Abstract
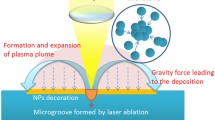
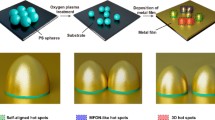
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) has been widely used as an effective technique for low-concentration molecules detections in the past decades. This work proposes a rapid and accessible process to fabricate SERS-active substrates with high uniformity and controllability based on two-step laser ablation. Laser beams directly ablate the surface of Si, concurrently creating microstructures and ejecting molten materials caused by the thermal effect that nucleate in ambient air. The nuclei grow into nanoparticles and deposit over the surface. These nanoparticles, together with microstructures, improve the light collection efficiency of the SERS-active substrates. Especially after Au thin film deposition, these nanoparticles can provide nanogaps as hotspots for SERS. By orthogonal experiment design, laser processing parameters for better performances are determined. Compared with substrates fabricated by single 1064 nm master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) laser ablation, substrates ablated by the primary 1064 nm MOPA laser and secondary UV pulsed laser show more uniform nanoparticles’ deposition over the surface. The optimized large-area substrate has a SERS detection limit of 10−8 mol/L for 4-aminothiophenol (4-ATP), indicating the potential real-world applications for trace detection.
摘要
近几十年来,表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)作为一种有效的低浓度分子检测技术得到了广泛应用。本文提出了一种基于1064 nm MOPA脉冲光纤激光和紫外脉冲激光的两步激光烧蚀成形法,以提升SERS活性衬底的硅基表面多尺度微纳结构的均匀性和可控性。利用激光束直接烧蚀硅表面并形成微结构,在此过程中硅材料因为光热效应产生的热影响区而逐渐熔融,并向四周喷射出而形成等离子体羽,这些高速离子在空气中冷却成核,然后重新沉积回微结构表面上而形成多尺度结构,进一步提高了基底的光收集效率,随后沉积的Au薄膜中的纳米颗粒可以提供纳米间隙作为SERS的热点。本研究通过正交试验设计确定了优化的激光加工参数,与仅使用MOPA激光烧蚀加工相比,1064 nm MOPA激光和紫外激光的两步复合激光烧蚀可以使硅纳米颗粒分布更加均匀,从而提升沉积金属层的表面均匀性。经过试验,所加工的大面积SERS 基底对4-ATP 的SERS 检测极限可以达到10−8 mol/L,表明其在痕量物质检测方面具有很好的应用前景。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SONG Shi-ping, QIN Yu, HE Yao, et al. Functional nanoprobes for ultrasensitive detection of biomolecules [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(11): 4234–4243. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c000682n.
ZHANG Lei, WENG Yi-jin, LIU Xiao, et al. Fe(III) mixed IP6@Au NPs with enhanced SERS activity for detection of 4-ATP [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5752. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62495-w.
BHARATI M S S, SOMA V R. Flexible SERS substrates for hazardous materials detection: Recent advances [J]. OptoElectronic Advances, 2021, 4(11): 210048. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2021.210048.
CAMPION A, KAMBHAMPATI P. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 1998, 27(4): 241. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/a827241z.
CIALLA D, MÄRZ A, BÖHME R, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): Progress and trends [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 403(1): 27–54. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5631-x.
MORTON S M, JENSEN L. Understanding the molecule-surface chemical coupling in SERS [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(11): 4090–4098. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja809143c.
SCHATZ G C, YOUNG M A, DUYNE R P. Electromagnetic mechanism of SERS [M]//Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer, 2006: 19–45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-33567-6_2.
XU Kai-chen, ZHANG Chen-tao, ZHOU Rui, et al. Hybrid micro/nano-structure formation by angular laser texturing of Si surface for surface enhanced Raman scattering [J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(10): 10352–10358. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.010352.
LU Gang, LI Hai, WU Shi-xin, et al. High-density metallic nanogaps fabricated on solid substrates used for surface enhanced Raman scattering [J]. Nanoscale, 2012, 4(3): 860–863. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr10997a.
DIEBOLD E D, MACK N H, DOORN S K, et al. Femtosecond laser-nanostructured substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering [J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(3): 1790–1794. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la803357q.
