Abstract
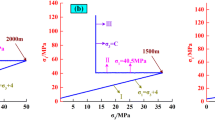
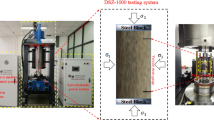
To investigate the influence of confining pressure and pore water pressure on strength characteristics, energy storage state and energy release intensity at peak failure of deep sandstone, a series of triaxial compression tests under hydraulic coupling conditions are carried out. By analyzing the process of rock deformation and failure, the stress thresholds of the rock are obtained. The change trend of total energy density, elastic energy density and dissipated energy density of deep sandstone in the pre-peak stage is obtained by the graphical integration method. By comparing the dynamic energy storage level of rocks under different confining pressures, the influence of pore water pressure on the energy dissipation at stress thresholds of crack closure stress, crack initiation stress, crack damage stress and peak stress is analyzed. Based on the ratio of pre-peak total energy density to post-peak total energy density, the interaction mechanism of confining pressure and pore water pressure for the rock burst proneness of deep sandstone is studied. The experimental results show that the peak stress of sandstone increases with the increase of confining pressure, while the existence of pore water pressure can weaken the peak stress of sandstone. In the stress stage from crack closure stress to peak stress, the dynamic energy storage level of rock presents a trend of the inverse “check mark”. Meanwhile, the larger the confining pressure, the higher the energy storage level of rock. However, the pore water pressure increases the degree of energy dissipation of rock and reduces the energy storage capacity of rock, and the degree of dissipation is linear with pore water pressure. The increase of confining pressure aggravates the instability and failure of deep sandstone, while pore water pressure has the opposite effect. The research results will provide necessary data support for the stability analysis of rock mass excavation in sandstone stratum under high stress and high pore water pressure.
摘要
为了研究围压和孔隙水压对深部砂岩强度特征、储能状态和峰值破坏时能量释放烈度的影响规 律, 开展一系列水力耦合条件下的三轴压缩试验。通过分析岩石变形破坏过程, 获得其应力阈值。利 用图形积分方法获得深部砂岩在峰前阶段总能量密度、弹性能量密度、耗散能量密度的变化趋势。对 比不同围压下岩石的动态储能水平, 分析孔隙水压对岩石闭合应力、起裂应力、损伤应力、峰值应力 等应力阈值处能量耗散的影响。基于峰前、后总能量密度的比值, 研究围压与孔隙水压对深部砂岩岩 爆倾向性的相互作用机理。实验结果表明, 砂岩峰值应力随着围压的增加而增加, 而孔隙水压的存在 可以削弱砂岩的峰值应力。在自闭合应力至峰值应力间的应力阶段, 岩石的动态储能水平呈现出反“对 勾”的演化趋势。同时随着围压的增加, 动态储能水平上升。然而, 孔隙水压增大岩石的能量耗散程 度, 降低岩石的储能能力, 耗散程度与孔隙水压呈线性关系。围压的增大加剧深部砂岩的失稳破坏现 象, 而孔隙水压具有相反作用。研究成果将为高应力、高孔隙水压下砂岩地层工程岩体开挖稳定性分 析提供有力的数据支撑。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CAI Mei-feng, BROWN E T. Challenges in the mining and utilization of deep mineral resources [J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(4): 432–433. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.04.027.
FENG Xia-ting, LIU Jian-po, CHEN Bing-rui, XIAO Ya-xun, FENG Guang-liang, ZHANG Feng-peng. Monitoring, warning, and control of rockburst in deep metal mines [J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(4): 538–545. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.04.013.
KANG Hong-pu. Support technologies for deep and complex roadways in underground coal mines: A review [J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 2014, 1(3): 261–277. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-014-0043-0.
CUI Fang-peng, WU Qiang, LIN Yuan-hui, ZENG Yi-fan, ZHANG Ke-li. Damage features and formation mechanism of the strong water inrush disaster at the Daxing Co Mine, Guangdong province, China [J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2018, 37(2): 346–350. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-0530-4.
LUO Yong, GONG Feng-qiang, LI Xi-bing, WANG Shan-yong. Experimental simulation investigation of influence of depth on spalling characteristics in circular hard rock tunnel [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(3): 891–910. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4339-5.
YIN Li-ming, MA Kai, CHEN Jun-tao, XUE Yan-chao, WANG Zi-qi, CUI Bo-qiang. Mechanical model on water inrush assessment related to deep mining above multiple aquifers [J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2019, 38(4): 827–836. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-019-00623-3.
LI Xi-bing, GONG Feng-qiang, TAO Ming, DONG Long-jun, DU Kun, MA Chun-de, ZHOU Zi-long, YIN Tu-bing. Failure mechanism and coupled static-dynamic loading theory in deep hard rock mining: A review [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 9(4): 767–782. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2017.04.004.
SI Xue-feng, GONG Feng-qiang. Strength-weakening effect and shear-tension failure mode transformation mechanism of rockburst for fine-grained granite under triaxial unloading compression [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 131: 104347. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104347.
