Abstract
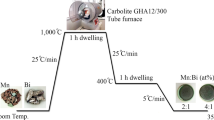
Implementation of manganese-bismuth (MnBi) alloys as high-performance permanent magnets is a challenge for physicists and engineers because the ferromagnetic low-temperature phase (LTP) is not exclusively obtained. In this work, melting powered by four commercial magnetrons of 2000–2500 W in a microwave furnace is demonstrated as a new route to alloy MnBi. Under an argon atmosphere, microwave heating transferred to pieces of broken Bi ingots and Mn flakes for 2 h gave rise to products of inhomogeneous composition and morphology. Scanning electron micrographs were classified into three regions according to morphology and elemental composition. Cubic-like clusters characterized as Mn precipitated over light solidified Bi-rich regions, and the MnBi phase was formed in homogeneous regions with a balanced composition between Mn and Bi. A ferromagnetic hysteresis loop was obtained in the ground powder with a coercivity of 40 kA/m. Subsequent annealing at 553 K under a pressure of 414 kPa for 12 h enhanced the MnBi phase with extended regions of balanced composition. It follows that the coercivity was increased to 60 kA/m. However, remanent magnetization was slightly reduced. This MnBi alloyed by microwave radiation can be further used in rare-earth-free magnets.
摘要
得到高性能永磁体锰铋(MnBi)合金对物理学家和工程师来说是一个挑战,因为纯的铁磁低温相 (LTP)不容易获得。在本工作中,在微波炉中由四个2000–2500 W 的商用磁控管驱动的熔化被证明是 一种新的合成MnBi 的路线。在氩气气氛下,微波加热碎Bi 锭和Mn 片2 h,得到成分和形貌不均匀 的产物。按形貌和元素组成将扫描电子显微照片分为三个区域。立方团簇状的Mn 沉淀在明亮的富铋 固化区,MnBi 相在Mn 与Bi 组分平衡、均匀的区域形成。在矫顽力为40 kA/m 的磨碎粉末中存在铁 磁磁滞回线。随后在414 kPa、553 K 下退火12 h,MnBi 相得到扩展,矫顽力提高到60 kA/m,但残 余磁化强度略有降低。微波辐射法得到的MnBi 合金可用于无稀土磁体。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
POUDYAL N, LIU X, WANG W, NGUYEN V V, MA Y, GANDHA K, ELKINS K, LIU J P, SUN K, KRAMER M J, CUI J. Processing of MnBi bulk magnets with enhanced energy product [J]. AIP Advances, 2016, 6: 056004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4942955.
KIM S, MOON H, JUNG H, KIM S M, LEE H S, CHOI-YIM H, LEE W. Magnetic properties of large-scaled MnBi bulk magnets [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 708: 1245–1249. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.067.
NGUYEN V V, NGUYEN T X. Effect of microstructures on the performance of rare-earth-free MnBi magnetic materials and magnets [J]. Physica B, 2018, 532: 103–107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.06.018.
PARK J, HONG Y K, LEE J, LEE W, KIM S G, CHOI C J. Electronic structure and maximum energy product of MnBi [J]. Metals, 2014, 4(3): 455–464. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/met4030455.
XIANG Z, WANG T, MA S, QIAN L, LUO Z, SONG Y, YANG H, LU W. Microstructural evolution and phase transformation kinetics of MnBi alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 741: 951–956. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.147.
CUI J, KRAMER M, ZHOU L, LIU F, GABAY A, HADJIPANAYIS G, BALASUBRAMANIAN B, SELLMYER D. Current progress and future challenges in rare-earth-free permanent magnets [J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 158: 118–137. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.07.049.
JANOTOVA I, SVEC P, SVEC P, MATKO I, JANICKOVIC D, KUNCA B, MARCIN J, SKORVANEK I. Formation of magnetic phases in rapidly quenched Mn-based systems [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 749: 128–133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.208.
MARKER M C J, TERZIEFF P, KAINZBAUER P, BOBNAR M, RICHTER K W, IPSER H. BiMn: Synthesis, separation by centrifugation, and characterization [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 741: 682–688. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.235.
CUI J, CHOI J P, POLIKARPOV E, BOWDEN M E, XIE W, LI G, NIE Z, ZARKEVICH N, KRAMER M J, JOHNSON D. Effect of composition and heat treatment on MnBi magnetic materials [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 79: 374–381. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.07.034.
KANARI K, SARAFIDIS C, GJOKA M, NIARCHOS D, KALOGIROU O. Processing of magnetically anisotropic MnBi particles by surfactant assisted ball milling [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2017, 426: 691–697. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.141.
LI B, MA Y, SHAO B, LI C, CHEN D, SUN J, ZHENG Q, YIN X. Preparation and magnetic properties of anisotropic MnBi powders [J]. Physica B, 2018, 530: 322–326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.11.085.
GABAY A M, HADJIPANAYIS G C, CUI J. Preparation of highly pure a-MnBi phase via melt-spinning [J]. AIP Advances, 2018, 8: 056702. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5006491.
SAITO T, NISHIMURA R, NISHIO-HAMANE D. Magnetic properties of Mn-Bi melt-spun ribbons [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2014, 349: 9–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.08.031.
NGUYEN V V, NGUYEN T X. An approach for preparing high-performance MnBi alloys and magnets [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2017, 46(6): 3333–3340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5409-9.
