Abstract
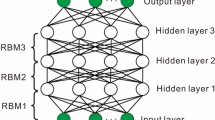
To improve magnetotelluric (MT) nonlinear inversion accuracy and stabilitythis work introduces the deep belief network (DBN) algorithm. Firstlya network frame is set up for training in different 2D MT models. The network inputs are the apparent resistivities of known modelsand the outputs are the model parameters. The optimal network structure is achieved by determining the numbers of hidden layers and network nodes. Secondlythe learning process of the DBN is implemented to obtain the optimal solution of network connection weights for known geoelectric models. Finallythe trained DBN is verified through inversion testsin which the network inputs are the apparent resistivities of unknown modelsand the outputs are the corresponding model parameters. The experiment results show that the DBN can make full use of the global searching capability of the restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) unsupervised learning and the local optimization of the back propagation (BP) neural network supervised learning. Comparing to the traditional neural network inversionthe calculation accuracy and stability of the DBN for MT data inversion are improved significantly. And the tests on synthetic data reveal that this method can be applied to MT data inversion and achieve good results compared with the least-square regularization inversion.
摘要
为进一步提高大地电磁非线性反演的准确度和稳定性, 本文将深度置信网络引入大地电磁反演。 首先, 针对建立的大地电磁二维地电模型数据库设计深度置信网络结构, 对网络隐含层数和各层节点 数进行优选, 网络输入为已知地电模型的视电阻率参数, 输出为该地电模型参数; 然后, 根据优选的 网络参数进行深度置信网络学习训练, 计算出多种地电模型网络连接权值和阈值的最优解; 最后, 将 网络最优连接权值和阈值对未知模型进行反演测试, 网络输入为测试地电模型的视电阻率参数, 输出 为该地电模型电阻率参数。模型实验表明: 相比传统的 BP 神经网络算法, 深度置信网络算法具有全 局寻优的能力, 在保证较快收敛效率的同时, 明显提高了网络收敛成功率和稳定性, 在反演测试中能 够更加准确地逼近真实模型; 相比经典的最小二乘正则化反演法, 深度置信网络算法具有较好的泛化 性能和自学习能力, 反演效率更高, 反演效果更精确。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CONSTABLE S CPARKER R LCONSTABLE C G. Occam's inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from EM sounding data [J]. Geophysics198752(3): 289–300.
SMITH J TBOOKER J R. Rapid inversion of two and three dimensional magnetotelluric data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research199196: 3905–3922.
RODI WMACKIE R L. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion [J]. Geophysics200166(1): 174–187.
MONTAHAEI MOSKOOI B. Magnetotelluric inversion for azimuthally anisotropic resistivities employing artificial neural networks [J]. Acta Geophysica201462(1): 12–43.
LIU BLI S CNIE L CWANG JL XZHANG Q S. 3D resistivity inversion using an improved genetic algorithm based on control method of mutation direction [J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics201287: 1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.08.002.
DITTMER J KSZYMANSKI J E. The stochastic inversion of magnetics and resistivity data using the simulated annealing algorithm [J]. Geophysical Prospecting199543(3): 397–416.
HU Zu-zhiHE Zhan-xiangYANG Wen-caiHU Xiang-yun. Constrained inversion of magnetotelluric data with the artificial fish swarm optimization method [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics201558(7): 2578–2587DOI: https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20150732. (in Chinese)
LIU Jian-fengHU Wen-baoHU Xiang-yun. Inversion of 2-D magnetotelluric data by differential ant colony algorithm [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting201550(3): 548–555. (in Chinese)
SUJAN GRAVINESH C DNATHAN J DNAWIN R. Self-adaptive differential evolutionary extreme learning machines for longterm solar radiation prediction with remotely-sensed MODIS satellite and Reanalysis atmospheric products in solar-rich cities [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment2018212: 176–198. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.05.003.
WANG HeJIANG HuanWANG LiangXI Zhen-zhuZHANG Dao-jun. Magnetotelluric inversion using artificial neural network [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology201546(5): 1707–1714. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.05.019. (in Chinese)
JIANG Fei-boDONG LiDAI Qian-wei. Electrical resistivity imaging inversion: An ISFLA trained kernel principal component wavelet neural network approach [J]. Neural Networks2018104: 114–123. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.012.
HINTON G EOSINDERO STEH Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets [J]. Neural Computer200618(7): 1527–1554.
GOODFELLOW IBENGIO YCOURVILLE A. Deep learning [M]. Boston: MIT Press2016.
LECUN YBENGIO YHINTON G E. Deep learning [J]. Nature2015521: 436–444. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539.
CHENG Xiang-yiLIU Hua-pingXU Xin-yingSUN Fu-chun. Denoising deep extreme learning machine for sparse representation [J]. Memetic Comp20179: 199–212. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-016-0185-2.
LEONARDO BCLAUDIA CLUCIANO FGIORGIO M. Integrating articulatory data in deep neural network-based acoustic modeling [J]. Computer Speech and Language201636: 173–195. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2015.05.005.
ZEYNETTIN AALFIIA GASSAF HDANIEL L RBRADLEY J E. Deep learning for brain MRI segmentation: State of the art and future directions [J]. J Digit Imaging201730: 449–459. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-9983-4.
KASIPRASAD MPANYAM N SMALOJI S. A novel adaptive fractional deep belief networks for speaker emotion recognition [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal201756: 485–497. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2016.09.002.
TANG Bin-binLIU XiaoLEI JieSONG Ming-liTAO Da-pengSUN Shui-faDONG Fang-min. Deep Chart: Combining deep convolutional networks and deep belief networks in chart classification [J]. Signal Processing2016124: 156–161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.09.027.
DENG LeiFU Shan-shanZHANG Ru-xia. Application of deep belief network in polarimetric SAR image classification [J]. Journal of Image and Graphics201621(7): 933–941. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11834/jig.20160711. (in Chinese)
LALOY EHERAULT RLEE JJACQUES DLINDE N. Inversion using a new low-dimensional representation of complex binary geological media based on a deep neural network [J]. Advances in Water Resources2017110: 387–405. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.09.029.
ZHU Lin-qiZHANG ChongWei YANGZhou Xue-qingHUANG Yu-yangZHANG Chao-mo. Inversion of the permeability of a tight gas reservoir with the combination of a deep Boltzmann kernel extreme learning machine and nuclear magnetic resonance logging transverse relaxation time spectrum data [J]. Interpretation20175(3): T341–T350. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/INT-2016-0188.1.
CAO Jun-xingWU Shi-kai. Deep Learning: Chance and challenge for deep gas reservoir identification [C]//International Geophysical Conference. QingdaoChina2017: 711–712. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/IGC2017-180.
MAURICIO A PJOSPH JAMIR ATAYLOR D. Deep-learning tomography [J]. The Leading Edge201837(1): 58–66. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/tle37010058.1.
QIAN FengYIN MiaoLIU Xiao-yangWANG Yao-junLU CaiHU Guang-min. Unsupervised seismic facies analysis via deep convolutional auto encoders [J]. Geophysics201883(3): A39–A43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2017-0524.1.
LAROCHELLE HBENGIO YLOURADOUR JLAMBLIN P. Exploring strategies for training deep neural networks [J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research200910(1): 1–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(41304090) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2016YFC0303104) supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China; Project(DY135-S1-1-07) supported by Ocean 13th Five-Year International Marine Resources Survey and Development of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Liu, W., Xi, Zz. et al. Nonlinear inversion for magnetotelluric sounding based on deep belief network. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2482–2494 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4188-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4188-2