Abstract
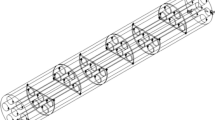
Heat transfer mechanisms and their thermal performances need to be comprehensively studied in order to optimize efficiency and minimize energy losses. Different nanoparticles in the base fluid are investigated to upgrade the thermal performance of heat exchangers. In this numerical study, a finned shell and tube heat exchanger has been designed and different volume concentrations of nanofluid were tested to determine the effect of utilizing nanofluid on heat transfer. Fe2O3/water nanofluids with volume concentration of 1%, 1.5% and 2% were utilized as heat transfer fluid in the heat exchanger and the obtained results were compared with pure water. ANSYS Fluent software as a CFD method was employed in order to simulate the mentioned problem. Numerical simulation results indicated the successful utilization of nanofluid in the heat exchanger. Also, increasing the ratio of Fe2O3 nanoparticles caused more increment in thermal energy without important pressure drop. Moreover, it was revealed that the highest heat transfer rate enhancement of 19.1% can be obtained by using nanofluid Fe2O3/water with volume fraction of 2%.
摘要
为了优化效率和减少能量损失,需要对传热机理及热性能进行全面研究。在基液中加入不同的纳米颗粒可提高热交换器的热性能。设计了一种翅片管壳式换热器,以体积浓度分别为1%、1.5%、2% 的Fe2O3/水纳米流体作为换热流体,研究不同体积浓度的纳米流体对传热的影响,并将所得结果与纯水作为换热流体结果进行比较。采用ANSYS Fluent 软件对传热过程进行数值模拟。数值模拟结果表明:纳米流体可成功应用于换热器中,提高Fe2O3纳米颗粒的体积分数可以获得更大的热能,而不会产生明显的压降。此外,当纳米流体中Fe2O3的体积分数为2% 时,其传热速率提高率最高,为19.1%
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area (m2)
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity of air (kJ/(kg·K))
- D :
-
Hydraulic diameter (m)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K))
- L :
-
Length (m)
- Ṁ :
-
Mass flow rate (kg/s)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- \({\dot Q}\) :
-
Heat flow rate (W)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- V :
-
Velocity (m/s)
- \({\vec v}\) :
-
Overall velocity vector (m/s)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W/(m2·K))
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- E :
-
Error rate (%)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pa·s)
- ρ :
-
Density of air (kg/m3)
- ϕ :
-
Volume fraction
- ε :
-
Turbulent dissipation rate (m2/s3)
- ω :
-
Specific dissipation rate (s−1)
- w:
-
Water
- h:
-
Hot
- c:
-
Cold
- in:
-
Inlet
- out:
-
Outlet
- bf:
-
Base fluid
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- p:
-
Particle
References
SIAVASHI M, TALESH BAHRAMI H R, AMINIAN E. Optimization of heat transfer enhancement and pumping power of a heat exchanger tube using nanofluid with gradient and multi-layered porous foams [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 138: 465–474. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.04.066.
ÇIFTÇI E. Distilled water-based AlN+ZnO binary hybrid nanofluid utilization in a heat pipe and investigation of its effects on performance [J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2021, 42(3): 1–21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-021-02792-2.
ÇIFTÇI E. Simulation of nucleate pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of the aqueous Kaolin and bauxite nanofluids [J]. Heat Transfer Research, 2021, 52(1): 77–92. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1615/heattransres.2020035191.
SHAHSAVAR A, TALEBIZADEH SARDARI P, TOGHRAIE D. Free convection heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of water-Fe3O4/CNT hybrid nanofluid in a concentric annulus [J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2019, 29(3): 915–934. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/hff-08-2018-0424.
SELIMEFENDIGIL F, ÖZTOP H F. Identification of pulsating flow effects with CNT nanoparticles on the performance enhancements of thermoelectric generator (TEG) module in renewable energy applications [J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 162: 1076–1086. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.07.071.
SHAHSAVAR A, JAFARI M, SELIMEFENDIGIL F. Two-phase mixture modeling of turbulent forced convective flow of water-silver nanofluid inside a rifled tube: Hydrothermal characteristics and irreversibility behavior [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2020: 1–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10303-y.
MAJID S, MOHAMMAD J. Optimal selection of annulus radius ratio to enhance heat transfer with minimum entropy generation in developing laminar forced convection of water-Al2O3 nanofluid flow [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(8): 1850–1865. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3593-7.
PINTO R V, FIORELLI F A S. Analysis of behaviour of computational model to evaluate performance of heat pipe containing nanofluids [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1306–1326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4089-4.
MASHAYEKHI R, KHODABANDEH E, BAHIRAEI M, BAHRAMI L, TOGHRAIE D, AKBARI O A. Application of a novel conical strip insert to improve the efficacy of water-Ag nanofluid for utilization in thermal systems: A two-phase simulation [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 151: 573–586. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.09.025.
