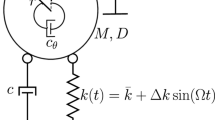Abstract
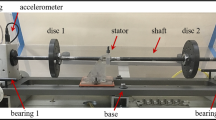
Vibration isolation is an effective method to mitigate unwanted disturbances arising from dynamic loading conditions. With smart materials as suitable substitutes, the conventional passive isolators have attained attributes of semi-active as well as the active control system. In the present study, the non-homogenous field-dependent isolation capabilities of the magnetorheological elastomer are explored under torsional vibrations. Torsional natural frequency was measured using the serial arrangement of accelerometers. Novel methods are introduced to evaluate the torsional stiffness variations of the isolator for a semi-definite and a motor-coupled rotor system. For the semi-definite system, the isolation effect was studied using the frequency response functions from the modal analysis. The speed-dependent variations for motor-coupled rotor system were assessed using the shift in frequency amplitudes from torque transducers. Finite element method magnetics was used to study the variations in the non-homogenous magnetic field across the elastomer. The response functions for the semi-definite rotor system reveal a shift in the frequency in the effect of the magnetic field. Speed-dependent variations in the frequency domain indicate an increment of 9% in the resonant frequency of the system.
摘要
隔振是一种减少在动态加载条件不必要干扰的有效方法. 以智能材料作为合适的替代品, 传统的无源隔离器具有主动控制和半主动控制的特点. 在本研究中, 探讨了磁流变弹性体在扭转振动下的非均匀场相关隔离能力, 利用加速度计的串联方式测量扭转固有频率, 介绍了一种新的方法来评估半定转子系统和电机耦合转子系统的隔振器的扭转刚度变化. 利用模态分析中的频响函数, 研究了半定系统的隔振效果. 利用转矩传感器的频率幅值的位移来评估电机耦合转子系统的速度相关变化. 用有限元方法研究了非均匀磁场在弹性体表面的变化. 半定转子系统的响应函数揭示了磁场作用下频率的变化. 频率域的速度相关变化表明系统的共振频率增加了 9%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RAN L, YACAMINI R, SMITH K S. Torsional vibrations in electrical induction motor drives during start-up [J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 1996, 118(2): 242–251. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2889655.
GAO P, XIANG C, LIU H, ZHOU H. Reducing variable frequency vibrations in a powertrain system with an adaptive tuned vibration absorber group [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibrations, 2018, 425: 82–101. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.03.034.
RAO S S. Mechanical vibrations [M]. Pearson, 2010.
RABINOW J. The magnetic fluid clutch [J]. Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 1948, 67: 1308–1315. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/T-AIEE.1948.5059821.
JOLLY M R, CARLSON J D, MUÑOZ B C. A model of the behaviour of magnetorheological materials [J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 1996, 5(5): 607–614. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/5/5/009.
VICENTE J, KLINGENBERG D J, HIDALGO-ALVAREZ R. Magnetorheological fluids: A review [J]. Soft Matter, 2011, 7(8): 3701–3710. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0sm01221a.
SUN S, DENG H, YANG J, LI W, DU H, ALICI G. Performance evaluation and comparison of magnetorheological elastomer absorbers working in shear and squeeze modes [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2015: 1757–1763. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X14568819.
EEM S H, JUNG H J, KOO J H. Application of MR elastomers for improving seismic protection of base-isolated structures [C]// IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2011: 2901–2904. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2156771.
LI Y, LI J, LI W, DU H. A state-of-the-art review on magnetorheological elastomer devices [J]. Smart Material Structure, 2014, 23(12): 123001–123024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/23/12/123001.
LI W, ZHANG X, DU H. Development and simulation evaluation of a magnetorheological elastomer isolator for seat vibration control [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2012, 23(9): 1041–1048. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X11435431.
QIAN L J, XIN F L, BAI X X, WERELEY N M. State observation-based control algorithm for dynamic vibration absorbing systems featuring magnetorheological elastomers: Principle and analysis [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2017, 28(18): 2539–2556. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X17692047.
LOKANDER M, STENBERG B. Improving the magnetorheological effect in isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials [J]. Polymer Testing, 2003, 22(6): 677–680. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9418(02)00175-7.
LOKANDER M, STENBERG B. Performance of isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials [J]. Polymer Testing, 2003, 22: 245–251. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9418(02)00043-0.
JOLLY M R, CARLSON J D, MUÑOZ B C. The magnetoviscoelastic response of elastomer composites consisting of ferrous particles embedded in a polymer matrix [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1996, 7(6): 613. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X9600700601.
