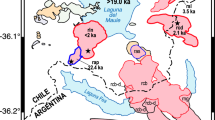
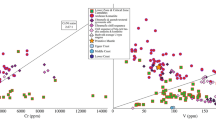
Abstract
The ilvaite-bearing skarn associations in the Galinge skarn deposit were studied to determine their physicochemical formation conditions. A thermodynamic model setting pressure of 50 MPa (Pf=Ps=50 MPa) was set up to trace the skarn evolution. Petrographic evidence for replacement of garnet and magnetite by ilvaite in the early retrograde stage (Stage I) combined with thermodynamic modeling suggests that the alteration may have occurred at 400–470 °C under moderately high fO2 with ΔlgfO2(HM) ranges from −4 to −4.2. The model is based on a maximum pressure of 50 MPa calculated from magmatic amphibole geobarometer. The continuous breakdown of ilvaite with quartz to form ferro-actinolite and magnetite occur in the late retrograde stage (Stage II). The reactions occurred at 400-440°C under moderate fO2 (ΔlgfO2(HM): −4 to −4.4). In Stage III, the breakdown of ilvaite to form calcite, pyrite and ferroactinolite depends on XCO2 which can be estimated to be in a range of 0.005 to 0.05, and the reaction would occur at higher temperatures with increasing XCO2. Under these conditions, the breakdown occurs at 270–350 °C and low fO2 (ΔlgfO2(HM): up to −5.2). The thermodynamic model for continuous evolution from Stage I to Stage III completely records the conditions of the retrograde alteration, which is inconsistent with the thermobarometry imprints of fluid inclusions. Therefore, the petrography and phase relations of ilvaite are useful indicators of reaction conditions in various skarn deposit types.
摘要
尕林格大型矽卡岩铁矿位于祁漫塔格斑岩-矽卡岩成矿带内, 发育一套典型的 Ca 质退化蚀变矽 卡岩系列. 其中, 含黑柱石退化蚀变组合可以很好地反演流体交代热动力学过程. 岩石学证据表明在 早期退化蚀变阶段 (Stage I), 黑柱石交代石榴子石和磁铁矿, 该反应根据岩浆角闪石地质温压计设定 最大压力条件 50 MPa, 获得热动力学 T=400~470 °C 和 ΔlgfO2(HM)=−4~−4.2; 在晚期退化蚀变阶段 (Stage II), 黑柱石和石英反应生成磁铁矿和铁阳起石, 该反应发生在 400~440 °C 和 ΔlgfO2(HM)=−4~−4.4 热动力学条件范围内; 到了方解石-石英-硫化物阶段(Stage III), 黑柱石分解形成方解石、黄铁矿 和铁阳起石, 该反应发生温度随着 XCO2 的升高而升高, 在XCO2=0.005−0.05 范围内, 分解反应条件为 T=270−350 °C 和ΔlgfO2(HM)<−5.2. 随着黑柱石的连续演化, 该热动力学模型完整地记录了退化蚀 变反应的发生过程. 除此之外, 流体体系中Fe 和Mg 的含量会强烈影响黑柱石在矽卡岩体系中的稳 定性. 因此, 黑柱石的岩石学和相变关系可以很好地指示不同类型矽卡岩矿床的交代反应过程.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GHOSE S, SEN GUPTA P K, SCHLEMPER E O. Electron ordering in ilvaite, a mixed-valence iron silicate: Crystal structure refinement at 138 K [J]. American Mineralogist, 1985, 70: 1248–1252.
GHOSE S, TSUKIMURA K, HATCH D. Phase transitions in ilvaite, a mixed-valence iron silicate [J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 1989, 16(5): 483–496.
BARTHOLOMÉ P, DIMANCHE F. On the paragenesis of ilvaite in Italian skarns [J]. Ann Soc Geol Belg, 1967, 90: 533–565.
BURT D M. Multisystems analysis of the relative stabilities of babingtonite and ilvaite [J]. Carnegie Inst Wash Year Book, 1971, 70: 189–197.
PLIMER I R, ASHLEY P M. Manganoan ilvaite from broken hill, N.S.W. and Ban Ban, Queensland, Australia [J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1978, 42(321): 85–88.
EINAUDI M T, BURT D M. A special issue devoted to skarn deposits (Introduction; terminology, classification, and composition of skarn deposits) [J]. Economic geology, 1982, 77(4): 745–754.
