Abstract
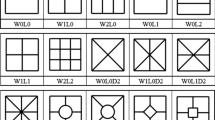
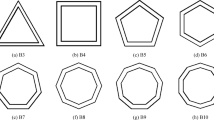
In this paper, crashworthiness performance of multi-cell conical tubes with new sectional configuration design (i.e. square, hexagonal, octagonal, decagon and circular) has been evaluated under axial and three different oblique loads. The same weight conical tubes were comparatively studied using an experimentally validated finite element model generated in LS-DYNA. Complex proportional assessment (COPRAS) method was then employed to select the most efficient tube using two conflicting criteria, namely peak collapse force (PCF) and energy absorption (EA). From the COPRAS calculations, the multi-cell conical tube with decagonal cross-section (MCDT) showed the best crashworthiness performance. Furthermore, the effects of possible number of inside ribs on the crashworthiness of the decagonal conical tubes were also evaluated, and the results displayed that the tubes performed better as the number of ribs increased. Finally, parameters (the cone angle, θ, and ratio of the internal tube size to the external one, S) of MCDT were optimized by adopting artificial neural networks (ANN) and genetic algorithm (GA) techniques. Based on the multi-objective optimization results, the optimum dimension parameters were found to be θ=7.9°, S=0.46 and θ=8°, S=0.74 from the minimum distance selection (MDS) and COPRAS methods, respectively.
摘要
本文对采用新型截面结构设计(正方形、六边形、八边形、十边形和圆形)的多元锥管在轴向和 三种不同斜向载荷作用下的耐撞性能进行了评价。利用 LS-DYNA 建立的有限元模型对相同重量的不 同结构的锥管进行了对比研究。采用了复比例评估法(COPRAS), 利用峰值临界力(PCF)和能量吸收 (EA)两个相互矛盾的准则来选择最优管结构。从 COPRAS 计算结果可以看出, 具有十边形截面的多元 锥形管(MCDT)具有最优耐撞性能。评价了可能的内肋数对十边形截面锥形管耐撞性的影响, 结果表 明, 随着内肋数的增加, 十边形截面锥形管的耐撞性能得到增强。采用了人工神经网络(ANN)和遗传 算法(GA)对MCDT 的参数(锥角θ 和内外管尺寸比S)进行了优化。基于多目标优化的结果, 利用最小 距离选择法(MDS)和COPRAS 方法得到的最优尺寸分别是θ=7.9°, S=0.46 和θ=8°, S=0.74。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HOSSEINI-TEHRANI P, PIRMOHAMMAD S. Collapse study of thin-walled polygonal section columns subjected to oblique loads [J]. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part D: J Automobile Eng, 2007, 221(7): 801–810.
ELMARAKBI A, LONG Y X, MACINTYRE J. Crash analysis and energy absorption characteristics of S-shaped longitudinal members [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2013, 68: 65–74.
ZOU X, GAO G, ZHANG J, ZHOU X, CHEN W, GUAN W. A comparative crashworthiness analysis of multi-cell polygonal tubes under axial and oblique loads [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(9): 2198–2208.
HOSSEINI-TEHRANI P, NIKAHD M. Effects of ribs on S-frame crashworthiness [J]. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part D: J Automobile Eng, 2006, 220: 1679–1689.
HOSSEINI-TEHRANI P, NIKAHD M. Two materials S-frame representation for improving crashworthiness and lightening [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2006, 44: 407–414.
EYVAZIAN A, MOZAFARI H, HAMOUDA A M. Experimental study of corrugated metal-composite tubes under axial loading [J]. Procedia Eng, 2017, 173: 1314–1321.
MARZBANRAD J, MASHADI B, AFKAR A, PAHLAVANI M. Dynamic rupture and crushing of an extruded tube using artificial neural network (ANN) approximation method [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(4): 869–879.
PIRMOHAMMAD S, ESMAEILI-MARZDASHTI S. Crashworthiness optimization of combined straight-tapered tubes using genetic algorithm and neural networks [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2018, 127: 318–332.
