Abstract
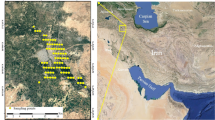
Vegetation encroachment occurred in bauxite residue disposal area (BRDA) following natural weathering processes, whilst the typical indicators of soil formation are still uncertain. Residue samples were collected from the BRDA in Central China, and related physical, chemical and biological indicators of bauxite residue with different storage years were determined. The indicators of soil formation in bauxite residue were selected using principal component analysis, factor analysis, and comprehensive evaluation to establish soil quality diagnostic index model on disposal areas. Following natural weathering processes, the texture of bauxite residue changed from silty loam to sandy loam. The pH and EC decreased, whilst porosity, nutrient element content and microbial biomass increased. The identified minimum data set (MDS) included available phosphorus (AP), moisture content (MC), C/N, sand content, total nitrogen (TN), microbial biomass carbon (MBC), and pH. The soil quality index of bauxite residue increased, and the relative soil quality index decreased from 1.89 to 0.15, which indicated that natural weathering had a significant effect on improveing the quality of bauxite residue and forming a new soil-like matrix. The diagnostic model of bauxite residue was established to provide data support for the regeneration on disposal area.
摘要
以华中某赤泥堆场为研究对象,分析不同堆存年限的赤泥物理、化学、生物学特性,运用主成 分分析、综合评价法等方法建立赤泥堆场土壤质量诊断模型。结果表明:在自然风化过程中,赤泥质 地由类粉质壤土转变为类砂质壤土,孔隙度增加,pH、EC 降低,养分含量增加,微生物量碳(MBC) 升高;确定的最小数据集(MDS)为:速效磷(AP)、含水率(MC)、C/N、砂粒含量、全氮(TN)、MBC、 pH;建立了赤泥堆场土壤化诊断模型,随着赤泥堆存年限的延长,综合质量指数上升,相对质量指数 从1.89 下降到0.15,逐渐形成一种新的类土基质。赤泥堆场土壤化诊断模型的建立,为赤泥生态化处 置及堆场生态修复提供理论依据。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
XUE Sheng-guo, ZHU Feng, KONG Xiang-feng, WU Chuan, HUANG Ling, HUANG Nan, HARTLEY W. A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (red mud) [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(2): 1120–1132. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-015–4558-8.
SANTINI T C, FEY M V. Spontaneous vegetation encroachment upon bauxite residue (red mud) as an indicator and facilitator of in situ remediation processes [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2013, 47(21): 12089–12096. DOI: 10.1021/es402924g.
VALLE S R, CARRASCO J. Soil quality indicator selection in chilean volcanic soils formed under temperate and humid conditions [J]. Catena, 2018, 162: 386–395. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.024.
ZHU Feng, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, HUANG Ling, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-bin. Novel predictors of soil genesis following natural weathering processes of bauxite residues [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(3): 2856–2863. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-015-5537-9.
KIRWAN L J, HARTSHORN A, MCMONAGLE J B, FLEMING L, FUNNELL D. Chemistry of bauxite residue neutralisation and aspects to implementation [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 119: 40–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.minpro.2013.01.001.
XUE Sheng-guo, KONG Xiang-feng, ZHU Feng, HARTLEY W, LI Xiao-fei, LI Yi-wei. Proposal for management and alkalinity transformation of bauxite residue in China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(13): 12822–34. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-016-6478-7.
COURTNEY R, HARRIS J A, PAWLETT M. Microbial community composition in a rehabilitated bauxite residue disposal area: A case study for improving microbial community composition [J]. Restoration Ecology, 2014, 22(6): 798–805. DOI: 10.1111/rec.12143.
LI Yi-wei, JIANG Jun, XUE Sheng-guo, MILLAR G, KONG, Xiang-feng, LI Xiao-fei, LI Meng, LI Chu. Effect of ammonium chloride on leaching behavior of alkaline anion and sodium ion in bauxite residue [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(10): 2125–2134. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64857-5.
COURTNEY R, MULLEN G. Use of germination and seedling performance bioassays for assessing revegetation strategies on bauxite residue [J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2009, 197(1–4): 15–22. DOI: 10.1007/s11270-008–9787-8.
