Abstract
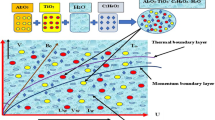
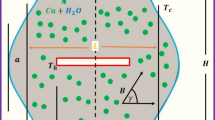
The optimal design of heating and cooling systems must take into account heat radiation which is a non-linear process. In this study, the mixed convection in a radiative magnetohydrodynamic Eyring-Powell copper-water nanofluid over a stretching cylinder was investigated. The energy balance is modeled, taking into account the non-linear thermal radiation and a thermal slip condition. The effects of the embedded flow parameters on the fluid properties, as well as on the skin friction coefficient and heat transfer rate, are analyzed. Unlike in many existing studies, the recent spectral quasi-linearization method is used to solve the coupled nonlinear boundary-value problem. The computational result shows that increasing the nanoparticle volume fraction, thermal radiation parameter and heat generation parameter enhances temperature profile. We found that the velocity slip parameter and the fluid material parameter enhance the skin friction. A comparison of the current numerical results with existing literature for some limiting cases shows excellent agreement.
摘要
供热冷却系统的优化设计必须考虑非线性过程的热辐射。 本文研究了铜-水纳米流体在伸缩圆 筒上的Eyring-Powell 磁热辐射的混合对流动力学。 考虑非线性热辐射和热滑移条件, 建立了能量守 衡模型, 分析了表面摩擦系数和换热速率等流动参数对流体特性的影响。不采用现有的研究方法, 应 用最近的谱准线性化方法求解耦合非线性边界值问题。 计算结果表明, 增大纳米粒子的体积分数、热 辐射参数和热源参数可增强温度分布。 速度滑移参数和流体材料参数增大了表面摩擦力。 对比分析了 极限情况下的数值结果和文献结果, 结果表明: 采用本文研究方法计算结果达到同等精度。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHOI S U S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluid with nanoparticles, developments and applications of non-Newtonian flow [J]. ASME FED, 1995, 231: 95–105.
SAIDA Z, SAIDUR R, RAHIMB N A, ALIMA M A. Analyses of exergy efficiency and pumping power for a conventional flat plate solar collector using SWCNTs based nanofluid [J]. Energy and Buildings, 2014, 97: 1–9.
JAIN S, HIRST D G, O€ULLIVAN J M. Gold nanoparticles as novel agents for cancer therapy [J]. The British Journal of Radiology, 2012, 85: 101–113.
BUONGIORNO J J. Convective transport in nanofluids [J]. ASME, 2005, 128: 240–250.
DAS S, JANA R N. Natural convective magneto-nanofluid flow and radiative heat transfer past a moving vertical plate [J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2015, 54(1): 55–64.
BACHOK N, ISHAK A, POP I. Stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid [J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2011, 6(1): 623.
RAMZAN M, FAROOQ M, HAYAT T, ALSAEDI A, CAO J. MHD stagnation point flow by a permeable stretching cylinder with Soret-Dufour effects [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(2): 707–716.
HAYAT T, FAROOQ M, ALSAEDI A. Stagnation point flow of carbon nanotubes over stretching cylinder with slip conditions [J]. Open Physics, 2015, 13(1): 188–197.
ISHAK A, NAXARI R, POP I. Post-stagnation-point boundary layer flow mixed convection heat transfer over a vertical linearly stretching sheet [J]. Archive of Mechanics, 2008, 60(4): 303–322.
PAL D, MAL G, VAJRAVALU K. Mixed convection stagnation-point flow of nanofluids over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a porous medium with internal heat generation/absorption [J]. Communications in Numerical Analysis, 2015, 2015(1): 30–50.
ABBAS Z, MASOOD T, OLANREWAJU P O. Dual solutions of MHD stagnation point flow heat transfer over a stretching/shrinking sheet with generalized slip condition [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(6): 2376–2384.
MUKHOPADHYAY S. MHD boundary layer slip flow along a stretching cylinder [J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2013, 4(2): 317–324.
MUKHOPADHYAY S. Effects of thermal radiation variable fluid viscosity on stagnation point flow past a porous stretching sheet [J]. Meccanica, 2013, 48(1): 1717–1730.