OLIVEIRA D A, WORSWICK M J, GRANTAB R, WILLIAMS B W, MAYER R. Effect of forming process variables on the crashworthiness of aluminum alloy tubes [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2006, 32(5): 826–846.
HANSSEN A G, LANGSETH M, HOPPERSTAD O S. Static and dynamic crushing of square aluminium extrusions with aluminium foam filler [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2000, 24(4): 347–383.
HANSSEN A G, LANGSETH M, HOPPERSTAD O S. Static crushing of square aluminium extrusions with aluminium foam filler [J]. Int J Mech Sci, 1999, 41(8): 967–993.
SEITZBERGER M, RAMMERSTORFER F G, DEGISCHER H P, GRADINGER R. Crushing of axially compressed steel tubes filled with aluminium foam [J]. Acta Mech, 1997, 125(1–4): 93–105.
SEITZBERGER M, RAMMERSTORFER F G, GRADINGER R, DEGISCHER H, BLAIMSCHEIN M, WALCH C. Experimental studies on the quasi-static axial crushing of steel columns filled with aluminium foam [J]. Int J Solids Struct, 2000, 37: 4125–4147.
SONG J, GUO F. A comparative study on the windowed and multi-cell square tubes under axial and oblique loading [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2013, 66: 9–14.
GHAMARIAN A, ZAREI H R, ABADI M T. Experimental and numerical crashworthiness investigation of empty and foam-filled end-capped conical tubes [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2011, 49: 1312–1319.
QIU N, GAO Y, FANG J, FENG Z, SUN G, LI Q. Theoretical prediction and optimization of multi-cell hexagonal tubes under axial crashing [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2016, 102: 111–121.
NAJAFI A, RAIS-ROHANI M. Influence of cross-sectional geometry on crush characteristics of multi-cell prismatic columns [C]// 49th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. 2008.
QIU N, GAO Y, FANG J, FENG Z, SUN G, LI Q. Crashworthiness analysis and design of multi-cell hexagonal columns under multiple loading cases [J]. Finite Elem Anal Des, 2015, 104: 89–101.
SONG X G, SUN G Y, LI G Y, GAO W Z, LI Q. Crashworthiness optimization of foam-filled tapered thin-walled structure using multiple surrogate models [J]. Struct Multidisc Optimiz, 2013, 47(2): 221–231.
WU S, ZHENG G, SUN G, LIU Q, LI G. On design of multi-cell thin-walled structures for crashworthiness [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2016, 88: 102–117.
SUN G, LIU T, FANG J, STEVEN G P, LI Q. Configurational optimization of multi-cell topologies for multiple oblique loads [J]. Struct Multidisc Optimiz, 2018, 57(2): 469–488.
ZHANG X, CHENG G. A comparative study of energy absorption characteristics of foam-filled and multi-cell square columns [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2007, 34: 1739–1752.
ZHANG X, CHENG G, WANG B, ZHANG H. Optimum design for energy absorption of bitubal hexagonal columns with honeycomb core [J]. Int J Crashworthiness, 2008, 13(1): 99–107.
HOSSEINI-TEHRANI P, PIRMOHAMMAD S. Study on crashworthiness characteristics of several concentric thin wall tubes [C]// ASME 2010 10th Biennial Conference on Engineering Systems Design and Analysis. Istanbul, Turkey, 2010, 3: 1–8.
ZHANG Y, SUN G, LI G, LUO Z, LI Q. Optimization of foam-filled bitubal structures for crashworthiness criteria [J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 38: 99–109.
FANG J, GAO Y, SUN G, ZHANG Y, LI Q. Crashworthiness design of foam-filled bitubal structures with uncertainty [J]. Int J Non-Linear Mech, 2014, 67: 120–132.
