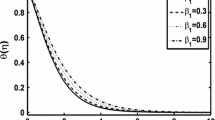
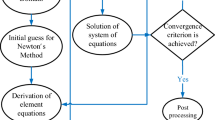
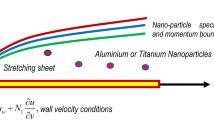
Abstract
In industrial applications involving metal and polymer sheets, the flow situation is strongly unsteady and the sheet temperature is a mixture of prescribed surface temperature and heat flux. Further, a proper choice of cooling liquid is also an important component of the analysis to achieve better outputs. In this paper, we numerically investigate Darcy-Forchheimer nanoliquid flows past an unsteady stretching surface by incorporating various effects, such as the Brownian and thermophoresis effects, Navier’s slip condition and convective thermal boundary conditions. To solve the governing equations, using suitable similarity transformations, the nonlinear ordinary differential equations are derived and the resulting coupled momentum and energy equations are numerically solved using the spectral relaxation method. Through the systematically numerical investigation, the important physical parameters of the present model are analyzed. We find that the presence of unsteadiness parameter has significant effects on velocity, temperature, concentration fields, the associated heat and mass transport rates. Also, an increase in inertia coefficient and porosity parameter causes an increase in the velocity at the boundary.
摘要
在金属和聚合物薄片的工业应用中, 流动情况非常不稳定, 并且薄片温度由设定的表面温度和 热通量共同决定。此外, 合理选择冷却液对实验结果也十分重要。本研究中, 结合了各种效应(如布 朗效应、热泳效应、Navier 滑动条件和对流边界条件), 对流过不稳定拉伸片表面的Darcy-Forchheimer 流体进行了数值分析。为了求解控制方程, 使用了适当的相似变换, 导出了非线性常微分方程, 并使 用谱松弛法对得到的耦合动量和能量方程进行了数值求解。通过系统的数值求解, 分析了现有模型中 的重要物理参数。发现不稳定参数的存在对速度、温度和浓度场以及相关的热量和质量传输速率具有 显着影响。同时, 增大惯性系数和孔隙率可加快边界处的速度。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHOI S, EASTMAN J A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles [J]. ASME-Publ Fed, 1995, 231: 99–106.
BUONGIORNO J. Convective transport in nanofluids [J]. J Heat Trans, 2006, 128(3): 240–250. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2150834.
KHAN W A, POP I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(11, 12): 2477–2483. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.01.032.
NIELD D A, KUZNETSOV A V. The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2009, 52(25, 26): 5792–5795. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.07.024.
MUSTAFA M, HAYAT T, POP I, ASGHAR S, OBAIDAT S. Stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid towards a stretching sheet [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 54(25, 26): 5588–5594. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.07.021.
BACHOK N, ISHAK A, POP I. Unsteady boundary-layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(7, 8): 2102–2109. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.12.013.
RAMESH G K, PRASANNAKUMARA B C, GIREESHA B J, SHEHZAD S A, ABBASI F M. Three dimensional flow of Maxwell fluid with suspended nanoparticles past a bidirectional porous stretching surface with thermal radiation [J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2017, 1: 6–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2017.02.006.
FORCHHEIMER P. Wasserbewegung durch boden [J]. Zeit Ver Deut Ing, 1901, 45: 1782–1788.
MUSKAT M. The flow of homogeneous fluids through porous media [M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1937.
PAL D, MONDAL H. Hydromagnetic convective diffusion of species in Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium with non-uniform heat source/sink and variable viscosity [J]. Int Com Heat Mass Transfer, 2012, 39(7): 913–917. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2012.05.012.
HAYAT T, MUHAMMAD T, Al-MEZAL S, LIAO S J. Darcy-Forchheimer flow with variable thermal conductivity and Cattaneo-Christov heat flux [J]. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow, 2016, 26(8): 2355–2369. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-08-2015-0333.
VISHNU GANESH N, ABDUL HAKEEM A K, GANGA B. Darcy-Forchheimer flow of hydromagnetic nanofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a thermally stratified porous medium with second order slip, viscous and Ohmic dissipations effects [J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2018, 9(4): 939–951. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2016.04.019.
ADIL SADIQ M, HAYAT T. Darcy-Forchheimer flow of magneto Maxwell liquid bounded by convectively heated sheet [J]. Results in Physics, 2016, 6: 884–890. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.10.019.
