Abstract
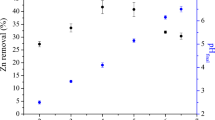
This study presents the deep removal of copper (II) from the simulated cobalt electrolyte using fabricated polystyrene-supported 2-aminomethylpyridine chelating resin (PS-AMP) in a fixed-bed. The effects of bed height (7.0–14.0 cm), feed flow rate (4.5–9.0 mL/min), initial copper (II) concentration of the feed (250–1000 mg/L), feed temperature (25–40 °C) and the value of pH (2.0–4.0) on the adsorption process of the PS-AMP resin were investigated. The experimental data showed that the PS-AMP resin can deeply eliminate copper (II) from the simulated cobalt electrolyte. The bed height, feed flow rate, initial copper (II) concentration of the feed, feed temperature and feed pH value which corresponded to the highest removal of copper (II) were 7.0 cm with 35 mm of the column diameter, 4.5 mL/min, 40 °C, 1000 mg/L and 4.0, respectively. The breakthrough capacity, the saturated capacity of the column and the mass ratio of Cu/Co (g/g) in the saturated resin were correspondingly 16.51 mg/g dry resin, 61.72 mg/g dry resin and 37.67 under the optimal experimental conditions. The copper (II) breakthrough curves were fitted by the empirical models of Thomas, Yoon-Nelson and Adam-Bohart, respectively. The Thomas model was found to be the most suitable one for predicting how the concentration of copper (II) in the effluent changes with the adsorption time.
摘要
介绍了在固定床中使用自制聚苯乙烯基2-氨基甲基吡啶螯合树脂(PS-AMP)从模拟钴电解液中 深度去除铜(II)的研究。研究了床高(7.0≈14.0 cm), 进料流速(4.5≈9.0 mL/min), 初始铜(II)浓度(250≈1000 mg/L), 料液温度(25≈40 °C)和 pH 值(2.0≈4.0)对 PS-AMP 树脂吸附过程的影响。实验数据表明, PS-AMP 树脂可以从模拟钴电解液中深度除铜(II)。选用玻璃柱直径为35 mm 时, 去除铜的最佳床高, 进料流 速, 料液初始铜(II)浓度, 料液温度和 pH 值分别为 7.0 cm, 4.5 mL/min, 1000 mg/L, 40 °C 和4.0。在 最佳实验条件下, 穿透容量, 饱和容量和饱和树脂中 Cu/Co (g/g)的质量比相应地为16.51 mg/g 干树脂, 61.72 mg/g 干树脂和37.67。铜(II)穿透曲线分别由 Thomas 模型, Yoon-Nelson 模型和 Adam-Bohart 模 型拟合。Thomas 模型是最适合预测流出物中铜(II)浓度如何随吸附时间变化的模型。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MENG Xian-xuan. Jinchuan cobalt smelting production technology progress [J]. Nonferrous Metals, 1997 (4): 1–6. (in Chinese)
HE Huan-hua, CAI Qiao-fang. China nickel and cobalt metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
LI Xin-ying, Francis Ruzagiliza Innocent, Chen Quan-yuan, Xue Gang. Treatment of copper-containning wastewater by precipitation and characterization of precipitate [J]. Science of Environmental Protection, 2014, 40(2): 35–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53599-3.10005-8. (in Chinese)
SADEGHALVAD B, AZADMEHR A R, MOTEVALIAN H. Statisticaldesign and kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Ni (II) adsorption on bentonite [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(7): 1529–1536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3557-y.
ZHUO Wen, YE Xian-ying. Solvent extraction process for separating copper in nickel, cobalt and copper system, CN102234722A [P]. 2011-11-09. (in Chinese)
JURRIUS Y, SOLE K C, HARDWICK E. Removalof copper and zinc from a cobalt electrolyte by ion exchange at Kamoto Copper Company’s Luilu plant [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014(2): 281–293. https://doi.org/www.soleconsulting.co.za/publications/cobaltnickel/Co3.pdf.
SHEN C, CHANG Y, FANG L, MIN M, XIONG C H. Selective removal of copper with polystyrene–1, 3-diaminourea chelating resin: Synthesis and adsorption studies [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 40: 3588–3596. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02703A.
LI Jiang-tao, CHEN Ai-liang. Deep removal of copper from nickel electrolyte using manganese sulfide[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(11): 3802–3807. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64024-9.
SUDHA P N, CELINE S. Removalof heavy metal cadmium fromindustrial wastewater using chitosan coated coconut charcoal [J]. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology, 2008, 7(4): 601–604.
WANG Cheng-yan. Extraction and separation of copper, nickel and cobalt in ammonia solution [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2002, 54(1): 23–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2002.01.007. (in Chinese)
SINGH A, GEHLOT C L, SINGH D K. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of a new chelating resin containing 4-2-(Thiazolylazo) resorcinol (TAR) [J]. Separation Science & Technology, 2012, 47(16): 2399–2407. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2012.672513.
LI Yu-biao, WANG Xin-yu, XIAO Qing, ZHANG Xu. Study on selective removal of impurity iron from leached copper-bearing solution using a chelating resin [J]. Minerals, 2016, 6(4): 106–117. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040106.
SHEN C, CHANG Y, FANG L, MIN M, XIONG C H. Selective removal of copper with polystyrene–1, 3-diaminourea chelating resin: Synthesis and adsorption studies [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 40: 3588–3596. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02703A.
