of speciated atmospheric mercury concentrations at a rural site of Yangtze Delta, China. Dissertation for the Master Degree. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2012
Wang ZW, Zhang X S, Xiao J S, Zhijia C, Yu P Z. Mercury fluxes and pools in three subtropical forested catchments, southwest China. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(3): 801–808
Fu X W, Feng X B, Zhu W Z, Rothenberg S, Yao H, Zhang H. Elevated atmospheric deposition and dynamics of mercury in a remote upland forest of southwestern China. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(6): 2324–2333
Huang J, Kang S C, Zhang Q G, Yan H Y, Guo J M, Jenkins M G, Zhang G S, Wang K. Wet deposition of mercury at a remote site in the Tibetan Plateau: Concentrations, speciation, and fluxes. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 62: 540–550
Dai Z H, Feng X B, Sommar J, Li P, Fu XW. Spatial distribution of mercury deposition fluxes in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou Province, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(14): 6207–6218
Guo Y N, Feng X B, Li Z G, He T R, Yan H Y, Meng B, Zhang J F, Qiu G L. Distribution and wet deposition fluxes of total and methyl mercury in Wujiang River Basin, Guizhou, China. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(30): 7096–7103
Wangberg I, Munthe J, Berg T, Ebinghaus R, Kock H H, Temme C, Bieber E, Spain T G, Stolk A. Trends in air concentration and deposition of mercury in the coastal environment of the North Sea Area. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(12): 2612–2619
Graydon J A, St Louis V L, Hintelmann H, Lindberg S E, Sandilands K A, Rudd J W M, Kelly C A, Hall B D, Mowat L D. Long-term wet and dry deposition of total and methyl mercury in the remote boreal ecoregion of Canada. Environmental Science and Technology, 2008, 42(22): 8345–8351
Prestbo E M, Gay D A. Wet deposition of mercury in the US and Canada, 1996–2005: Results and analysis of the NADP mercury deposition network (MDN). Atmospheric Environment, 2009, 43(27): 4223–4233
Caldwell C A, Swartzendruber P, Prestbo E. Concentration and dry deposition of mercury species in arid south central New Mexico (2001–2002). Environmental Science and Technology, 2006, 40(24): 7535–7540
Marsik F J, Keeler G J, Landis M S. The dry-deposition of speciated mercury to the Florida Everglades: Measurements and modeling. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(1): 136–149
Feng X B, Li G H, Qiu G L. A preliminary study on mercury contamination to the environment from artisanal zinc smelting using indigenous methods in Hezhang county, Guizhou, China-Part 1: Mercury emission from zinc smelting and its influences on the surface waters. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(36): 6223–6230
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Zheng D, Zheng N, Lu X. Mercury distribution and bioaccumulation up the soil-plant-grasshopper-spider food chain in Huludao City, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2010, 22(8): 1179–1183
Li Z, Feng X, Li G, Bi X, Sun G, Zhu J, Qin H, Wang J. Mercury and other metal and metalloid soil contamination near a Pb/Zn smelter in east Hunan Province, China. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(2): 160–166
Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Q, Liang Z. Mercury contamination due to zinc smelting and chlor-alkali production in NE China. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(2): 188–193
Yin X, Yao C, Song J, Li Z, Zhang C, Qian W, Bi D, Li C, Teng Y, Wu L, Wan H, Luo Y. Mercury contamination in vicinity of secondary copper smelters in Fuyang, Zhejiang Province, China: levels and contamination in topsoils. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(6): 1787–1793
Jaffe D, Strode S. Sources, fate and transport of atmospheric mercury from Asia. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 5(2): 121–126
Selin N E, Jacob D J, Yantosca R M, Strode S, Jaegle L, Sunderland E M. Global 3-D land-ocean-atmosphere model for mercury: Present-day versus preindustrial cycles and anthropogenic enrichment factors for deposition. Global Biogeochemical Cycle, 2008, 22: GB2011
Lin C J, Pan L, Streets D G, Shetty S K, Jang C, Feng X, Chu HW, Ho T C. Estimating mercury emission outflow from East Asia using CMAQ-Hg. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(4): 1853–1864