DJAMALUDDIN F, ABDULLAH S, ARIFFIN A.K, NOPIAH Z M. Non-linear finite element analysis of bitubal circular tubes for progressive and bending collapses [J]. Int J Mech Sci, 2015, 99: 228–236.
SHARIFI S, SHAKERI M, EBRAHIMI H, BODAGHI M. Experimental investigation of bitubal circular energy absorbers under quasi-static axial load [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2015, 89: 42–53.
LI Jian, GAO Guang-jun, ZOU Xiang, GUAN Wei-yuan. Crushing analysis and multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of bitubular polygonal tubes with internal walls [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(11): 3040–3050.
AHMAD Z, THAMBIRATNAM D P. Crashing response of foam-filled conical tubes under quasi-static axial loading [J]. Materials & Design, 2009, 30(7): 2393–2403.
AHMAD Z, THAMBIRATNAM D P. Dynamic computer simulation and energy absorption of foam-filled conical tubes under axial impact loading [J]. Com put and Struct, 2009, 87(3,4): 186–197.
AHMAD Z, THAMBIRATNAM D P, TAN A C. Dynamic energy absorption characteristics of foam-filled conical tubes under oblique impact loading [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2010, 37(5): 475–488.
GHAMARIAN A, ZAREI H R, ABADI M T. Experimental and numerical crashworthiness investigation of empty and foam-filled end-capped conical tubes [J]. Int J Impact Eng, 2011, 49(10): 1312–1319.
HOU S, HAN X, SUN G, LONG S, LI W, YANG X, LI Q. Multiobjective optimization for tapered circular tubes [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2011, 49(7): 855–863.
PIRMOHAMMAD S, EKBATAN M H, ESMAEILI-MARZDASHTI S. Crashworthiness of double-cell conical tubes with different cross sections subjected to dynamic axial and oblique loads [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(3): 632–645.
QI C, YANG S, DONG F. Crushing analysis and multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of tapered square tubes under oblique impact loading [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2012, 59: 103–119.
HOSSEINI-TEHRANI P, PIRMOHAMMAD S, GOLMOHAMMADI M. Study on the collapse of tapered tubes subjected to oblique loads [J]. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part D: J Automobile Eng, 2008, 222(11): 2025–2039.
PIRMOHAMMAD S, ESMAEILI-MARZDASHTI S E. Crashing behavior of new designed multi-cell members subjected to axial and oblique quasi-static loads [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2016, 108: 291–304.
MOHSENIZADEH S, ALIPOUR R, SHOKRI RAD M, FAROKHI NEJAD A, AHMAD Z. Crashworthiness assessment of auxetic foam-filled tube under quasi-static axial loading [J]. Material & Design, 2015, 88: 258–268.
LI Z, ZHENG Z, YU J, GUO L. Crashworthiness of foam-filled thin-walled circular tubes under dynamic bending [J]. Material & Design, 2013, 52: 1058–1064.
ZAVADSKAS E K, KAKLAUSKAS A, TURSKIS Z, TAMOSAITIEN J. Selection of the effective dwelling house walls by applying attributes values determined at intervals [J]. J Civil Eng Manage, 2008, 14(2): 85–93.
ZAVADSKAS E K, TURSKIS Z, TAMOSAITIENE J, MARINA V. Multi criteria selection of project managers by applying grey criteria [J]. Technol Econ Dev Econ, 2008, 14(4): 462–477.
ZAVADSKAS E K, KAKLAUSKAS A, PELDSCHUS F, TURSKIS Z. Multi-attribute assessment of road design solutions by using the COPRAS method [J]. Bait J Road Bridg Eng, 2007, 2: 195–203.
ESMAEILI S, PIRMOHAMAD S, ESMAEILI S. Crashworthiness analysis of S-shaped structures under axial impact loading [J]. Lat Am J Solids Struct, 2017, 14(5): 743–764.
DEMUTH H, BEALE M, HAGAN M. Neural network tool box™ 6 user’s guide [M]. The Math Works, Inc, 2010.