KONG Xiang-feng, LI Meng, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, CHEN Cheng, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-fei, LI Yi-wei. Acid transformation of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 382–390. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.073.
XUE Sheng-guo, WU Yu, LI Yi-wei, KONG Xiang-feng, ZHU Feng, HARTLEY W, LI Xiao-fei, YE Yu. Industrial wastes applications for alkalinity regulation in bauxite residue: A comprehensive review [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 268–288.
XUE Sheng-guo, LI Meng, JIANG Jun, GRAEME J M, LI Chu-xuan, KONG Xiang. Phosphogypsum stabilization of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 77: 1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.016.
ZHANG Guang, BAI Jun, XI Min, ZHAO Qing, LU Qiong, JIA Jia. Soil quality assessment of coastal wetlands in the yellow river delta of China based on the minimum data set [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 66: 458–466. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.01.046.
YAO Rong, YANG Jing, GAO Peng, ZHANG Jian, JIN Wen. Determining minimum data set for soil quality assessment of typical salt-affected farmland in the coastal reclamation area [J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2013, 128: 137–148. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2012.11.007.
SANTINI T C, KERR J L, WARREN L A. Microbially-driven strategies for bioremediation of bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 293: 131–157. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.024.
EZE P N, KNIGHT J, EVANS M. Tracing recent environmental changes and pedogenesis using geochemistry and micromorphology of alluvial soils, sabie-sand river basin, south Africa [J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 268: 312–321. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.06.023.
ZUBER S M, BEHNKE G D, NAFZIGER E D, VILLAMIL M B. Multivariate assessment of soil quality indicators for crop rotation and tillage in Illinois [J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2017, 174: 147–155. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2017. 07.007.
BABU A G, REDDY M S. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and nutrient status of bermudagrass grown in alkaline bauxite processing residue [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(1): 25–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.032.
XENIDIS A, HAROKOPOU A D, MYLONA E, BROFAS G. Modifying alumina red mud to support a revegetation cover [J]. JOM, 2005, 57(2): 42–46. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-005–0214-y.
EASTHAM J, MORALD T. Effective nutrient sources for plant growth on bauxite residue: II. Evaluating the response to inorganic fertilizers [J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2006, 171(1–4): 315–331. DOI: 10.1007/s11270-005-9055–0.
LIAO Jia-xin, JIANG Jun, XUE Sheng-guo, CHENG Qing, WU Hao, MANIKANDAN R, WILLIAM H, HUANG Long. A novel acid-producing fungus isolated from bauxite residue: The potential to reduce the alkalinity [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2018, 35(10): 840–847. DOI: 10.1080/01490451.2018.1479807.
COURTNEY R, HARRINGTON T. Growth and nutrition of holcus lanatus in bauxite residue amended with combinations of spent mushroom compost and gypsum [J]. Land Degradation and Development, 2012, 23(2): 144–149. DOI: 10.1002/ldr.1062.
KRISHNA P, REDDY M S, PATNAIK S K. Aspergillus tubingensis reduces the pH of the bauxite residue (red mud) amended soils [J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2005, 167(1–4): 201–209. DOI: 10.1007/s11270-005-0242-9.
VERMEIRE M L, CORNU S, FEKIACOVA Z, DETIENNE M, DELVAUX B, CORNÉLIS J T. Rare earth elements dynamics along pedogenesis in a chronosequence of podzolic soils [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 446: 163–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.008.
TSAI Heng, HSEU Zeng, KUO Hung, HUANG Wen, CHEN Zueng. Soilscape of west-central taiwan: its pedogenesis and geomorphic implications [J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 255: 81–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.09.014.
LIU Jie, WU Li, CHEN Dong, YU Zhu, WEI Chang. Development of a soil quality index for camellia oleifera forestland yield under three different parent materials in southern china [J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2018, 176: 45–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2017.09.013.
REZAEI S A, GILKES R J, ANDREWS S S. A minimum data set for assessing soil quality in rangelands [J]. Geoderma, 2006, 136(1, 2): 229–234. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.03.021.
