Abstract
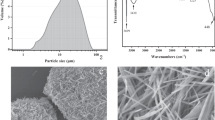
In order to investigate the characteristics of pure Nano-Al13, Nano-Al13 was separated and purified from a series of poly-aluminum chloride (PAC) solutions which had the same Al13 percentage but different total Al concentrations, by using column chromatography, ethanol-acetone resolving and SO2− 4/Ba2+ displacement. The Al13 species yield was characterized by Al-ferron timed complexation spectrophotometry and 27Al-NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance). The coagulation efficiency of Nano-Al13, PAC and AlCl3 in synthetic water was also investigated by Jar tests. The dynamic process and aggregation state of kaolin suspensions coagulating with Nano-Al13, PAC and AlCl3 were similarly investigated using a photometric dispersion analyzer 2000 (PDA2000). The experimental results indicated that the ethanol-acetone resolving method was simple and could separate the PAC solution at different concentrations, while column chromatography could separate PAC solutions at low concentrations. The SO4 2−/Ba2+ displacement method could separate PAC solutions at high concentrations. However, extra inorganic cation and anion could be added in the solution during separation. The coagulation efficiency and dynamic experimental results showed that Nano-Al13 with high positive-charged species was effective in removing turbidity and color. The dynamic process results showed that Nano-Al13 also had the best recovery capability after shearing compared with PAC and AlCl3 because the Nano-Al13 conformation is more effective in charge neutralization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng L, Tang H X. Research progress of Al13 species. Advance in Environmental Sciences, 1997, 5(6): 44–51 (in Chinese)
Tang H X. Flocculation morphology for hydroxyl polymer of poly aluminum-chloride. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1998, 18(1): 1–10 (in Chinese)
Peng G, Hu C W, Chen L D, Wang E B. Synthesis of novel inorganic nanoclusters between Keggin-type cation [AlO4Al12 (OH)24(H2O)12] and heteropolyoxometalates. Chem J Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(10): 1692–1631 (in Chinese)
Tang H X, Luan Z K. The difference of flocculation and coagulation action of polyaluminum chloride and traditional floculant. Environmental Chemistry, 1997, 16(6): 497–505 (in Chinese)
Wang D S, Tang H X, Gao Q, Shao J L. Initial study on the separation and purification of Al13. Environmental Chemistry, 2000, 19(5): 389–394 (in Chinese)
Zhao H Z, Luan Z K, Du Y, Wang S. Purification and characterization of Al13 species. Chem J Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(5): 751–755 (in Chinese)
Feng L, Luan Z K, Tang H X. Study on the analytical methods of Al species. Environmental Chemistry, 1993, 12(5): 373–379 (in Chinese)
Chu Y B, Gao B Y, Yue Q Y Wang Y, Liu Y Z, Kong C Y. Purification and Characterization of Nano Al13 species. Environmental Science, 2004, 25(5): 80–84 (in Chinese)
Gao B Y, Li C P, Yu H, Yue Q Y. Study on the speciation of aluminum in PSAA solution. China Environmental Science, 1997, 17(3): 279–282 (in Chinese)
Gregory D, Carlson K. Relationship of pH and floc formation kinetics to granular media filtration performance. Environ Sci & Technol, 2003, 37(7): 1398–1403
Akitt J W, Farthing A. Aluminum-27 NMR studies of the hydrolysis aluminum (III). J Chem Soc Dalton Trans, 1981, 1606–1626
Wang D S. Coagulation calculation model and mechanism of inorganic polymer flocculant. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 1999 (in Chinese)
Hahn H H, Srumm W. Kinetics of coagulation with hydrolyzed Al(III). J Coll Interf Sci, 1968, 28: 133–142
Wang D, Tang H, Gregory T. Relative importance of charge neutralization and precipitation on coagulation of kaolin with PACl: Effect of sulfate ion. Environ Sci Technol, 2002, 36(8): 1815–1823
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2005, 25(6): 767–772 [译自: 环境科学学报]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, B., Chu, Y., Yue, Q. et al. Separating method and dynamic processes of Nano-Al13 . Front.Environ.Sci.Eng.China 1, 368–373 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-007-0063-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-007-0063-8