XIE W, POLIKARPOV E, CHOI J P, BOWDEN M E, SUN K, CUI J. Effect of ball milling and heat treatment process on MnBi powders magnetic properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 680: 1–5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.097.
MIYAZAKI D, MITSUI Y, UMETSU R Y, TAKAHASHI K, UDA S, KOYAMA K. Enhancement of the phase formation rate during in-field solid-phase reactive sintering of Mn-Bi [J]. Materials Transactions, 2017, 58(5): 720–723. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.mbw201609.
RAMAKRISHNA V V, KAVITA S, GAUTAM R, RAMESH T, GOPALAN R. Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of Al and Cu doped MnBi alloy [J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2018, 458: 23–29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.02.076J.
CÉSPEDES E, VILLANUEVA M, NAVÍO C, MOMPEÁN F J, GARCÍA-HERNÁNDEZ M, INCHAUSTI A, PEDRAZ P, OSORIO M R, CAMARERO J, BOLLERO A. High coercive LTP-MnBi for high temperature applications: From isolated particles to film-like structures [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 729: 1156–1164. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.234.
TEREKHOV A V, SOLOVJOV A L, PROKHVATILOV A I, MELESHKO V V, ZOLOCHEVSKII I V, CWIK J, LOS A, SHEVCHENKO A D, IVASISHIN O M, KOVALYUK Z D. Anomalous anisotropic magnetoresistance and magnetization in Mn3.69Bi95.69Fe0.62 [J]. East European Journal of Physics, 2017, 4(4): 12–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26565/2312-4334-2017-4-02.
LIU B G, YU Y T, PENG J H, SRINIVASAKANNAN C, ZHANG L B, GUO S H. Preparation of microsized hematite powder from ferrous sulfate via microwave calcination [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(8): 1720–1726. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3579-5.
NGUYEN T X, NGUYEN V V. Fabrication of MnBi alloys with high ferromagnetic phase content: Effects of heat treatment regimes and dopants [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30: 6888–6894. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01003-x.
KAUSHAL S, GUPTA D, BHOWMICK H. On development and wear behavior of microwave processed functionally graded Ni-SiC clads on SS-304 substrate [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(2): 777–786. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-3110-z.
VOROKH A S. Scherrer formula: Estimation of error in determining small nanoparticle size [J]. Nanosystems: Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics, 2018, 9(3): 364–369. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17586/2220-8054-2018-9-3-364-369.
SIRISATHITKUL C, CHAROENSUK T. Effects of composition and heat treatment on manganese-bismuth magnets [J]. Micro & Nano Letters, 2019, 14(6): 661–664. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2018.5227.
FANG H L, LI J H, SHAFEIE S, HEDLUND D, CEDERVALL J, EKSTROM F, GOMEZ C S, BEDNARCIK J, SVEDLINDH P, GUNNARSSON K, SAHLBERG M. Insights into phase transitions and magnetism of MnBi crystals synthesized from self-flux [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 781: 308–314. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.146.
ANAND K, CHRISTOPHER N, SINGH N. Evaluation of structural and magnetic property of Cr-doped MnBi permanent magnet material [J]. Applied Physics A, 2019, 125: 870. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3156-x.
MOON K W, JEON K W, KANG M, KANG M K, BYUN Y, KIM J B, KIM H, KIM J. Synthesis and magnetic properties of MnBi(LTP) magnets with high-energy product [J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2014, 50: 2103804. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2014.2329555.
CHEN Y, SAWATZKI S, ENER S, SEPEHRI-AMIN H, LEINEWEBER A, GREGORI G, QU F, MURALIDHAR S, OHKUBO T, HONO K, GUTFLEISCH O, KRONMÜLLER H, SCHÜTZ G, GOERING E. On the synthesis and microstructure analysis of high permanence MnBi [J]. AIP Advances, 2016, 6: 125301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4971759.
LEWIS L H, CREW D C. The coercivity-remanence tradeoff in nanocrystalline permanent magnets [J]. Materials Research Society Symposia Proceedings, 2002, 703: 565–369. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/proc-703-u2.8.
ZHANG W, BALASUBRAMANIAN B, KHAREL P, PAHARI R, VALLOPPILLY S R, LI X Z, YUE L P, SKOMSKI R, SELLMYER D J. High energy product of MnBi by field annealing and Sn alloying [J]. APL Materials, 2019, 7: 121111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5128659.
QIAN H D, PARK J H, LIM J T, YANG Y, SI P Z, KIM J W, CHOI C J, CHO K M. Magnetic properties of MnBi bulk magnets with NaCl and C addition [J]. AIP Advances, 2019, 9: 115213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5122677.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by Thailand Center of Excellence in Physics (Grant No. ThEP-60-PIP-WU3). It is partially supported by the New Strategic Research (P2P) project, Walailak University, Thailand. The authors would like to thank P. JANTARATANA and D. SRINUAM for facility supports and P. SAETANG for assistance. P. HARDING thanks the National Science Technology and Innovation Policy Office for Integrated Research and Innovation Plan (Grant No. 256113A3050001) for XRD services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(ThEP-60-PIP-WU3) supported by the Thailand Center of Excellence in Physics
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thongjumpa, P., Charoensuk, T., Boonyang, U. et al. Phase investigations of manganese-bismuth alloyed in a microwave furnace. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 2220–2226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4443-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4443-6