XIONG Yu-jie, MCLELLAN J M, CHEN Jing-yi, et al. Kinetically controlled synthesis of triangular and hexagonal nanoplates of palladium and their SPR/SERS properties [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(48): 17118–17127. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja056498s.
ABDELSALAM M E, MAHAJAN S, BARTLETT P N, et al. SERS at structured palladium and platinum surfaces [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(23): 7399–7406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja071269m.
GUTIERREZ-RIVERA L, PETERS R, DEW S, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of protein-ligand binding using D-glucose and glucose binding protein on nanostructured plasmonic substrates [J]. AIMS Materials Science, 2017, 4(2): 522–539. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3934/matersci.2017.2.522.
TAO Zhi-xiang, ZHAO Wei, WANG Shang, et al. Annealing treatment of focused gallium ion beam processing of SERS gold substrate [J]. Nanotechnology and Precision Engineering, 2021, 4(4): 043004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/10.0007286.
MANDAL P, TEWARI B S. Progress in surface enhanced Raman scattering molecular sensing: A review [J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2022, 28: 101655. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101655.
XU Kai-chen, ZHANG Chen-tao, LU T H, et al. Hybrid metal-insulator-metal structures on Si nanowires array for surface enhanced Raman scattering [J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017(2): 185–191, 245. (in Chinese)
ZHANG C, JIANG S Z, HUO Y Y, et al. SERS detection of R6G based on a novel graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles/silicon pyramid arrays structure [J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(19): 24811–24821. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.23.024811.
HU A, LU Q B, DULEY W W, et al. Spectroscopic characterization of carbon chains in nanostructured tetrahedral carbon films synthesized by femtosecond pulsed laser deposition [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2007, 126(15): 154705. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2727450.
BAI Shi, SERIEN D, HU An-ming, et al. 3D microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) chips fabricated by all-femtosecond-laser-processing for real-time sensing of toxic substances [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(23): 1706262. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201706262.
YANG Jing, LI Jia-bao, DU Zhe-ren, et al. Laser hybrid micro/nano-structuring of Si surfaces in air and its applications for SERS detection [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6657. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06657.
VERMA A K, DAS R, SONI R K. Laser fabrication of periodic arrays of microsquares on silicon for SERS application [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 427: 133–140. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.143.
YANG Jing, LUO Fang-fang, KAO T S, et al. Design and fabrication of broadband ultralow reflectivity black Si surfaces by laser micro/nanoprocessing [J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(7): e185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2014.66.
JIAO Lian-sheng, WANG Zhi-juan, NIU Li, et al. In situ electrochemical SERS studies on electrodeposition of aniline on 4-ATP/Au surface [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2006, 10(11): 886–893. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-005-0021-y.
ZHENG Jun-wei, ZHOU Yao-guo, LI Xiao-wei, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of 4-aminothiophenol in assemblies of nanosized particles and the macroscopic surface of silver [J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19(3): 632–636. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la011706p.
LI Y Y, HU C R. Experiment design and data processing [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
le RU E C, BLACKIE E, MEYER M, et al. Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: A comprehensive study [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(37): 13794–13803. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0687908.
SUN Lan-lan, ZHAO Dong-xu, ZHANG Zhen-zhong, et al. DNA-based fabrication of density-controlled vertically aligned ZnO nanorod arrays and their SERS applications [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(26): 9674. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm10830a.
SUN Lan-lan, ZHAO Dong-xu, DING Meng, et al. A white-emitting ZnO−Au nanocomposite and its SERS applications [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(20): 7813–7819. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.04.039.
Funding
Project(2020H0006) supported by the Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Programme, China; Project(62175203) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(RD2020050301) supported by the Innovation Laboratory for Science and Technology of Energy Materials of Fujian Province Applied Research Project, China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors
The overall goals and concepts were developed by ZHOU Rui. LI Long-fan performed the experiments and analyzed the data. LI Long-fan wrote the original manuscript. All authors discussed the results and edited the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
LI Long-fan, ZHOU Rui, CUI Jing-qin, YAN Huang-ping and WANG Zhen-zhong declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Lf., Zhou, R., Cui, Jq. et al. Improved uniformity of deposited metallic layer on hybrid micro/nano-structured Si substrates fabricated by two-step laser ablation for SERS application. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 3312–3322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5154-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5154-y
Key words
- laser ablation
- surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)
- light trapping effect
- orthogonal experiment design