ISHAK A, NAZAR R, POP I. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow and heat transfer due to a stretching cylinder [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2008, 49(11): 3265–3269. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2007.11.013.
PAL D, MONDAL H. Influence of chemical reaction and thermal radiation on mixed convection heat and mass transfer over a stretching sheet in Darcian porous medium with Soret and Dufour effects [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2012, 62: 102–108. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2012.03.017.
HAYAT T, MUHAMMAD T, SHEHZAD S A, ALSAEDI A. An analytical solution for magnetohydrodynamic Oldroyd-B nanofluid flow induced by a stretching sheet with heat generation/absorption [J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2017, 111: 274–288. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2016.08.009.
HAYAT T, AZIZ A, MUHAMMAD T, ALSAEDI A. On magnetohydrodynamic three-dimensional flow of nanofluid over a convectively heated nonlinear stretching surface [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 100: 566–572. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.04.113.
MUHAMMAD T, ALSAEDI A, SHEHZAD S A, HAYAT T. A revised model for Darcy-Forchheimer flow of Maxwell nanofluid subject to convective boundary condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Physics, 2017, 55(3): 963–976. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2017.03.006.
MUHAMMAD T, ALSAEDI A, HAYAT T, SHEHZAD S A. A revised model for Darcy-Forchheimer three-dimensional flow of nanofluid subject to convective boundary condition [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 2791–2797. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.052.
HAYAT T, HAIDER F, MUHAMMAD T, ALSAEDI A. On Darcy-Forchheimer flow of viscoelastic nanofluids: A comparative study [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 233: 278–287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.03.035.
HAYAT T, AZIZ A, MUHAMMAD T, ALSAEDI A. Darcy-forchheimer three-dimensional flow of williamson nanofluid over a convectively heated nonlinear stretching surface [J]. Commun Theor Phys, 2017, 68: 387. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0253-6102/68/3/387.
MAITY S. Unsteady flow of thin nanoliquid film over a stretching sheet in the presence of thermal radiation [J]. The European Physical Journal Plus, 2016, 131: 49. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16049-y.
ZHANG Yan, ZHANG Min, BAI Yu. Unsteady flow and heat transfer of power-law nanofluid thin film over a stretching sheet with variable magnetic field and power-law velocity slip effect [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 70: 104–110. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.10.052.
NAVEED M, ABBAS Z, SAJID M. Hydromagnetic flow over an unsteady curved stretching surface [J]. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 2016, 19(2): 841–845. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2015.11.009.
OYELAKIN I S, MONDAL S, SIBANDA P. Unsteady Casson nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with thermal radiation, convective and slip boundary conditions [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2016, 55(2): 1025–1035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2016.03.003.
MANSUR S, ISHAK A. Unsteady boundary layer flow of a nanofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet with a convective boundary condition [J]. Journal of the Egyptian Mathematical Society, 2016, 24(4): 650–655. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joems.2015.11.004.
MANSUR S, ISHAK A. Unsteady boundary layer flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet with a convective boundary condition in a nanofluid [C]// AIP Conference Proceedings. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: AIP Publishing LLC, 2014, 1602: 311–316. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4882504.
NAVIER C L M H. Mémoiresur les lois du mouvement des fluids [J]. Mem Acad Sci Inst de France, 1823, 6: 389–440.
AZIZ A. A similarity solution for laminar thermal boundary layer over a flat plate with a convective surface boundary condition [J]. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul, 2009, 14(4): 1064–1068. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2008.05.003.
MAKINDE O D, AZIZ A. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with a convective boundary condition [J]. Int J Therm Sci, 2011, 50(7): 1326–1332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.02.019.
RAMESH G K, CHAMKHA A J, GIREESHA B J. Boundary layer flow past an inclined stationary/moving flat plate with convective boundary condition [J]. Afrika Matematika, 2016, 27(1, 2): 87–95. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-015-0323-x.
RAMESH G K, GIREESHA B J, GORLA R S R. Boundary layer flow past a stretching sheet with fluid-particle suspension and convective boundary condition [J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 51(8): 1061–1066. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1477-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Project(NRF-2016R1A2B4011009) supported by National Research Foundation of Korea; Project(KSTePS/VGST-KFIST(L1)/2017) supported by Vision Group of Science and Technology, Government of Karnataka, India
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, Y., Ramesh, G.K., Roopa, G.S. et al. Navier’s slip condition on time dependent Darcy-Forchheimer nanofluid using spectral relaxation method. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2000–2010 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4147-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4147-y