Pan L, Lin C J, Carmichael G R, Streets D G, Tang Y H, Woo J H, Shetty S K, Chu H W, Ho T C, Friedli H R, Feng X B. Study of atmospheric mercury budget in East Asia using STEM-Hg modeling system. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(16): 3277–3291
Seigneur C, Vijayaraghavan K, Lohman K, Karamchandani P, Scott C. Global source attribution for mercury deposition in the United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(2): 555–569
Durnford D, Dastoor A, Figueras-Nieto D, Ryjkov A. Long range transport of mercury to the Arctic and across Canada. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10(13): 6063–6086
Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (MEP). Emission standard of air pollutants for thermal power plants (GB 13223-2011). Beijing, 2011
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Database of information collected in the electric utility steam generating unit mercury emissions information collection effort. Research Triangle Park, NC, USA: US EPA, 2001
Brown T D, Smith D N, Hargis R A, O’Dowd JWJ, O’Dowd WJ. Mercury measurement and its control: what we know, have learned, and need to further investigate. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 1999, 49(12): 1469–1473
Black & Veatch. Effective mercury reduction strategy for western coal/K-Fuel technology, 2003
KFx. Final Report of K-Fuel™ Test Burn Validates Initial Emissions Data. 2006
Miller C, Feeley T, Aljoe W, Lani B, Schroeder K, Kairies C, McNemar A, Jones A, Murphy J. Mercury capture and fate using wet FGD at coal-fired power plants. Pittsburgh, PA, USA: 2006
Bustard J, Sjostrom S, Starns T, Durham M. Full scale evaluation of mercury control technologies with PRB coals. Clean Air Technologies and Strategies Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005
Vosteen B W, Lindau L. Bromine based mercury abatementpromising results from further full scale testing. MEC3 Conference, Katowice, Poland, 2006
Sloss L. Implications of emission legislation for existing coal-fired plants. 2009
Chu P. Effects of SCRs on mercury. Mercury Experts Conference, Glasgow, Scotland, 2004
Winberg S, Winthum J, Tseng S, Locke J. Evaluation of mercury emissions from coal-fired facilities with SCR-FGD systems. DOE/NETL Mercury Control Technology R&D Program Review, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2004
GAO. Preliminary observations on the effectiveness and costs of mercury control technologies at coal-fired power plants. Washington, DC, USA: 2009
Srivastava R K, Jozewicz W. Flue gas desulfurization: the state of the art. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 2001, 51(12): 1676–1688
Modern Power Systems. Can Enviroscrub clean up in the multipollutant control business. 2002
McLarnon C R, Jones M D. Pilot testing and scale-up of a multipollutant control technology at FirstEnergy. PowerGen International Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 2000
Ferrell R. Controlling NOX emissions: a cooler alternative. 2000
Altman R, Buckley W, Ray I. Multi-pollutant control with dry-wet hybrid ESP technology. Combined Utility Air Pollutant Control Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 2003
Zhao Y. Study on air pollutant emission of coal-fired power plants in China and its environmental impacts. Dissertation for the Doctor Degree. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2008
China Electricity Council (CEC). Annual Development Report of China’s Power Industry 2011. Beijing: China Market Press, 2011
China Electric Power Yearbook Editorial Committee. China Electric Power Yearbook. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2011
Lei Y, Zhang Q, Nielsen C, He K. An inventory of primary air pollutants and CO2 emissions from cement production in China, 1990–2020. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(1): 147–154
Wang S X, Zhang L, Wu Y, Ancora M P, Zhao Y, Hao J M. Synergistic mercury removal by conventional pollutant control strategies for coal-fired power plants in China. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2010, 60(6): 722–730
Wang S X, Zhang L, Zhao B, Meng Y, Hao J M. Mitigation potential of mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants in China. Energy and Fuels, 2012, 26(8): 4635–4642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, L., Wang, L. et al. A review of atmospheric mercury emissions, pollution and control in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 8, 631–649 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0673-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0673-x