Abstract
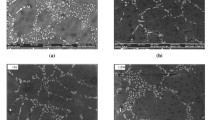
Copper alloyed with various compositions of nickel and tin were cast into molds under argon atmosphere. The cast rods were homogenized, solution heat treated, followed by aging for different time duration. The specimens were characterized for microstructure and tested for microhardness and wear rate. A hybrid model with a linear function and radial basis function was developed to analyze the influence of nickel, tin, and aging time on the microhardness and tribological behavior of copper-nickel-sin alloy system. The results indicate that increase in the composition of nickel and tin increases the microhardness and decreases the wear rate of the alloy. The increase in the concentration of nickel and tin decreases the peak aging time of the alloy system.
摘要
将含有不同成分镍和锡的铜合金在氩气气氛下进行模铸。对铸棒进行均匀化、固溶热处理后进 行不同时间时效处理。对试样进行了显微组织表征,并对试样的显微硬度和磨损率进行了测试。建立 了线性函数和径向基函数的混合模型,分析了镍、锡和时效时间对Cu-Ni-Sn 合金显微硬度和摩擦学 行为的影响。结果表明,镍、锡成分的增加使合金基体的显微硬度增加,磨损率降低。镍和锡浓度的 增加降低了合金体系的峰值时效时间。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ILANGOVAN S, SELLAMUTHU R. Measurement of the variation of mechanical properties with aging temperatures for sand cast Cu-5Ni-5Sn alloy [J]. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2016, 11(11): 1609–1619.
DITCHEK B, SCHWARTZ L H. Diffraction study of spinodal decomposition in Cu-10 wt%Ni-6 wt% Sn [J]. Acta Metall, 1980, 28 (6): 807–822.
SCHWARTZ L H, MAHAJAN S, PLEWES J T. Spinodal decomposition in a Cu-9 wt% Ni-6 wt% Sn alloy [J]. Acta Metall, 1974, 22(5): 601–609.
SCHWARTZ L H, PLEWES J T. Spinodal decomposition in Cu-9wt% Ni-6wt% Sn—II. A critical examination of mechanical strength of spinodal alloys [J]. Acta Metall, 1974, 22(7): 911–921.
BABURAJ E G, KULKARNI U D, MENON E S K, KRISHNAN R. Initial stages of decomposition in Cu-9Ni-6Sn [J]. J Appl Crystallogr, 1979, 12(5): 476–480.
KATO M, MORI T, SCHWARTZ L H. Hardening by spinodal modulated structure [J]. Acta Metall, 1980, 28(3): 285–290.
SINGH J B, CAI W, BELLON P. Dry sliding of Cu–15 wt%Ni–8 wt%Sn bronze: Wear behaviour and microstructures [J]. Wear, 2007, 263(1): 830–841.
ILANGOVAN S, VAIRA VIGNESH R, PADMANABAN R, GOKULACHANDRAN J. Comparison of statistical and soft computing models for predicting hardness and wear rate of Cu-Ni-Sn alloy [C]// Progress in Computing, Analytics and Networking. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 2018: 559–571.
DIÁNEZ M, DONOSO E, SAYAGUÉS M, PEREJÓN A, SÁNCHEZ-JIMÉNEZ P, PÉREZ-MAQUEDA L, CRIADO J. The calorimetric analysis as a tool for studying the aging hardening mechanism of a Cu-10 wt% Ni-5.5 wt% Sn alloy [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 688(1): 288–294.
DONOSO E, DIÁNEZ M, PEREJÓN A, SÁNCHEZJIMÉNEZ P, PÉREZ-MAQUEDA L, SAYAGUÉS M, CRIADO J. Microcalorimetry: A powerful tool for quantitative analysis of aging hardening response of Cu-Ni-Sn alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 694(1): 710–714.
ILANGOVAN S, SELLAMUTHU R. An investigation of the effect of Ni content and hardness on the wear behaviour of sand cast Cu–Ni–Sn alloys [J]. Int J Microstruct Mater Prop, 2012, 7(4): 316–328.
ZHANG S, JIANG B, DING W. Dry sliding wear of Cu–15Ni–8Sn alloy [J]. Tribol Int, 2010, 43(1): 64–68.
LEI Q, LI Z, GAO Y, PENG X, DERBY B. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a high strength Cu-Ni-Si alloy treated by combined aging processes [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 695(1): 2413–2423.
WANG Y, ZHANG L, XIAO J, CHEN W, FENG C, GAN X, ZHOU K. The tribo-corrosion behavior of Cu-9 wt% Ni-6 wt% Sn alloy [J]. Tribol Int, 2016, 94(1): 260–268.
RAMALINGAM V V, RAMASAMY P. Modelling corrosion behavior of friction stir processed aluminium alloy 5083 using polynomial: Radial basis function [J]. Trans Indian Inst Met, 2017, 70(10): 2575–2589.
VAIRA VIGNESH R, PADMANABAN R. Influence of friction stir processing parameters on the wear resistance of aluminium alloy AA5083 [J]. Mater Today: Proc, 2018, 5(2): 7437–7446.
ZHAO D M, DONG Q M, LIU P, KANG B X, HUANG J L, JIN Z H. Structure and strength of the age hardened Cu–Ni–Si alloy [J]. Mater Chem Phys, 2003, 79(1): 81–86.
ZHANG S Z, JIANG B H, DING W J. Wear of Cu–15Ni–8Sn spinodal alloy [J]. Wear, 2008, 264(3): 199–203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilangovan, S., Vaira Vignesh, R., Padmanaban, R. et al. Effect of composition and aging time on hardness and wear behavior of Cu-Ni-Sn spinodal alloy. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2634–2642 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4200-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4200-x