ZHOU G Y. Shear properties of a magnetorheological elastomer [J]. Smart Material Structure, 2003, 12: 139–146. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/12/1/316.
YANG J, GONG X, DENG H, QIN L, XUAN S. Investigation on the mechanism of damping behavior of magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Smart Material Structure, 2012, 21(12): 125015–125026. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/21/12/125015.
GONG X L, ZHANG X Z, ZHANG P Q. Fabrication and characterization of isotropic magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Polymer Testing, 2005, 24(5): 669–676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2005.03.015.
XIN F, BAI X, QIAN L. Modeling and experimental verification of frequency-, amplitude-, and magneto-dependent viscoelasticity of magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Smart Material Structure, 2016, 25(10): 105002–105018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/25/10/105002.
PAYNE A R. The dynamic properties of carbon black loaded natural rubber vulcanizates. Part II [J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1962, 6(21): 368–372. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1962.070062115.
LI J F, GONG X L. Dynamic damping property of magnetorheological elastomer [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(1): 261–265. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0359-2.
CHEN L, GONG X L. Damping of magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(1): 271–274. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0361-8.
POOJARY U R, HEGDE S, GANGADHARAN K V. Dynamic blocked transfer stiffness method of characterizing the magnetic field and frequency dependent dynamic viscoelastic properties of MRE [J]. Korea Aust Rheol J, 2016, 28(4): 301–313. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0031-6.
HOANG N, ZHANG N, LI W H, DU H. Development of a torsional dynamic absorber using a magnetorheological elastomer for vibration reduction of a powertrain test rig [J]. Journal of Intelligent material systems and structures, 2013, 24(16): 2036–2044. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X13489361.
HOANG N, ZHANG N, DU H. A dynamic absorber with a soft magnetorheological elastomer for powertrain vibration suppression [J]. Smart Material Structure, 2009, 18(7): 074009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/18/7/074009.
POOJARY U R, HEGDE S, GANGADHARAN K V. Dynamic deformation-dependent magnetic field-induced force transmissibility characteristics of magnetorheological elastomer [J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2017, 28(11): 1491–1500. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X16672730.
KUANG J H, LIN J F. Accelerometer pair measurements for shaft dynamic parameters analysis [C]// Proceedings of SPIE. The International Society for Optical Engineering, 1994: 1649–1655.
HOORZAD H. Characterization of viscoelastic materials using atomic force microscopy [D]. Alberta: University of Calgary, 2017: 61.
GRAESSER E, WONG C. The relationship of traditional damping measures for materials with high damping capacity: A review [M]. STP1169-EB M D: Mechanics and Mechanisms Damping. ASTM, 1991: 316–328. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1520/STP17969S.
CARFAGNI M, LENZI E, PIERINI M. The loss factor as a measure of mechanical damping [C]// SPIE Proceedings Series, 1998: 580–584.
WILSON W K. Practical solution of torsional vibration problems: With examples from marine, electrical, aeronautical, and automobile engineering practice, vol. 1 [M]. Chapman & Hall, 1956.
SHENOY K P, SINGH A K, RAMAN K S A, GANGADHARAN K V. Experimental investigation of torsional vibration isolation using magneto rheological elastomer [C]// MATEC Web of Conferences, 2018: 144. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201714401007.
STACER R G, HÜBNER C, HUSBAND D M. Binder/filler interaction and the nonlinear behavior of highly-filled elastomer [J]. Rubber Chemical Technology, 1990, 63(4): 488–502. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3538268.
HEGDE S, KIRAN K, GANGADHARAN K V. A novel approach to investigate effect of magnetic field on dynamic properties of natural rubber based isotropic thick magnetorheological elastomers in shear mode [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(7): 2612–2619. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2791-4.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from SOLVE: The Virtual Lab @ NITK (Grant number: No.F.16-35/2009-DL, Ministry of Human Resources Development) and experimental facility provided by Centre for System Design (CSD): A Centre of Excellence (http://csd.nitk.ac.in/) at National Institute of Technology Karnataka, India. The authors would also wish to thank Mr Umanath Poojary, Senior Research Fellow, CSD, for his invaluable inputs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praveen, S.K., Kuchibhatla, S.A.R., Singh, A.K. et al. Performance of magnetorheological elastomer based torsional vibration isolation system for dynamic loading conditions. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 144–154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4284-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4284-3
Key words
- torsional vibration isolation
- semi-definite system
- magnetorheological elastomer
- speed-dependent isolation