SÖZEN A, GÜRÜ M, MENLIK T, KARAKAYA U, ÇIFTÇI E. Experimental comparison of Triton X-100 and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate surfactants on thermal performance of TiO2-deionized water nanofluid in a thermosiphon [J]. Experimental Heat Transfer, 2018, 31(5): 450–469. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08916152.2018.1445673.
BADALI Y, KOÇYIğIT S, AYTIMUR A, ALTINDAL Ş, USLU İ. Synthesis of boron and rare earth stabilized graphene doped polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanocomposite piezoelectric materials [J]. Polymer Composites, 2019, 40(9): 3623–3633. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25225.
GHOLAMALIPOUR P, SIAVASHI M, DORANEHGARD M H. Eccentricity effects of heat source inside a porous annulus on the natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation of Cu-water nanofluid [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 109: 104367. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2019.104367.
IZADI A, SIAVASHI M, RASAM H, XIONG Qin-gang. MHD enhanced nanofluid mediated heat transfer in porous metal for CPU cooling [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 168: 114843. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114843.
SELIMEFENDIGIL F, ÖZTOP H F. Hydro-thermal performance of CNT nanofluid in double backward facing step with rotating tube bundle under magnetic field [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 185: 105876. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105876.
HOSSEINNEZHAD R, AKBARI O A, HASSANZADEH AFROUZI H, BIGLARIAN M, KOVEITI A, TOGHRAIE D. Numerical study of turbulent nanofluid heat transfer in a tubular heat exchanger with twin twisted-tape inserts [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2018, 132(1): 741–759. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6900-5.
HEMMAT ESFE M, HAJMOHAMMAD H, TOGHRAIE D, ROSTAMIAN H, MAHIAN O, WONGWISES S. Multi-objective optimization of nanofluid flow in double tube heat exchangers for applications in energy systems [J]. Energy, 2017, 137: 160–171. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.06.104.
SIAVASHI M, MIRI JOIBARY S M. Numerical performance analysis of a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger with using nanofluid and both sides partly filled with porous media [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2019, 135(2): 1595–1610. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7829-z.
POURFATTAH F, MOTAMEDIAN M, SHEIKHZADEH G, TOGHRAIE D, ALI AKBARI O. The numerical investigation of angle of attack of inclined rectangular rib on the turbulent heat transfer of Water-Al2O3 nanofluid in a tube [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2017, 131–132: 1106–1116. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.07.049.
SIAVASHI M, GHASEMI K, YOUSOFVAND R, DERAKHSHAN S. Computational analysis of SWCNH nanofluid-based direct absorption solar collector with a metal sheet [J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 170: 252–262. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.05.020.
NOROUZI A M, SIAVASHI M, KHALIJI OSKOUEI M. Efficiency enhancement of the parabolic trough solar collector using the rotating absorber tube and nanoparticles [J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 145: 569–584. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.027.
SELIMEFENDIGIL F, ÖZTOP H F. The potential benefits of surface corrugation and hybrid nanofluids in channel flow on the performance enhancement of a thermo-electric module in energy systems [J]. Energy, 2020, 213: 118520. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118520.
NAYAK M K, MEHMOOD R, MAKINDE O D, MAHIAN O, CHAMKHA A J. Magnetohydrodynamic flow and heat transfer impact on ZnO-SAE50 nanolubricant flow over an inclined rotating disk [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1146–1160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4077-8.
POURRAHMANI H, MOGHIMI M, SIAVASHI M, SHIRBANI M. Sensitivity analysis and performance evaluation of the PEMFC using wave-like porous ribs [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 150: 433–444. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.01.010.
HEYHAT M M, MOUSAVI S, SIAVASHI M. Battery thermal management with thermal energy storage composites of PCM, metal foam, fin and nanoparticle [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 28: 101235. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101235.
GÜRBÜZ E Y, SÖZEN A, KEÇEBAŞ A, ÖZBAŞ E. Experimental and numerical investigation of diffusion absorption refrigeration system working with ZnOAl2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles added ammonia/water nanofluid [J]. Experimental Heat Transfer, 2020: 1–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08916152.2020.1838668.
MAGHRABIE H M, ATTALLA M, A A MOHSEN A. Performance assessment of a shell and helically coiled tube heat exchanger with variable orientations utilizing different nanofluids [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 182: 116013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.116013.
BHATTAD A, SARKAR J, GHOSH P. Experimentation on effect of particle ratio on hydrothermal performance of plate heat exchanger using hybrid nanofluid [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 162: 114309. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114309.
ZARRINGHALAM M, KARIMIPOUR A, TOGHRAIE D. Experimental study of the effect of solid volume fraction and Reynolds number on heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop of CuO-water nanofluid [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2016, 76: 342–351. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.03.026.
RANJBARZADEH R, MEGHDADI ISFAHANI A H, AFRAND M, KARIMIPOUR A, HOJAJI M. An experimental study on heat transfer and pressure drop of water/graphene oxide nanofluid in a copper tube under air cross-flow: Applicable as a heat exchanger [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125: 69–79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.110.
