Abstract
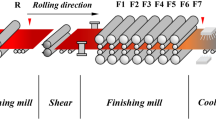
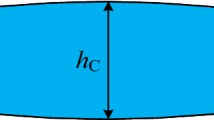
To make up the poor quality defects of traditional control methods and meet the growing requirements of accuracy for strip crown, an optimized model based on support vector machine (SVM) is put forward firstly to enhance the quality of product in hot strip rolling. Meanwhile, for enriching data information and ensuring data quality, experimental data were collected from a hot-rolled plant to set up prediction models, as well as the prediction performance of models was evaluated by calculating multiple indicators. Furthermore, the traditional SVM model and the combined prediction models with particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm and the principal component analysis combined with cuckoo search (PCA-CS) optimization strategies are presented to make a comparison. Besides, the prediction performance comparisons of the three models are discussed. Finally, the experimental results revealed that the PCA-CS-SVM model has the highest prediction accuracy and the fastest convergence speed. Furthermore, the root mean squared error (RMSE) of PCA-CS-SVM model is 2.04 µm, and 98.15% of prediction data have an absolute error of less than 4.5 µm. Especially, the results also proved that PCA-CS-SVM model not only satisfies precision requirement but also has certain guiding significance for the actual production of hot strip rolling.
摘要
为了弥补传统控制方法的缺陷,满足日益增长的板凸度精度要求,提出了一种基于支持向量机 (SVM)的优化模型,以提高热轧带钢产品的质量。为了丰富数据信息并保证数据质量,建立预测模型 的实验数据均来自于某热轧厂,并通过计算多项评价指标来评估模型的预测性能。建立主成分分析结 合布谷鸟搜索(PCA-CS)算法优化的预测模型,并与粒子群优化算法(PSO)优化的模型及传统SVM 模 型进行对比,分析并讨论了这三种模型的预测性能。实验结果表明,PCA-CS-SVM 模型具有最高的预 测精度和最快的收敛速度,模型的均方根误差(RMSE)为2.04 μm,且98.15%的预测数据的绝对误差小 于4.5 μm。结果证明,PCA-CS-SVM 模型不仅能够满足板凸度精度要求,而且对热轧带钢的实际生 产具有一定指导意义。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DENG Ji-fei, SUN Jie, PENG Wen, HU Yao-hui, ZHANG Dian-hua. Application of neural networks for predicting hot-rolled strip crown [J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 78: 119–131. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.02.030.
SUN W Q, LI B, SHAO J. Research on crown & flatness allocation strategy of hot rolling mills [J]. International Journal of Simulation Modelling, 2016, 15(2): 327–340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2507/ijsimm15(2)co6.
HE You-liang, HILINSKI E J. Skew rolling and its effect on the deformation textures of non-oriented electrical steels [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 242: 182–195. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.11.033.
LI Hong-bo, ZHAO Zhen-wei, ZHANG Jie, KONG Ning, BAO Ren-ren, JIA Sheng-hui, HE Fei. Analysis of flatness control capability based on the effect function and roll contour optimization for 6-h CVC cold rolling mill [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 100(9–12): 2387–2399. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2838-4.
ZAMANIAN A, NAM S Y, HWANG S M. A new mill design for the production of a strip with zero strip crown [J]. Steel Research International, 2019, 90(11): 1900252. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201900252.
ZHAO Jian-wei, WANG Xiao-chen, YANG Quan, WANG Qiu-na, LIU Chao, SONG Guang-yi. High precision shape model and presetting strategy for strip hot rolling [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 265: 99–111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.10.005.
SCHAUSBERGER F, STEINBOECK A, KUGI A. Feedback control of the contour shape in heavy-plate hot rolling [J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(3): 842–856. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCST.2017.2695168.
TAO Liang, GUO Jian-chun, ZHAO Zhi-hong, YIN Qi-wu. Refracturing candidate selection for MFHWs in tight oil and gas reservoirs using hybrid method with data analysis techniques and fuzzy clustering [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(1): 277–287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4295-0.
DING Jing-guo, MA Geng-sheng, PENG Wen. Load distribution optimization based on max-Min ant colony algorithm in hot strip rolling process [J]. Metallurgist, 2018, 62(7): 837–846. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-018-0727-6.
BOUKHALFA G, BELKACEM S, CHIKHI A, BENAGGOUNE S. Genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization tuned fuzzy PID controller on direct torque control of dual star induction motor [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(7): 1886–1896. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4142-3.
