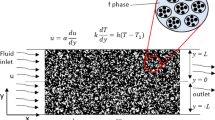
Abstract
In this study, the laminar heat transfer and nanofluid flow between two porous horizontal concentric cylinders was investigated. The problem is investigated in two different geometries and the Re=10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and volume fraction 0, 0.2%, 0.5%, 2% and 5% that related to copper nanoparticles, and porous medium porosity of 0.5 and 0.9. Compared to the first geometry, the convective coefficient in the second geometry increases by 8.3%, 7% and 5.5% at Reynolds numbers of 100, 75 and 50, respectively. Comparison of the outlet temperatures for two heat fluxes of 300 and 1200 W/m2 indicates a 2.5% temperature growth by a fourfold increase in the heat fluxes. Also, the higher Nusselt number is associated with the second geometry occurring at porosities of 0.9 and 0.5, respectively. In both geometries, the Nusselt number values at the porosity of 0.9 are higher, which is due to the increased nanofluid convection at higher porosities. The velocity of the nanofluid experiences a two-fold increase at the outlet compared to its inlet velocity in the first geometry and for both porosities. Similarly, a three-fold increase was achieved in the second geometry and for both porosities.
摘要
研究了在Re=10, 25, 50, 75, 100 和铜纳米粒子体积分数分别为0, 0.2%, 0.5%, 2%和5%, 多孔介质孔隙率分别为0.5 和0.9 条件下多孔水平同心圆柱间的层流传热和纳米流体流动。在雷诺数 分别为100、75 和50 时, 与第一种几何形式相比, 第二种几何形式的对流系数分别增加了8.3%、7% 和5.5%。对300 和1200 W/m2 两种热通量的出口温度进行比较, 发现热通量增加4 倍, 温度增加了 2.5%。此外, 较高的Nusselt 数与第二种几何形状相关, 分别出现在0.9 和0.5 的孔隙度。在这两种几 何结构中, 孔隙度为0.9 时的Nusselt 数值较高, 这是由于孔隙度较高时纳米流体对流增加所致。在第 一几何形状和孔隙度下, 纳米流体的出口的速度比进口速度增加2 倍。同样, 在第二个几何图形和两 个孔隙度上都实现3 倍的增长。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HEMMAT ESFE M, HASSANI AHANGAR M R, REJVANI M, TOGHRAIE D, HAJMOHAMMAD M H. Designing an artificial neural network to predict dynamic viscosity of aqueous nanofluid of TiO2 using experimental data [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf, 2016, 75: 192–196.
AFRAND M, TOGHRAIE D, SINA N. Experimental study on thermal conductivity of water-based Fe3O4 nanofluid: Development of a new correlation and modeled by artificial neural network [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf, 2016, 75: 262–269.
ZARRINGHALAM M, KARIMIPOUR A, TOGHRAIE D. Experimental study of the effect of solid volume fraction and Reynolds number on heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop of CuO-water nanofluid [J]. Exp Therm Fluid Sci, 2016, 76: 342–351.
SAJADIFAR S A, KARIMIPOUR A, TOGHRAIE D. Fluid flow and heat transfer of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a microtube considering slip velocity and temperature jump boundary conditions [J]. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 2017, 61: 25–32.
NAZARI S, TOGHRAIE D. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and fluid flow of water-CuO nanofluid in a sinusoidal channel with a porous medium [J]. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2017, 87: 134–140.
FARIDZADEH M R, SEMIROMI D T, NIROOMAND A. Analysis of laminar mixed convection in an inclined square lid-driven cavity with a nanofluid by using an artificial neural network [J]. Heat Transfer Research, 2013, 45(4): 361–390.
ESFAHANI M A, TOGHRAIE D. Experimental investigation for developing a new model for the thermal conductivity of Silica/Water-Ethylene glycol (40%–60%) nanofluid at different temperatures and solid volume fractions [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 232: 105–112.
AGHANAJAFI A, TOGHRAIE D, MEHMANDOUST B. Numerical simulation of laminar forced convection of Water-CuO nanofluid inside a triangular duct [J]. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2017, 85: 103–108.
ZADKHAST M, TOGHRAIE D, KARIMIPOUR A. Developing a new correlation to estimate the thermal conductivity of MWCNT-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid via an experimental investigation [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2017, 129(2): 859–867. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6213-8.
HEMMAT ESFE M, AFRAND M, YAN W M, YARMAND H, TOGHRAIE D, DAHARI M. Effects of temperature and concentration on rheological behavior of MWCNTs/SiO2 (20–80)-SAE40 hybrid nano-lubricant [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf, 2016, 76: 133–138.