RAFIAI H, JAFARI A. Artificial neural networks as a basis for new generation of rock failure criteria [J]. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci, 2011, 48(7): 1153–1159.
MAHDI E S, El-KADI H. Crashing behavior of laterally compressed composite elliptical tubes: Experiments and predictions using artificial neural networks [J]. Composite Struct, 2008, 83(4): 399–412.
MAHDEVARI S, TORABI S R, MONJEZI M. Application of artificial intelligence algorithms in predicting tunnel convergence to avoid TBM jamming phenomenon [J]. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci, 2012, 55: 33–44.
SCHALKOFF R J. Artificial neural networks [M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1997.
HAYKIN S. Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation [M]. Canada: Prentice Hall, 1994.
EBRAHIMABADI A, AZIMIPOUR M, BAHREINI A. Prediction of roadheaders’ performance using artificial neural network approaches (MLP and KOSFM) [J]. J Rock Mech Geo Eng, 2015, 7(5): 573–583.
QI C, YANG S, DONG F. Crushing analysis and multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of tapered square tubes under oblique impact loading [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2012, 59: 103–119.
PIRMOHAMMAD S, NIKKHAH H. Crashworthiness investigation of bitubal columns reinforced with several inside ribs under axial and oblique impact loads [J], proc Inst Mech Eng, Part D: JAuto Eng, 2018, 232(3): 367–383.
SALARI D, DANESHVAR N, AGHAZADEH F, KHATAEE A R. Application of artificial neural networks for modeling of the treatment of wastewater contaminated with methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) by UV/H2O2 process [J]. J Haz Mat, 2005, 125(1-3): 205–210.
NARIMAN-ZADEH N, DARVIZEH A, JAMALI A. Pareto optimization of energy absorption of square aluminum columns using multi-objective genetic algorithms [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Int J Eng Manuf, 2006, 220(2): 213–224.
ETGHANI M M, SHOJAEEFARD M H, KHALKHALI A, AKBARI M. A hybrid method of modified NSGA-II and TOPSIS to optimize performance and emissions of a diesel engine using biodiesel [J]. Applied Thermal Eng, 2013, 59(1, 2): 309–315.
KHALKHALI A, KHAKSHOURANIA S, NARIMAN-ZADEH N. A hybrid method of FEM, modified NSGAII and TOPSIS for structural optimization of sandwich panels with corrugated core [J]. J Sandwich Struct and Mat, 2014, 16(4): 398–417.
RAQUEL C R, NAVAL P C. An effective use of crowding distance in mu0lti-objective particles warm optimization [C]// Proceeding of the 7th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. 2005: 257–264.
LIU D, TAN K C, GOH C K, HO W K. A multi objective memetic algorithm based on particles warm optimization [J]. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, Part B: Cybern, 2007, 37(1): 42–50.
MELANIE M. An introduction to genetic algorithms [M]. London: MIT Press, 1999.
GREGORY J E. Foundations of genetic algorithms [M]. Rawlins: Kaufmann Publishers, 1991.
BARAKAT S, BANI-HANI K, TAHA M Q. Multi-objective reliability-based optimization of prestressed concrete beams [J]. Struct Safety, 2004, 26(3): 311–342.
ZHANG Y, SUN G, XU X, LI G, LI Q. Multiobjective crashworthiness optimization of hollow and conical tubes for multiple load cases [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2014, 82: 331–342.
LI G, ZHANG Z, SUN G, HUANG X, LI Q. Comparison of functionally-graded structures under multiple loading angles [J]. Thin-Walled Struct, 2015, 94: 334–347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirmohammad, S., Esmaeili-Marzdashti, S. Multi-objective optimization of multi-cell conical structures under dynamic loads. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2464–2481 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4187-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4187-3
Keywords
- crashworthiness
- multi-cell conical tube
- axial and oblique loads
- complex proportional assessment (COPRAS)
- multi-objective optimization