Abstract
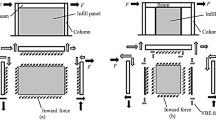
In spite of the good performance of the steel plate shear wall (SPSW) in recent earthquakes and experimental studies, the need for huge columns to surround the infill plate is a major shortcoming of the system. This shortcoming can be resolved by using semi-supported SPSW. The semi-supported SPSW has secondary columns that prevent the transfer of stress from the infill plate to the main columns. In spite of extensive experimental and numerical investigations on SPSWs, there are many ambiguities regarding the behavior of the semi-supported SPSW. Although stress in the columns is reduced, incomplete diagonal tension field action is formed in the infill plate that creates new problems. In this paper, a new type of semi-supported SPSW is presented in which the steel plate and the secondary columns are angled. The creation of the angle of the plate and the secondary column makes it possible to use the full capacity of the steel plate as well as the capacity of the secondary columns. Numerical results showed that the wall with a 60° angle has a favorable performance relative to the semi-supported wall. Moreover, with the 60° angle, stiffness, strength and energy absorption is increased. The angle of the secondary columns has little effect on the non-elastic stiffness. Nevertheless, using a wall with an angle of more than 90° can neutralize the wall’s behavior relative to conventional walls. Therefore, the wall with a 60° angle as an optimal angle is recommended.
摘要
最近的地震和实验研究表明钢板剪力墙(SPSW)的性能良好,但该系统的一个主要缺点是需要巨 大的柱子来包围填充板,而利用半支撑SPSW 可以解决这一不足。半支撑SPSW 有二级柱,可防止应 力从填充板转移到主柱。尽管对SPSW 进行了大量的实验和数值研究,但关于半支撑SPSW 的行为仍 存在许多争议。虽然柱内的应力减小了,但填充板内形成了不完全的对角张力场作用,从而产生了新 的问题。本文提出了一种新型的半支撑式钢结构,钢板和次柱之间形成一个夹角,使钢板的全部承载 力和次柱的承载力得以利用。数值模拟结果表明,与半支撑墙体相比,60°角的墙体具有良好的性能。 此外,当夹角为60°时,刚度、强度和能量吸收都有所增加。二次柱的角度对非弹性刚度影响不大。 然而,若使用角度大于90°的墙将抵消相对于传统墙的优势。因此,推荐60°为墙体的最佳角度。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KAHRAMAN A. Effect of axial vibrations on the dynamics of a helical gear pair [J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 1993, 115(1): 33–39.
BROUJERDIAN V, GHAMARI A, GHADAMI A. An investigation into crack and its growth on the seismic behavior of steel shear walls [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2016, 101: 205–212.
BROUJERDIAN V, SHAYANFAR M A, GHAMARI A. Corner crack effect on the seismic behavior of steel plate shear wall system [J]. Civil Engineering Infrastructures Journal, 2017, 50 (2): 311–332.
HATAMI F, GHAMARI A, RAHAI A. Investigating the properties of steel shear walls reinforced with carbon fiber polymers (CFRP) [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2012, 70: 36–42.
LANHUI G, RONGB Q, QUC B, LIUD J. Testing of steel plate shear walls with composite columns and infill plates connected to beams only [J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 136: 165–179.
WANG P, XUE Z, XIAO S. Seismic behavior of self-buckling-restrained steel plate shear wall made by two incline-slotted infill plates [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 133: 47–64.
LV Yang, LI Zhong-xian, LU Guo-xing. Shear capacity prediction of steel plate shear walls with precompression from columns [J]. The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings, 2017, 26, e1375.
JIANG L, ZHENG H, HU Y. Experimental seismic performance of steel- and composite steel-panel wall strengthened steel frames [J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 17: 520–524.
OZCELIK Y, CLAYTON P M. Seismic design and performance of SPSWS with beam-connected web plates [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2018, 142: 55–67.
WEI M W, LIEW J Y R, YONG D, FU X Y. Experimental and numerical investigation of novel partially connected steel plate shear walls [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 132: 1–15.
SHEKASTEHBAND B, AZARAXSH A, SHOWKATI H. Experimental and numerical study on seismic behavior of LYS and HYS steel plate shear walls connected to frame beams only [J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 1: 154–168.
ZHOU Y, LU X, DONG Y. Seismic behavior of composite shear walls with multi-embedded steel sections, Part I: experiment [J]. The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings, 2010, 19(6): 618–636.
CLAYTONA P, BERMANB J, LOWESB L. Seismic performance of self-centering steel plate shear walls with beam-only-connected web plates [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2015, 106: 198–208.
KURATA M, LEON R T, ROCHES R D, NAKASHIMA M. Steel plate shear wall with tension-bracing for seismic rehabilitation of steel frames [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2012, 71: 92–103.
HATAMI F, GHAMARI A, HATAMI F. Effect of fiber angle on LYP steel shear walls behavior [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21: 768–774.
CHEN S J, JHANG C H. Cyclic behavior of low yield point steel shear walls [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2006, 44: 730–738.
SABELLI R, BRUNEAU M. Design Guide 20: Steel Plate Shear Walls [M]. American Institute of Steel Structures, 2006.
JAHANPOUR A, MOHARRAMI H. Evaluation of behavior of the secondary columns in semi-supported steel shear walls [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2015, 93: 94–101.
GUO L, RONG Q, MA X, ZHANG S. Behavior of steel plate shear wall connected to frame beams only [J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2011, 11: 467–479.
LI Bei-bei, WANG Jing-feng, LU Yong, ZHANG Zeng-de, WANG Jia-xin. Seismic response tests and analytical assessment of blind bolted assembly CFST frames with beam-connected SPSWs [J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 178: 343–360.
MOHARRAMI H, HABIBNEJAD KORAYEM A. Advantages of thin steel shear wall for retrofitting of steel structures [J]. Journal of Steel Structures: In Persian, 2016, 4: 1–13.
SHEKASTEHBAND B, AZARAXSH A, SHOWKATI H. Experimental and numerical study on seismic behavior of LYS and HYS steel plate shear walls connected to frame beams only [J]. Achieves of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 17: 154–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghamari, A., Akbarpour, A. & Ghanbari, A. Improving behavior of semi-supported steel plate shear walls. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2891–2905 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4222-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4222-4