ZHOU Zhong, YANG Hao, WANG Xiang-can, ZHANG Qi-fang. Fractured rock mass hydraulic fracturing under hydrodynamic and hydrostatic pressure joint action [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(10): 2695–2704. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3331-6.
COOKNGW. The failure of rock [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1965, 2(4): 389–403. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(65)90004-5.
YOU Shuang, JI Hong-guang, ZHANG Zi-jian, ZHANG Cheng-han. Damage evaluation for rock burst proneness of deep hard rock under triaxial cyclic loading [J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2018(1): 1–7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8193638.
GONG Feng-qiang, LUO Yong, LI Xi-bing, SI Xue-feng, TAO Ming. Experimental simulation investigation on rockburst induced by spalling failure in deep circular tunnels [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 81: 413–427. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.07.035.
ZHANG Yu, XU Wei-ya, GU Jin-jian, WANG Wei. Triaxial creep tests of weak sandstone from fracture zone of high dam foundation [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(9): 2528–2536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1765-7.
FENG Xia-ting, KONG Rui, ZHANG Xi-wei, YANG Cheng-xiang. Experimental study of failure differences in hard rock under true triaxial compression [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(7): 2109–2122. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1700-1.
SHANG Jun-long. Rupture of veined granite in polyaxial compression: insights from three-dimensional discrete element method modeling [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2020, 125(2): e2019JB019052. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB019052.
WANG Lu, LIU Jian-feng, PEI Jian-liang, XU Hui-ning, BIAN Yu. Mechanical and permeability characteristics of rock under hydro-mechanical coupling conditions [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(10): 5987–5996. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4190-4.
ZHOU Hong-wei, WANG Zi-hui, REN Wei-guang, LIU Ze-lin, LIU Jian-feng. Acoustic emission based mechanical behaviors of Beishan granite under conventional triaxial compression and hydro-mechanical coupling tests [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 123: 104125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104125.
LI Zhi-hao, XIONG Zi-ming, CHEN Hao-xiang, LU Hao, HUANG Mu, MA Chao, LIU Yi-ming. Analysis of stress-strain relationship of brittle rock containing microcracks under water pressure [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(4): 1909–1918. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01660-6.
XIE He-ping, LI Li-yun, PENG Rui-dong, JU Yang. Energy analysis and criteria for structural failure of rocks [J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 1(1): 11–20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1235.2009.00011.
MENG Qing-bin, ZHANG Ming-wei, HAN Li-jun, PU Hai, NIE Tao-yi. Effects of acoustic emission and energy evolution of rock specimens under the uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading compression [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(10): 3873–3886. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1077-y.
HOU Peng, GAO Feng, YANG Yu-gui, ZHANG Xiang-xiang, ZHANG Zhi-zhen. Effect of the layer orientation on mechanics and energy evolution characteristics of shales under uniaxial loading [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2016, 26(5): 857–862. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2016.05.041.
LI Di-yuan, SUN Zhi, XIE Tao, LI Xi-bing, RANJITH P G. Energy evolution characteristics of hard rock during triaxial failure with different loading and unloading paths [J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 228: 270–281. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.006.
PEI Feng, JI Hong-guang, ZHANG Tong-zhao. Energy evolution and mechanical features of granite subjected to triaxial loading-unloading cycles [J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2019, 2019(1): 1–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9871424.
GONG Feng-qiang, YAN Jing-yi, LUO Song, LI Xi-bing. Investigation on the linear energy storage and dissipation laws of rock materials under uniaxial compression [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(12): 4237–4255. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01842-4.
GONG Feng-qiang, LUO Song, YAN Jing-yi. Energy storage and dissipation evolution process and characteristics of marble in three tension-type failure tests [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2018, 51: 3613–3624. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1564-4.
XIA Ying-jie, LI Lian-chong, TANG Chun-an, BAO Chun-yan, LI Ai-shan, HUANG Bo. Experiment and numerical research on failure characteristic and brittleness index for reservoir sandstone [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(1): 10–28. http://www.rockmech.org/CN/abstract/abstract29682.shtml. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Cheng-han, YOU Shuang, JI Hong-guang, LI Fei, WANG Hong-tao. Hydraulic properties and energy dissipation of deep hard rock under H-M coupling and cycling loads [J]. Thermal Science, 2019, 23(S3): S943–S950. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2298/tsci180702181z.
GOODMAN R E. Introduction to rock mechanics [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were developed by LI Fei, YOU Shuang, JI Hong-guang and ELMO Davide. LI Fei and WANG Hong-tao carried out mechanical tests. LI Fei analyzed the data. LI Fei and YOU shuang wrote the paper. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflicts of interest
LI Fei, YOU Shuang, JI Hong-guang, ELMO Davide and WANG Hong-tao declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Project(2016YFC0600801) supported by the National Key Research Development Program of China; Project(51774021) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019SDZY05) supported by the Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., You, S., Ji, Hg. et al. Strength and energy exchange of deep sandstone under high hydraulic conditions. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 27, 3053–3062 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4528-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4528-2