GOODARZI M, AMIRI A, GOODARZI M S, SAFAEI M R, KARIMIPOUR A, LANGURI E M, DAHARI M. Investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop of a counter flow corrugated plate heat exchanger using MWCNT based nanofluids [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 66: 172–179. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.05.002.
MORAVEJ M, BOZORG M V, GUAN Yu, LI L K B, DORANEHGARD M H, HONG Kun, XIONG Qin-gang. Enhancing the efficiency of a symmetric flat-plate solar collector via the use of rutile TiO2-water nanofluids [J]. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2020, 40: 100783. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100783.
VAHABZADEH BOZORG M, SIAVASHI M. Two-phase mixed convection heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of a non-Newtonian nanofluid inside a cavity with internal rotating heater and cooler [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 151: 842–857. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.12.036.
GÜRBÜZ E Y, SÖZEN A, VARIYENLI H İ, KHANLARI A, TUNCER A D. A comparative study on utilizing hybrid-type nanofluid in plate heat exchangers with different number of plates [J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2020, 42(10): 1–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02601-1.
GÜRBÜZ E Y, VARIYENLI H İ, SÖZEN A, KHANLARI A, ÖKTEN M. Experimental and numerical analysis on using CuO-Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid in a U-type tubular heat exchanger [J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2021, 31(1): 519–540. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/hff-04-2020-0195.
ALSABERY A I, SELIMEFENDIGIL F, HASHIM I, CHAMKHA A J, GHALAMBAZ M. Fluid-structure interaction analysis of entropy generation and mixed convection inside a cavity with flexible right wall and heated rotating cylinder [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 140: 331–345. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.06.003.
YAN W M, HO C J, TSENG Y T, QIN Cai-yan, RASHIDI S. Numerical study on convective heat transfer of nanofluid in a minichannel heat sink with micro-encapsulated PCM-cooled ceiling [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 153: 119589. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119589.
HO C J, GUO Yu-wei, YANG T F, RASHIDI S, YAN W M. Numerical study on forced convection of water-based suspensions of nanoencapsulated PCM particles/Al2O3 nanoparticles in a mini-channel heat sink [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 157: 119965. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119965.
MUKESH KUMAR P C, CHANDRASEKAR M. CFD analysis on heat and flow characteristics of double helically coiled tube heat exchanger handling MWCNT/water nanofluids [J]. Heliyon, 2019, 5(7): e02030. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02030.
NAZARI M A, AHMADI M H, SADEGHZADEH M, SHAFII M B, GOODARZI M. A review on application of nanofluid in various types of heat pipes [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(5): 1021–1041. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4068-9.
MIRZAEYAN M, TOGHRAIE D. Numerical investigation of laminar heat transfer and nanofluid flow between two porous horizontal concentric cylinders [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(7): 1976–1999. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4146-z.
AĞBULUT Ü, GÜREL A E, SARIDEMIR S. Experimental investigation and prediction of performance and emission responses of a CI engine fuelled with different metal-oxide based nanoparticles-diesel blends using different machine learning algorithms [J]. Energy, 2021, 215: 119076. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119076.
NOROUZI A M, SIAVASHI M, AHMADI R, TAHMASBI M. Experimental study of a parabolic trough solar collector with rotating absorber tube [J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 168: 734–749. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.12.088.
XUAN Yi-min, ROETZEL W. Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2000, 43(19): 3701–3707. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(99)00369-5.
AFSHARI F, ZAVARAGH H G, SAHIN B, GRIFONI R C, CORVARO F, MARCHETTI B, POLONARA F. On numerical methods optimization of CFD solution to evaluate fluid flow around a sample object at low Re numbers [J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2018, 152: 51–68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2018.04.004.
VERMAHMOUDI Y, PEYGHAMBARZADEH S M, HASHEMABADI S H, NARAKI M. Experimental investigation on heat transfer performance of Fe2O3/water nanofluid in an air-finned heat exchanger [J]. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 2014, 44: 32–41. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2013.10.002.
KUMAR N, SONAWANE S S. Experimental study of Fe2O3/water and Fe2O3/ethylene glycol nanofluid heat transfer enhancement in a shell and tube heat exchanger [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 78: 277–284. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2016.09.009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were developed by KHANLARI Ataollah and TUNCER Azim Doğuş. KHANLARI Ataollah and SÖZEN Adnan provided the measured landslides displacement data, and analyzed the measured data. AFSHARI Faraz, SÖZEN Adnan, KHANLARI Ataollah established the CFD models and calculated the predicted results. SÖZEN Adnan and TUNCER Azim Dogus analyzed the calculated results. The initial draft of the manuscript was written by AFSHARI Faraz, SÖZEN Adnan, KHANLARI Ataollah and TUNCER Azim Dogus. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
AFSHARI Faraz, SÖZEN Adnan, KHANLARI Ataollah, and TUNCER Azim Doğuş declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afshari, F., Sözen, A., Khanlari, A. et al. Heat transfer enhancement of finned shell and tube heat exchanger using Fe2O3/water nanofluid. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 3297–3309 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4856-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4856-x