SARI M R, KEZZAR M, ADJABI R. Heat transfer of copper/water nanofluid flow through converging-diverging channel [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(2): 484–496.
MAJID S, MOHAMMAD J. Optimal selection of annulus radius ratio to enhance heat transfer with minimum entropy generation in developing laminar forced convection of water-Al2O3 nanofluid flow [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(8): 1850–1865.
MAHMOODI M, KELOUSI S. Kerosene–alumina nanofluid flow heat transfer for cooling application [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(4): 983–990.
WUSIMAN K, CHUNG H, MD J N, HANDRY A, EOM Y, KIM J, JEONG H. Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluid through circular tube [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(1):142–148.
POWELL R E, EYRING H. Mechanisms for the relaxation theory of viscosity [J]. Nature, 1944, 154(1): 427–428.
JAVED T, ALI N, ABBAS Z, SAJID M. Flow of an Eyring-Powell non-Newtonian fluid over a stretching sheet [J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 2013, 200(3): 327–336.
HAYAT T, IQBAL Z, QASIM M, OBAIDAT S. Steady flow of an Eyring-Powell fluid over a moving surface with convective boundary conditions [J]. International Journal of Heat Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(7): 1817–1822.
AKBAR N S, EBAID A, KHAN Z H. Numerical analysis of magnetic field effects on Eyring-Powell fluid flow towards a stretching sheet [J]. Journal of Magnetism Magnetic Materials, 2015, 382: 355–358.
BABU J M, SEEP N, RAJU C S K. Heat and mass transfer in MHD Eyring-Powell nanofluidf flow due to cone in porous medium [J]. International Journal of Engineering Research in Africa, 2015, 19: 57–74.
HAYAT T, KHAN M I, WAQAS M, ALSAEDI A. Effectiveness of magnetic nanoparticles in radiative flow of Eyring-Powell fluid [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 231: 126–133.
RAMZAN M, BILAL M, KANWAL S, CHUNG J D. Effects of variable thermal conductivity non-linear thermal radiation past an eyring powell nanofluid flow with chemical reaction [J]. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 2017, 67(6): 723–731.
MALIK M Y, KHAN I, HUSSAIN A, SALAHUDDIN T. Mixed convection flow of MHD Eyring-Powell nanofluid over a stretching sheet: A numerical study [J]. AIP Advances, 2015, 5(11): 117118.
KHAN I, KHAN M, MALIK M Y, SALAHUDDIN T. Mixed convection flow of Eyring-Powell nanofluid over a cone plate with chemical reactive species [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 3716–3722.
MOTSA S S. A new spectral local linearization method for nonlinear boundary layer flow problems [J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2013. Article ID 423628. DOI: 1155/2013/423628.
ROSSELAND S. Astrophysik und atom-theoretische grundlagen [M]. Springer-Verlag, 1931.
BELLMAN R E, KALABA R E. Quasilinearization nonlinear boundary-value problems [M]. R Corporation, 1965.
MOTSA S S, DLAMINI P G, KHUMALO M. Spectral relaxation method spectral quasilinearization method for solving unsteady boundary layer flow problems [J]. Advances in Mathematical Physics, 2014, Article ID 341964. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/341964.
CANUTO C, HUSSAINI M Y, QUARTERONI A, THOMAS JR A. Spectral methods in fluid dynamics [M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
TREFETHEN L N. Spectral methods in MATLAB [M]. SIAM, 2000.
MAHAPATRA T R, GUPTA A S. Heat transfer in stragnation-point flow towards a stretching sheet [J]. Heat Mass Transfer, 2002, 38: 517–521.
ZAIMI K, ISHAK A. Stagnation-point flow towards a stretching vertical sheet with slip effects [J]. Mathematics, 2016, 4(2): 27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/math4020027.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogunseye, H.A., Sibanda, P. & Mondal, H. MHD mixed convective stagnation-point flow of Eyring-Powell nanofluid over stretching cylinder with thermal slip conditions. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 1172–1183 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4079-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4079-6
Key words
- Eyring-Powell model
- stretching cylinder
- nanofluid
- thermal radiation
- slip effects
- spectral quasi-linearization method