AFRAND M, TOGHRAIE D, RUHANI B. Effects of temperature and nanoparticles concentration on rheological behavior of Fe3O4-Ag/EG hybrid nanofluid: An experimental study [J]. Exp Therm Fluid Sci, 2016, 77: 38–44.
HEMMAT ESFE M, YAN W M, AFRAND M, SARRAF M, TOGHRAIE D, DAHARI M. Estimation of thermal conductivity of Al2O3 /water(40%)-Ethylene-glycol (60%) by artificial neural network and correlation using experimental data [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf, 2016, 74: 125–128.
TOGHRAIE D, CHAHARSOGHI V A, AFRAND M. Measurement of thermal conductivity of ZnO-TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid [J]. J Therm Anal Calorim, 2016, 125(1): 527–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5436-4.
TOGHRAIE D, ALEMPOUR S M B, AFRAND M. Experimental determination of viscosity of Water based magnetite nanofluid for application in heating and cooling systems [J]. Journal Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2016, 417: 243–248.
HEMMAT ESFE M, SAEDODIN S, WONGWISES S, TOGHRAIE D. An experimental study on the effect of diameter on thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Fe/water nanofluids [J]. Therm Anal, 2015, 119(3): 1817–1824. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4328-8
HEMMAT ESFE M, AFRAND M, GHAREHKHANI S, ROSTAMIAND H, TOGHRAIE D, DAHARI M. An experimental study on viscosity of alumina-engine oil: Effects of temperature and nanoparticles concentration [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf, 2016, 76: 202–208.
MAGHREBI M J, NAZARI M, ARMAGHANI T. Forced convection heat transfer of nanofluids in a porous channel [J]. Transp Porous Med, 2012, 93: 401–413.
SHEIKHOLESLAMI M, GANJI D D, ROKNI H B. Nanofluid flow in a semi-porous channel in the presence of uniform magnetic field [J]. IJE TRANSACTIONS C: Aspects, 2013, 26(6): 653–662.
SALEH M H. Laminar free convection of nanofluid flow in horizontal porous annulus [J]. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering, 2013, 7(6): 1306–1313.
MAHDI R A, MOHAMMED H A, MUNISAMY K M. Improvement of convection heat transfer by using porous media and nanofluid: Review [J]. International Journal of Science and Research, 2013, 2(8): 34–48.
ARMAGHANI T, ALI J. CHAMKHA, MAGHREBI M J, NAZARI M. Numerical analysis of a nanofluid forced convection in a porous channel: A new heat flux model in LTNE condition [J]. Journal of Porous Media, 2014, 17(7): 637–646.
PAL D, MANDAL G, VAJRAVALU K. Mixed convection stagnation-point flow of nanofluids over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a porous medium with internal heat generation/absorption [J]. Communications in Numerical Analysis, 2015(1): 30–50.
SHEIKHOLESLAMI M, MUSTAFA M T, GANJI D D. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching porous cylinder considering thermal radiation [J]. Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, 2015, 39A3 (Special issue): 433–440.
ZEHFOROOSH A, HOSSAINPOUR S. Investigation of Brownian motion of CuO-water nanofluid in a porous cavity with internal heat generation by using of LTNE model [J]. J Nano Struct, 2015, 5(3): 237–250.
NOJOOMIZADEH M, KARIMIPOUR A. The effects of porosity and permeability on fluid flow and heat transfer of multiwalled carbon nano-tubes suspended in oil (MWCNT/Oil nano-fluid) in a microchannel filled with a porous medium, Physica E, 2016, 84: 423–433.
TU Wen-bin, WANG Yun, TANG Yong. Thermal characteristic of a tube fitted with porous media inserts in the single phase flow [J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2016, 110: 137–145.
KASAEIAN A, AZARIAN R D, MAHIAN O, KOLSI L, ALI J. Chamkha, Somchai Wongwises, Ioan Pop. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in porous media: A review of the latest developments [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 107: 778–791.
MOJUMDER S, SAHA S, RAHMAN M R, RAHMAN M M, RABBI K M, IBRAHIM T A. Numerical study on mixed convection heat transfer in a porous L-shaped cavity [J]. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 2017, 20: 272–282.
BIANCO V, MANCA O, NARDINI S, VAFAI K. Heat transfer enhancement with nano fluids [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2015.
ZHAO Ning-bo, YANG Jia-long, LI Hui, ZHANG Zhi-ying, LI Shu-ying. Numerical investigation of laminar heat transfer and flow performance of Al2O3-water nanofluids in a flat tube [J]. Int J of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 92: 268–272.
ERGUN S. Fluid flow through packed columns [J]. Chem Eng Prog, 1952, 48: 89–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzaeyan, M., Toghraie, D. Numerical investigation of laminar heat transfer and nanofluid flow between two porous horizontal concentric cylinders. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 1976–1999 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4146-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4146-z