WEN Jun-jie. The fundamental research on removing copper from cobalt electrolyte and nickel electrolyte by ion-exchange with novel silica-polyamine organic-inorganic composite resin [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010. (in Chinese)
LAN Bai. Amine/acid catalyzed synthesis of a new silica-aminomethyl pyridine material as a selective adsorbent of copper [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22: 17293–17301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM33831A.
QIU Xue-jing, HU Hui-ping, YANG Jin-peng, WANG Cai-xia, CHENG Ze-ying, JI Guang-fu. Selective removal of copper from simulated nickel electrolyte by polystyrene-supported2-aminomethylpyridine chelating resin [J]. Chemical Papers, 2018: 1–15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-018-0436-4.
DAVILA-GUZMAN N E, CERINOCÓRDOVA F J, SOTO-REGALADO E, LOREDO-CANCINO M, LOREDO-MEDRANO J A, GARCÍA-REYES R B. A mass transfer model for the fixed-bed adsorption of ferulic acid onto a polymeric resin: Axial dispersion and intraparticle diffusion [J]. Environmental Technology, 2016, 37(15): 1914–1922. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1135993.
MOHAN S, SINGH D K, KUMAR V, HASAN S H. Modelling of fixed bed column containing graphene oxide decorated by MgO nanocubes as adsorbent for Lead (II) removal from water [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2017, 17: 216–228. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.03.009.
YAHAYA N K E M, ABUSTAN I, LATIFT M F P M. Fixed-bed column study for Cu (II) removal from aqueous solutions using rice husk based activated carbon [J]. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 2013, 11(1): 186–190.
MALKOC E, NUHOGLU Y. Fixedbed studies for the sorption of chromium (VI) onto tea factory waste [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(13): 4363–4372. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2006.02.005.
JEROLD M, JOSEPH D, PATRA N, SIVASUBRAMANIAN V. Fixed-bed column studies for the removal of hazardous malachite green dye from aqueous solution using novel nano zerovalent iron algal biocomposite [J]. Nanotechnology for Environmental Engineering, 2016, 1(1): 8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-016-0007-2.
JI Fei, LI Chao-lin. Dynamic adsorption of Cu (II) from aqueous solution by zeolite/cellulose acetate blend fiber in fixed-bed [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 434: 88–94. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.05.045.
XIONG Chun-hua, LI Yan-li, WANG Guo-tao, FANG Lei, ZHOU Su-guo, YAO Cai-ping, CHEN Qing, ZHENG Xu-ming, QI Dong-ming, FU Ya-qin, ZHU Yao-feng. Selective removal of Hg (II) with polyacrylonitrile-2-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole chelating resin: Batch and column study [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 259: 257–265. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.114.
TALAT M, MOHAN S, DIXIT V, SINGH D K, HASAN S H, SRIVASTAVA O N. Effective removal of fluoride from water by coconut husk activated carbon in fixed bed column: Experimental and breakthrough curves analysis [J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2018, 7: 48–55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.03.001.
TAMILSELV S, ASAITHAMBI M. Columnmode adsorption studies of acid dye using a novel adsorbent [J]. Rasayan Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 8(1): 84–91.
PAULINO A T, BELFIORE L A, KUBOTA L T, MUNIZ E C, ALMEIDA V C, TAMBOURGI E B. Effect of magnetite on the adsorption behavior of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) in chitosan-based hydrogels [J]. Desalination, 2011, 275: 187–196. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.02.056.
BAEK K, SONG S, KANG S, RHEE Y, LEE C, LEE B, HUDSON S, HWANG T. Adsorptionkinetics of boron by anion exchange resin in packed column bed [J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2007, 13(3): 452–456.
HAN Run-ping, WANG Yi, ZOU Wei-hua, WANG Yuan-feng, SHI Jie. Comparison of linear and nonlinear analysis in estimating the Thomas model parameters for methylene blue adsorption onto natural zeolite in fixed-bed column [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 145: 331–335. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.027.
DALAL Z, HUSEIN, AL-RADADI T, DANISH E Y. Adsorption of phosphate using alginate-/zirconium-grafted newspaper pellets: Fixed-bed column study and application [J]. Arabian Journal for Science & Engineering, 2017, 42(4): 1399–1412. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2250-z.
RECEPOĞLU Y K, KABAY N, IPEK I Y, ARDA M, Yüksel M. Packed bed column dynamic study for boron removal from geothermal brine by a chelating fiber and breakthrough curve analysis by using mathematical models [J]. 2018, 437(1): 1–6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.02.022.
MAO Juan, KIM S, WU Xiao-hui, KWAK I S, ZHOU Tao, YUN Y S. A sustainable cationic chitosan/E. coli fiber biosorbent for Pt(IV) removal and recovery in batch and column systems [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 143(25): 32–39. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.01.023.
IDAN I J, ABDULLAH L C, JAMIL S N A B M. OBAID M K, CHOONG T S Y. Fixed-bed system for adsorption of anionic acid dyes from binary solution onto quaternized kenaf core fiber [J]. Bioresources, 2017, 12(4): 8870–8885. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.12.4.8870-8885.
NTIMBANI R N, SIMATE G S, NDLOVU S. Removalof copper ions from dilute synthetic solution using staple ion exchange fibres: Dynamic studies [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4: 3143–3150. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2014CB643401) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Projects(51134007, 51474256) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017TP1001) supported by the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yh., Hu, Hp. & Qiu, Xj. Fixed-bed column study for deep removal of copper (II) from simulated cobalt electrolyte using polystyrene-supported 2-aminomethylpyridine chelating resin. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 1374–1384 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4093-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4093-8