VASSILEVA R D, BONEV I K, ZOTOV N. High-Mn ilvaites from the skar Pb-Zn deposits in the Central Rhodopes [C]// Mineral Deposits at the Beginning of the 21st Century, 2001: 925–928.
BONEV I K, VASSILEVA R D, ZOTOV N, KOUZMANOV K. Manganilvaite, CaFe2+Fe3+(Mn, Fe2+)(Si2O7)O(OH), a new mineral of the ilvaite group from Pb-Zn skarn deposits in the Rhodope Moutntains, Bulgaria [J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2005, 43(3): 1027–1042.
LARSEN A O, DAHLGREN S. Ilvaite from the Oslo graben, Norway [J]. Neues Jahrbuch Für Mineralogie - Monatshefte, 2002, 4: 169–181.
KWAK T A P. The geology and geochemistry of the zoned, Sn-W-F-Be skarns at Mt. Lindsay, Tasmania, Australia [J]. Economic Geology, 1983, 78(7): 1440–1465.
MEINERT L D. Mineralogy and petrology of iron skarns in Western British Columbia, Canada [J]. Economic Geology, 1984, 79(5): 869–882.
FRANCHINI M B, MEINERT L D, VALLES J M. First occurrence of ilvaite in a gold skarn deposit [J]. Economic Geology, 2002, 97(5): 1119–1126.
TALLARICO F H B. Occurrence of ilvaite in the Igarapé Bahia Cu-Au deposit, Carajás Province, Brazil [J]. Revista Brasileira de Geociências, 2002, 32(1): 149–152.
GRASER G, MARKL G. Ca-rich ilvaite-epidote-hydrogarnet endoskarns: a record of late-magmatic fluid influx into the persodic ilimaussaq complex, South Greenland [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2007, 49(2): 239–265.
EINAUDI M T, MEINERT L D, NEWBERRY R J. Skarn deposits [J]. Economic Geology, 1981, 75: 317–391.
MEINERT L D. Skarns and skarn deposits [J]. Geoscience Canada, 1992, 19(4): 145–162.
MEINERT L D. Igneous petrogenesis and skarn deposits [J]. Mineral Deposit Modeling, 1993, 40: 569–583.
MISRA K C. Understanding mineral deposits [M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2000.
YU M, FENG C Y, BAO G Y, LIU H C, ZHAO Y M, LI D X, XIAO Y, LIU J N. Characteristics and zonation of skarn minerals in Galinge iron deposit, Qinghai Province [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(1): 55–76.
SHE H Q, ZHANG D Q, JING X Y, GUAN J, ZHU H P, FENG C Y, LI D X. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Ulan Uzhur porphyry copper deposit in Qinghai [J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(2): 306–314. (in Chinese)
LIU J N, FENG C Y, ZHAO Y M, LI D X, XIAO Y, ZHOU J H, MA Y S. Characteristics of intrusive rock, metasomatites, mineralization and alteration in Yemaquan skarn Fe-Zn polymetallic deposit, Qinghai Province [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(1): 77–93.
ZHAO Y M, FENG C Y, LI D X, LIU J N, XIAO Y, YU M, MA S C. Metallogenic setting and mineralization-alteration characteristics of major skarn Fe-polymetallic deposits in Qimantag area, western Qinghai Province [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(1): 1–19.
YU M, FENG C Y, SANTOSH M, MAO J W, ZHU Y F, ZHAO Y M, LI D X, LI B. The qiman tagh orogen as a window to the crustal evolution in northern Qinghai-Tibet plateau [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 167: 103–123.
WANG B Z, LUO Z H, LI H Y, CHEN H W, HU X L. Petrotectonic assemblages and temporal-spatial framework of the Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic intrusions in the Qimantage Corridor of the East Kunlun belt [J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(4): 769–782. (in Chinese)
LI W, NEUBAUER F, LIU Y, GENSER J, REN S, HAN G, LIANG C. Paleozoic evolution of the Qimantagh magmatic arcs, Eastern Kunlun Mountains: constraints from zircon dating of granitoids and modern river sands [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 77: 183–202.
WANG C, LIU L, XIAO P, CAO Y, YU H, MEERT J G, LIANG W. Geochemical and geochronologic constraints for Paleozoic magmatism related to the orogenic collapse in the Qimantagh-South Altyn region, northwestern China [J]. Lithos, 2014, 202: 1–20.
MENG F, CUI M, WU X, REN Y. Heishan mafic-ultramafic rocks in the Qimantag area of Eastern Kunlun, NW China: remnants of an Early Paleozoic incipient island arc [J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27(2): 745–759.
