Abstract
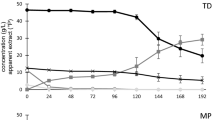
The present work focuses on the influence of various parameters, i.e., the dosage of cellulase, the inoculum concentration of yeast, the fermentation temperature and the fermentation time, on the alcohol content and sensory evaluation of the low-alcoholic health drink produced from corncob in a yeast-cellulase synchronous fermentation process. The fermentation was performed by inoculating the seed solution (containing corncob powder and yeast) and cellulase into the synchronous saccharification fermentation medium. Single-factor experiments and orthogonal experiments were performed, and the optimal processing conditions were obtained based on the characterizations of alcohol content and sensory evaluation. The results show that the alcohol content and sensory evaluation of the drink can reach 6.1 vol.% and 92, respectively, when the dosage of cellulase, inoculum concentration of yeast, the fermentation temperature and the fermentation time are 15 U/g, 7%, 32 °C and 84 h, respectively.
摘要
本研究主要关注包括纤维素酶添加量、酵母菌接种量、发酵温度与发酵时间等参数对以玉米芯 为原料, 采用纤维素酶和酵母菌同步糖化发酵法制备的低醇保健饮料的酒精度和口感的影响. 发酵过 程是在接种有种子液(包含玉米芯粉和酵母)和纤维素酶的同步糖化发酵培养基中进行的. 采用单因素 试验和正交试验, 通过检测酒精度及感官综合评分, 探讨玉米芯低醇保健饮料生产的最佳工艺条件. 研究结果表明: 当纤维素酶用量为15 U/g, 酵母菌接种量为7%, 在温度为32 °C 条件下发酵84 h, 制备的玉米芯低醇保健饮料酒精度6.1%, 感官综合评分92 分.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ZHANG Q, HU Z. Assessment of drought during corn growing season in Northeast China [J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2018, 133: 1315–1321. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2469-6.
XU Shu-fen. Talking about the comprehensive utilization of corncob [J]. Sci-Tech Information Development & Economy, 2011, 21(17): 174–175. (in Chinese)
GE Wen-xia, LIU Xu-wei, ZHANG Wen-ju, YANG Li-wei, LIU Xiao-na. Nutritional value, processing and application of maize cob in livestock production [J]. Cereal & Feed Industry, 2017(11): 51–54. (in Chinese)
XU Guo-hui, ZHU Zhen-yuan, XIAO Lin. Process of producing xylose by corn cob [J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2016, 7(7): 2909–2913. (in Chinese)
SUN Jun-tao, ZHANG Zhi-chao, WANG Jing-jing. Production of xylooligosaccharide from corncobs by ultrasound-assisted composite enzymatic hdrolysis [J]. The Food Industry, 2015, 36(3): 37–40. (in Chinese)
PRAJAPATI A S, PANCHAL K J, PAWAR V A, NORONHA M J, PATEL D H, SUBRAMANIAN R B. Review on cellulase and xylanase engineering for biofuel production [J]. Industrial Biotechnology, 2018, 14: 38–44. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/ind.2017.0027.
SHENG Di, ZHU Lan-bao, HE Ran-ran, ZHOU Kai-sheng. The optimization of response surface method-based microwave production of active carbon from corncob [J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition, 2019, 16(5): 93–101. (in Chinese)
LI Chang-wen, ZONG Wei, LI Jiang-tao, WANG Lu. Study on the extraction technology of soluble dietary fiber in corn cob [J]. The Food Industry, 2014, 35(2): 33–35. (in Chinese)
YAO Jia-min, JIANG Min, WU Hao, CHEN Ke-quan. Preparation of saccharification liquid for succinicacid by fermentation from corncob sulfuric acid hydrolysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2010, 8(3): 66–72. (in Chinese)
WANG Xue, KOU Jiao-long, ZHANG Xun, SUN Jing-song, GAO Chang-peng, ZHOU Yu-xiang. The production and nutrition analyses of mixed fodder fermented from corncob [J]. Nutrition and Feedstuffs, 2019, 55(6): 96–99. (in Chinese)
CUI You-zhi, DU Li-ping, MA Li-juan, SONG Pan, JIANG Feng-chao, MA Qing, XIAO Dong-guang. Optimization of 2,3-butanediol production using simultaneous saccharification and fermentation from corncob after delignification by oxidant [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2016, 42(10): 8–13. (in Chinese)
LI Yong-lian, LIU Wen-feng, YANG Yuan-e. Research on enzymatic degradation of corncob for produce bio-ethanol [J]. Journal of Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University, 2014(7): 47–51. (in Chinese)
TIAN Ya-hong, CHANG Li-xin, WANG Li-ping, XIAO Xiao-wa. Study on ethanol fermentation of corn straw, corncob [J]. Food Research and Development, 2014, 35(3): 47–50. (in Chinese)