ZHU Feng, CHENG Qing, XUE Sheng-guo, LI Chu-xuan, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan. TIAN Tao. Influence of natural regeneration on fractal features of residue microaggregates in bauxite residue disposal areas [J]. Land Degradation and Development, 2018, 29(1): 138–149. DOI: 10.1002/ldr.2848.
XUE Sheng-guo, YE Yu, ZHU Feng, WANG Qiong, JIANG Jun, HARTLEY W. Changes in distribution and microstructure of bauxite residue aggregates following amendments addition [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 78: 276–286. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.10.010.
PELLEGRINI S, GARCÍA G, PEÑAS C, JOSE M, VIGNOZZI N, COSTANTINI E A C. Pedogenesis in mine tails affects macroporosity, hydrological properties, and pollutant flow [J]. Catena, 2016, 136: 3–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2015.07.027.
ZHU Feng, HOU Jing, XUE Sheng-guo, WU Chuan, WANG Qiong, HARTLEY W. Vermicompost and gypsum amendments improve aggregate formation in bauxite residue [J]. Land Degradation and Development, 2017, 28(7): 2109–2120. DOI: 10.1002/ldr.2737.
ZHU Feng, ZHOU Jia, XUE Sheng-guo, WILLIAM H, WU Chuan, GUO Ying. Aging of bauxite residue in association of regeneration: A comparison of methods to determine aggregate stability and erosion resistance [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 92: 47–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.03.025.
ZHU Feng, LIAO Jia-xin, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, ZOU Qi, WU Hao. Evaluation of aggregate microstructures following natural regeneration in bauxite residue as characterized by synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 573: 155–163. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.108.
KONG Xiang-feng, JIANG Xing-xing, XUE Sheng-guo, HUANG Ling, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-bin. Migration and distribution of saline ions in bauxite residue during water leaching [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(3): 534–541. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64686-2.
SHUKLA M K, LAL R, EBINGER M. Soil quality indicators for reclaimed mine soils in southeastern ohio [J]. Soil Science, 2004, 169(2): 133–142. DOI: 10.1097/01.ss. 0000117785.98510.0f.
CHEN Jie, XIAO Guo, KUZYAKOV Y, JENERETTE G D, MA Ying, LIU Wei, WANG Zheng, SHEN Wei. Soil nitrogen transformation responses to seasonal precipitation changes are regulated by changes in functional microbial abundance in a subtropical forest [J]. Biogeosciences, 2017, 9(14): 2513–2525. DOI: 10.5194/bg-14-2513-2017.
JOHANNES A, MATTER A, SCHULIN R, WEISSKOPF P, BAVEYE P C, BOIVIN P. Optimal organic carbon values for soil structure quality of arable soils. Does clay content matter? [J]. Geoderma, 2017, 302: 14–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.04.021.
ZHENG Fen. Effect of vegetation changes on soil erosion on the loess plateau [J]. Pedosphere, 2006, 16(4): 420–427. DOI: 10.1016/s1002-0160(06)60071-4.
LENOIR L, PERSSON T, BENGTSSON J, WALLANDER H, WIRÉN D. Bottom–up or top–down control in forest soil microcosms? Effects of soil fauna on fungal biomass and C/N mineralization [J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2007, 43(3): 281–294. DOI: 10.1007/s00374-006-0103-8.
NABIOLLAHI K, GOLMOHAMADI F, TAGHIZADEH M R, KERRY R, DAVARI M. Assessing the effects of slope gradient and land use change on soil quality degradation through digital mapping of soil quality indices and soil loss rate [J]. Geoderma, 2018, 318: 16–28. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.12.024.
XU Er, ZHANG Hong. Spatially-explicit sensitivity analysis for land suitability evaluation [J]. Applied Geography, 2013, 45: 1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013. 08.005.
RAIESI F. A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of upland arid and semiarid regions [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 75: 307–320. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(41877551, 41842020) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Zhu, F., Wu, C. et al. Dynamic change and diagnosis of physical, chemical and biological properties in bauxite residue disposal areas. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 410–421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4013-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4013-y
Key words
- bauxite residue disposal area
- soil properties
- minimum data set
- diagnostic indices
- natural weathering
- soil formation in bauxite residue