CHEN J, WANG B, LI B, ZHANG Z, QIAO B, JIN T. Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Middle Triassic granodiorites from the Kaimuqi area, East Kunlun, Northwest China: Implications for slab breakoff [J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(2): 257–270.
YAO L, LÜ Z C, ZHAO C S, PANG Z S, YU X F, ZHU X Y, LI Y S, LIU P, LI S T, ZHANG M C. Geochronological study of granitoids from the Niukutou and B section of the Kaerqueka deposits, Qimantag area, Qinghai Province: Implications for Devonian magmatism and mineralization [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(7): 1158–1169. (in Chinese)
FENG C Y, LI D S, WU Z S, LI J H, ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG A K, SHU X F, SU S S. Major types, time-space distribution and metallogenesis of polymetallic deposits in the Qimantage metallogenic belt, eastern Kunlun area [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(4): 10–17.
MAO J W, ZHOU Z H, FENG C Y, WANG Y, ZHANG C, PENG H, MIAO Y. A preliminary study of the Triassic large-scale mineralization in China and its geodynamic setting [J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(6): 1437–1471. (in Chinese)
YU M, FENG C Y, ZHAO Y M, LI D X. Genesis of post-collisional calc-alkaline and alkaline granitoids in Qiman Tagh, East Kunlun, China [J]. Lithos, 2015, 239: 45–59.
LUO Z H, KE S, CAO Y Q, DENG J F, ZHAN H W. Late Indosinian mantle-derived magmatism in the East Kunlun [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(6): 292–297. (in Chinese)
LIU C, MO X, LUO Z, YU X, CHEN H, LI S, ZHAO X. Mixing events between the crust-and mantle-derived magmas in Eastern Kunlun: Evidence from zircon SHRIMP II chronology [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(8): 828–834. (in Chinese)
YU M. Geochemistry and zonation of the Galinge iron deposit, Qinghai province [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013. (in Chinese)
GAO Y, LI W, MA X. Genesis, geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the magmatic rocks in Galinge iron deposit, eastern Kunlun [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2012, 48(2): 36–47. (in Chinese)
YU M, FENG C, LIU H, LI D, ZHAO Y, LI D, LIU J, WANG H, ZHANG M. 40Ar-39Ar geochronology of the Galinge large skarn iron deposit in Qinghai province and geological significance [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(3): 510–521.
ARMSTRONG J T. Quantitative elemental analysis of individual microparticles with electron beam instruments [M]. Electron Probe Quantitation. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1991.
CARROZZINI B. Crystal structure refinements of ilvaite: new relationships between chemical composition and crystallographic parameters [J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 1994, 6(4): 465–480.
TAKÉUCHI Y, SAWADA H, TANIGUCHI H. The ilvaite problem [J]. The Institute of Natural Sciences Nihon University, 1993, 28: 39–43.
YU M, FENG C Y, ZHU Y F, MAO J W, ZHAO Y M, LI D X. Multistage amphiboles from the Galinge iron skarn deposit in Qiman Tagh, western China: Evidence of igneous rocks replacement [J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2017, 111(1): 81–97.
GUSTAFSON W I. The stability of andradite, hedenbergite, and related minerals in the system Ca: Fe: Si: O: H [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1974, 15(3): 455–496.
MARTIN J, DELGADO SOLERI GIL A. Ilvaite stability in skarns from the northern contact of the Maladeta batholith, central Pyrenees (Spain) [J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2010, 22(3): 363–380.
ZHAO Y M, TAN H J, XU Z N, YUAN R G, BI C, ZHENG R L, LI D X, SUN J H. Makeng type calcic skarn iron deposit in the Southwest of Fujian province [M]. Beijing: Bulletin of the institute of mineral deposit, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1983.
BERMAN R G. Internally-consistent thermodynamic data for minerals in the system Na2O-K2O-CaO-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-H2O-CO2 [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1988, 29(2): 445–522.
BERMAN R G. WinTWQ (version 2.3): A software package for performing internally-consistent thermobarometric calculations [R]. Natural Resources Canada/ESS/Scientific and Technical Publishing Services, 2007.
DICK J M. Calculation of the relative metastabilities of proteins using the CHNOSZ software package [J]. Geochemical Transactions, 2008, 9(1): 1–17.
BARTON M, van BERGEN M J. Secondary ilvaite in a dolerite dyke from Rogaland, SW Norway [J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1984, 48(348): 449–456.
WANG Y S. Analysis on special case of ilvaite enrichment in a certain iron deposit [J]. Qinghai Geology, 1994, 3(2): 19–20.