HU Hui-jun, LIU Ya, LIU Mao-fu, NIE Li-qiang. Surface defect classification in large-scale strip steel image collection via hybrid chromosome genetic algorithm [J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 181: 86–95. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.134.
WANG Zhen-hua, LIU Yuan-ming, GONG Dian-yao, ZHANG Dian-hua. A new predictive model for strip crown in hot rolling by using the hybrid AMPSO-SVR-based approach [J]. Steel Research International, 2018, 89(7): 1800003. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201800003.
LOTFAN S, FATHI R. Parametric modeling of carbon nanotubes and estimating nonlocal constant using simulated vibration signals-ARMA and ANN based approach [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(3): 461–472. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3750-7.
QIU Xue-heng, REN Ye, SUGANTHAN P N, AMARATUNGA G A J. Empirical mode decomposition based ensemble deep learning for load demand time series forecasting [J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 54: 246–255. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.01.015.
LI Yue-lin, LIU Bo-fu, WU Gang, LIU Zhi-qiang, DING Jing-feng, ABUBAKAR S. Intelligent prediction on air intake flow of spark ignition engine by a chaos radial basis function neural network [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(9): 2687–2695. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4491-y.
MAHMOOD A, TANG Xiao-wei, QIU Jiang-nan, GU Wen-jing, FEEZAN A. A hybrid approach for evaluating CPT-based seismic soil liquefaction potential using Bayesian belief networks [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(2): 500–516. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4312-3.
QURESHI A S, KHAN A, ZAMEER A, USMAN A. Wind power prediction using deep neural network based meta regression and transfer learning [J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 58: 742–755. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.05.031.
WANG Zhen-hua, GONG Dian-yao, LI Xu, LI Guang-tao, ZHANG Dian-hua. Prediction of bending force in the hot strip rolling process using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm (ANN-GA) [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 93(9–12): 3325–3338. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0711-5.
SHEN Chun-guang, WANG Chen-chong, WEI Xiao-lu, LI Yong, van der ZWAAG S, XU Wei. Physical metallurgy-guided machine learning and artificial intelligent design of ultrahigh-strength stainless steel [J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 179: 201–214. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.08.033.
GAO Yi, CAI Ping, CHEN Feng, QIN Ru. Study on temperature rise modeling of main motor of hot rolling mill based on support vector machines [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2017, 870: 427–431. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.870.427.
PENG Kai-xiang, ZHONG Hao, ZHAO Liang, XUE Kai, JI Yi-dao. Strip shape modeling and its setup strategy in hot strip mill process [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 72(5–8): 589–605. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5649-2.
LI Xiao-feng, WU Shi-jing, LI Xiao-yong, YUAN Hao, ZHAO Deng. Particle swarm optimization-support vector machine model for machinery fault diagnoses in high-voltage circuit breakers [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 33(1): 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-019-0428-5.
CHANDRASEKARAN K, SIMON S P. Multi-objective scheduling problem: Hybrid approach using fuzzy assisted cuckoo search algorithm [J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 5: 1–16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2012.01.001.
MALVONI M, DE GIORGI M G, CONGEDO P M. Photovoltaic forecast based on hybrid PCA-LSSVM using dimensionality reducted data [J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 211: 72–83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.104.
MA Chi, ZHAO Liang, MEI Xue-song, SHI Hu, YANG Jun. Thermal error compensation of high-speed spindle system based on a modified BP neural network [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 89(9–12): 3071–3085. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9254-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were developed by JI Ya-feng and SUN Jie. JI Ya-feng provided the hot rolling data. SONG Le-bao and JI Ya-feng edited the initial draft of the manuscript. PENG Wen, LI Hua-ying and MA Li-feng analyzed the measured data and reviewed and edited the draft of manuscript. SONG Le-bao and SUN Jie analyzed the calculated results. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
JI Ya-feng, SONG Le-bao, SUN Jie, PENG Wen, LI Hua-ying and MA Li-feng declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Project(52005358) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2018YFB1307902) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Project(201901D111243) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, China; Project(2019-KF-25-05) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Yf., Song, Lb., Sun, J. et al. Application of SVM and PCA-CS algorithms for prediction of strip crown in hot strip rolling. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 2333–2344 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4773-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4773-z
Key words
- strip crown
- support vector machine
- principal component analysis
- cuckoo search algorithm
- particle swarm optimization algorithm