LIU Bin, LIAN Zhan, LIU Zhong-yang, ZHAO Rong-wen, YANG Li, ZHANG Xiu-shuang, TAN Li-ping, LIU Tong-jun. Optimization of saccharification and fermentation technology of corncob to ethanol by alkaline pretreatment [J]. China Brewing, 2019, 38(5): 127–130. (in Chinese)
JIAO Kai-lin. Optimization of medium for mulberries fermented low alcohol beverages using minitab [J]. The Food Industry, 2015, 36(10): 90–92. (in Chinese)
LU Bu-shi, LI Xin-she, DAI Yuan-yuan, YIN Hai-yan, XIE Hong. Research on enzymatic degradation of corncob to produce low alcohol drink [J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology, 2019(9): 41–45. (in Chinese)
PI Shuang-shuang, WANG Jing-yi, CHEN Ya-shu, HU Kai, XIE Bi-jun, SUN Zhi-da. Study on the extraction, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of the soluble dietary fiber from black glutinous croncob [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(11): 219–231. (in Chinese)
ACOSTA-ESTRADA B A, VILLELA-CASTREJ N J, PEREZ-CARRILLO E, G MEZ-SNCHEZ C E, GUTI RREZ-URIBE J A. Effects of solid-state fungi fermentation on phenolic content, antioxidant properties and fiber composition of lime cooked maize by-product (nejayote) [J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2019, 90: 102837. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2019.102837.
YANG J, XIAO A, WANG C. Novel development and characterisation of dietary fibre from yellow soybean hulls [J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 161: 367–375.
RODRÍGUEZ R, JIMÉNEZ A, FERNÁNDEZ-BOLAÑOS J, GUILLÉN R, HEREDIA A. Dietary fibre from vegetable products as source of functional ingredients [J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2006, 17: 3–15.
HUANG L, ZHANG X, XU M, AN S, LI C, HUANG C, CHAI K, WANG S, LIU Y. Dietary fibres from cassava residue: Physicochemical and enzymatic improvement, structure and physical properties [J]. AIP Advances, 2018, 8: 105035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5054639.
HOU Li-fen, SUN Xiang-yang, DING Chang-he. Effects of different pretreatment solution properties and micro structure of corn cob enzyme [J]. The Food Industry, 2015, 36(2): 32–35. (in Chinese)
YANG Pei-zhou, JIANG Shao-tong, ZHENG Zhi, LUO Shui-zhong. Saccharification of fuel ethanol production with turgrass [J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2011, 27(Supp 1): 143–146. (in Chinese)
WANG Xiao-ming, SUN Yu-hui, ZHANG Huan, LIU Qi, DONG Xiao-ying, CAO Yan-xin, SHAO Li-jie, ZHANG Da-lei, KOU Wei. Studies on the conditions of solid-state fermentation for cellulase production by Trichoderma viride and cellulase immobilization [J]. Acta Agriculture Zhejiangensis, 2014, 26(1): 186–193. (in Chinese)
LV Li-shuang. Preparation and antioxidation mechanism of stilibene glycoside from polygonum multiflorum thunb [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2006. (in Chinese)
SUN Yuan-lin, BAI Yu-ren, WANG Xiao-wen, ZHOU Su-mei. Optimization of enzymatic preparation conditions of feruloylated oligosaccharides from corn cob [J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39(20): 112–117. (in Chinese)
PANG Jian-guang, CHEN Xue-qiao, ZHANG Ming-xia, ZHU Zheng. Ethanol production from corncobs by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation after pretreatment with dilute acid enhanced by microwave [J]. Food Industry, 2016, 37(6): 6–9. (in Chinese)
ZHAO Cong-cong, YANG Jun-yan, LI Ze-tian, CHEN Ji-ke, LI Hong-qin, WU Ning, NING Yi. Traditional fermentation of Luoping yellow ginger and glutinous rice health wine [J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39(23): 87–91. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(17A192) supported by the Education Department of Hunan Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xs., Lu, Bs., Wang, J. et al. Brewing of low-alcoholic drink from corncobs via yeast-cellulase synchronous fermentation process. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 3008–3016 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4232-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4232-2