PETERSEN O V, MICHEELSEN H I, LEONARDSEN E S. Bavenite, Ca4Be3Al[Si9O25(OH)3], from the Ilimaussaq alkaline complex, South Greenland [J]. Neues Jahrbuch Für Mineralogie, Monatsheft, 1995, 7: 321–325.
ROGULINA L I, SVESHNIKOVA O L. The Nikolaevsky base-metal skarn deposit, Primorye, Russia [J]. Geology of Ore Deposits, 2008, 50(1): 60–74.
TANG P Z, WANG Y W, WANG J B, LONG L L, ZHANG H Q, LIAO Z. Finding and Significance of Ilvaite in the Cihai Iron Deposit, Xinjiang Autonomic Region, China [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, 31(1): 9–16.
LEHRMANN B. Polymetallic mineralisation in the Chillagoe district of north-east Queensland: Insights into base metal rich intrusion-related gold systems [D]. Townsville: James Cook University, 2012.
MARTIN J, DELGADO SOLERI GIL A. Ilvaite stability in skarns from the northern contact of the Maladeta batholith, Central Pyrenees (Spain) [J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2010, 22(3): 363–380.
MEINERT L D. Skarn zonation and fluid evolution in the Groundhog mine, Central mining district, New Mexico [J]. Economic Geology, 1987, 82(3): 523–545.
ASHLEY P M. Geology of the Ban Ban zinc deposit, a sulfide-bearing skarn, southeast Queensland, Australia [J]. Economic Geology, 1980, 75(1): 15–29.
BONAZZI P, BINDI L. Structural properties and heat-induced oxidation-dehydrogenation of manganoan ilvaite from Perda Niedda mine, Sardinia, Italy [J]. American Mineralogist, 2002, 87(7): 845–852.
BRATHWAITE R L, ISAAC M J, CHALLIS G A, BROOK F J. Tertiary limestone and Zn-Pb mineralised skarn at Motukokako, Cape Brett, northern New Zealand [J]. Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 1990, 20(4): 427–438.
GOLE M J. Ca-Fe-Si skarns containing babingtonite: first known occurrence in [J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1981, 19: 269–277.
GOLE M J. Iron calc-silicate rocks at black perry mountain, Talbingo, Southern New South Wales [M]. Sydney: Macquarie University, 1972.
PESQUERA A, VELASCO F. An occurrence of ilvaite layers in the Cinco villas metasomatic rocks, Western Pyrenees (Spain) [J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1986, 50(358): 653–656.
SALEMINK J. Skarn and ore formation at Seriphos, Greece as a consequence of granodiorite intrusion [D]. Utrecht: Utrecht University, 1985.
DÜNKEL I. The genesis of east Elba iron ore deposits and their interrelation with Messinian tectonics [D]. Baden-Waerttemberg: Universität Tübingen, 2002.
SCHIENER A. Lievrit von Seriphos [J]. Zeitschrift Für Kristallographie-Crystalline Materials, 1933, 85(1–6): 89–118.
VERKAEREN J, BARTHOLOME P. Petrology of the San Leone magnetite skarn deposit (S.W. Sardinia) [J]. Economic Geology, 1979, 74(1): 53–66.
LOGAN M A V. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Gualilán skarn deposit in the Precordillera of western Argentina [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2000, 17(1, 2): 113–138.
HIRTOPANU P, ANDERSEN J C, HARTOPANU I, UDUBASA S S. Ilvaite from the Cavnic deposit, Romania [J]. Romanian Journal of English Studies, 2012: 62–65.
MARESCH W V, MOTTANA A. The pyroxmangite-rhodonite transformation for the MnSiO3 composition [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 55(1): 69–79.
MOMOI H. Hydrothermal crystallization of MnSiO3 polymorphs [J]. Mineralogical Journal, 1974, 7(4): 359–373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(41172076, 41802080) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(1212011085528) supported by Geological Survey Program from the China Geological Survey; Project(2019CX035) supported by Innovation-driven Plan of Central South University, China; Project(201411025) supported by the Scientific Research Fund from Ministry of Land and Re-sources, China; Project(201309) supported by the Program of High-level Geological Talents, China; Project(201112) supported by the Youth Geological Talents of the China Geological Survey
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Dick, J.M., Mao, Jw. et al. Ilvaite as a thermodynamic recorder of multistage retrograde alteration in large Galinge skarn Fe deposit, western China. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 3534–3550 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4271-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4271-8