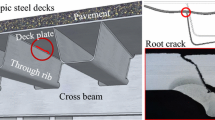
Abstract
To evaluate the effect of treating long cracks with the impact crack-closure retrofit (ICR) technique, three rib-to-deck welded specimens with a crack length of about 100 mm were tested. The metallographic structure, crack section, crack propagation life, and stress variation were analyzed. Finite-element models were also developed, and some optimal values of certain parameters are suggested according to the simulated results. The results show that new crack sources are generated on both sides of the ICR-treated region because of the stress distribution. The fatigue lives of cracked specimens with long cracks are significantly improved by the technique. Considerable residual compressive stress is also induced, and so it is suggested that the optimal impact angle to be applied to real bridges should be 70°. The stress at the weld root is distributed uniformly with the crack closed, and the optimal crack-closure depth is 4 mm. To evaluate the effect of different crack-closure depths in tests, it is recommended that a hot-spot stress method which is extrapolated by three reference points should be adopted.
摘要
为分析气动冲击技术对长裂纹的修复效果, 选取了三个裂纹长度均为100 mm 以上的顶板与U 肋试件, 开展了气动冲击修复试验及修复后疲劳加载, 并分析了微观结构变化、裂纹断面、裂纹扩展 速率、应力幅等。同时, 建立了相关有限元模型, 基于分析结果提出了部分关键的技术参数。研究表 明, 由于锤击后的应力重分布, 在锤击区域的两侧会产生新的疲劳源区, 但具有长裂纹试件的疲劳寿 命依然得到了显著的提高。气动冲击可产生可观的残余压应力, 为取得最佳效果, 气动冲击角度建议 为70°。裂纹闭合后焊根应力呈不均匀分布, 最佳的闭合深度为 4 mm。在裂纹闭合深度影响的试验研 究中, 建议采用三点外推得到的热点应力作为评判指标。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FU Zhong-qiu, JI Bo-hai, ZHANG Cheng-yi, LI Di. Experimental study on the fatigue performance of roof and U-rib welds of orthotropic steel bridge decks [J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017 (3): 1–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1725-0.
GUO Tong, LI Ai-qun, WANG Hao. Influence of ambient temperature on the fatigue damage of welded bridge decks [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2008, 30(6): 1092–1102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2007.08.004.
KAINUMA S, JEONG Y S, YANG Mu-ye, INOKUCHI S. Welding residual stress in roots between deck plate and U-rib in orthotropic steel decks [J]. Measurement, 2016, 92: 475–482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.06.040.
GE Han-bin, KANG Lan, TSUMURA Y. Extremely low-cycle fatigue tests of thick-walled steel bridge piers [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2013, 18(9): 858–870. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000429.
JI Bo-hai, LIU Rong, CHEN Ce, MAENO H, CHEN Xiong-fei. Evaluation on root-deck fatigue of orthotropic steel bridge deck [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel J. Cent. South Univ. (2019) 26: 2554-2568 2568 Research, 2013, 90(5): 174–183. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2013.07.036.
LI Ming, SUZUKI Y, WANG Hong-chang, AOKI Y, ADACHI Y, SUGIURA K. Experimental study of asphalt surfacing influence on rib-to-deck joints considering temperature and dynamic effects [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(11): 04016077. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000936.
ISHIKAWA T, YAMADA K, KAKIICHI T, LI Hui. Extending fatigue life of cracked out-of-plane gusset by ICR treatment [J]. JSCE Journal of Structural and Earthquake Engineering, 2010, 66(2): 264–272. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2208/jsceseee.28.21s.
FISHER J W, HAUSAMMANN H, SULLIVAN M D, PENSE A W. Detection and repair of fatigue damage in welded highway bridges [R]. Washington DC: NCHRP Report 206, 1979. http://onlinepubs.trb.org/Onlinepubs/nchrp/nchrp_rpt_206.pdf.
ISHIKAWA T, SHIMIZU M, TOMO H, KAWANO H, YAMADA K. Effect of compression overload on fatigue strength improved by ICR treatment [J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2013, 13(1): 175–181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-013-1016-7.
FISHER J W, ROY S. Fatigue damage in steel bridges and extending their life [J]. Advanced Steel Construction, 2015, 11(3): 250–268. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18057/IJASC.2015.11.3.1.
FU Zhong-qiu, JI Bo-hai, XIE Shu-hui, LIU Tian-jia. Crack stop holes in steel bridge decks: Drilling method and effects [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(10): 2372–2381. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3649-8.
FU Zhong-qiu, WANG Qiu-dong, JI Bo-hai, YUANZHOU Zhi-yuan. Rewelding repair effects of fatigue cracks in steel bridge deck welds [J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2017, 31(6): 04017094. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0001083.
YUANZHOU Zhi-yuan, JI Bo-hai, FU Zhong-qiu, GE Han-bin. Fatigue performance of cracked rib-deck welded joint retrofitted by ICR technique [J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2016, 16(3): 735–742. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-015-0089-x.
YAMADA K, ISHIKAWA T, KAKIICHI T. Rehabilitation and improvement of fatigue life of welded joints by ICR Treatment [J]. Advanced Steel Construction, 2015, 11(3): 294–304. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18057/IJASC.2015.11.3.4.
YAMADA K, ISHIKAWA T, KAKIICHI T. Extending fatigue durability by closing crack surface [J]. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers Ser A1, 2009, 65(4): 961–965. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2208/jsceja.65.961. (in Japanese)
YUANZHOU Zhi-yuan, JI Bo-hai, FU Zhong-qiu, GE Han-bin. Local stress variation in welded joints by ICR treatment [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 120: 45–51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.12.001.
YA S, YAMADA K. Fatigue durability evaluation of trough to deck plate welded joint of orthotropic steel deck [J]. Structural Engineering/earthquake Engineering, 2008, 64(3): 603–616. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2208/jsceja.64.603.
GB/T 8110. Welding electrodes and rods for gas shielding arc welding of carbon and low alloy steel [S]. 2008. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/346d4c0de418964bcf84b9d528ea81c758f52e9e.html. (in Chinese)
FU Zhong-qiu, JI Bo-hai, ZHANG Cheng-yi, WANG Qiu-dong. Fatigue performance of roof and U-rib weld of orthotropic steel bridge deck with different penetration rates [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 22(6): 04017016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001036.
YUANZHOU Zhi-yuan, JI Bo-hai, FU Zhong-qiu, SUN Tong. Retarding effects on crack propagation by closing crack surface using ICR treatment [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2018, 143: 11–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.12.015.
KINOSHITA K, BANNO Y, ONO Y, YAMADA S, HANDA M. Fatigue strength improvement and fatigue crack closure by portable pneumatic needle-peening treatment on welded joints [J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2019, 19(3): 693–703. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-018-0153-4.
HOBBACHER A. Recommendations for fatigue design of welded joints and components [M]. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23757-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51478163, 51678216) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017Y09) supported by the Transport Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Qd., Ji, Bh., Fu, Zq. et al. Effect of crack-closure treatment on fatigue durability of cracked rib-to-deck welded joints in steel bridge decks. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2554–2568 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4194-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4194-4
Key words
- steel bridge deck
- fatigue durability
- impact crack-closure retrofit technique
- fatigue life
- stress distribution