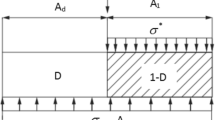
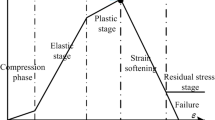
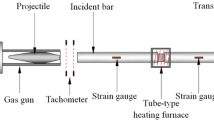
Abstract
With the gradual depletion of mineral resources in the shallow part of the earth, resource exploitation continues to move deeper into the earth, it becomes a hot topic to simulate the whole process of rock strain softening, deformation and failure in deep environment, especially under high temperature and high pressure. On the basis of Lemaitre’s strain-equivalent principle, combined with statistics and damage theory, a statistical constitutive model of rock thermal damage under triaxial compression condition is established. At the same time, taking into account the existing damage model is difficult to reflect residual strength after rock failure, the residual strength is considered in this paper by introducing correction factor of damage variable, the model rationality is also verified by experiments. Analysis of results indicates that the damage evolution curve reflects the whole process of rock micro-cracks enclosure, initiation, expansion, penetration, and the formation of macro-cracks under coupled effect of temperature and confining pressure. Rock thermal damage shows logistic growth function with the increase of temperature. Under the same strain condition, rock total damage decreases with the rise of confining pressure. By studying the electron microscope images (SEM) of rock fracture, it is inferred that 35.40 MPa is the critical confining pressure of brittle to plastic transition for this granite. The model parameter F reflects the average strength of rock, and M reflects the morphological characteristics of rock stress–strain curves. The physical meanings of model parameters are clear and the model is suitable for complex stress states, which provides valuable references for the study of rock deformation and stability in deep engineering.
摘要
随着地球浅部矿物资源逐渐枯竭, 资源开采不断走向地球深部, 模拟深部高温高压条件下岩石应变软化变形破坏行为是岩石力学研究的重要内容。 本文基于 Lemaitre 应变等价性理论, 结合统计学和损伤力学, 同时引入损伤变量修正系数考虑岩石残余强度对峰后曲线的影响, 建立了三轴压缩条件下岩石热力耦合统计损伤本构方程, 并通过试验验证模型的合理性。 研究结果表明: 温度–荷载总损伤演化曲线反映了岩石内部微裂纹闭合、 萌生、 扩展、 贯通、 直至出现宏观裂纹的全过程; 岩石的热损伤变量随温度的升高呈 logistic 函数增长; 同等应变情况下, 损伤变量随围压的升高而减小, 通过研究岩石破裂后 SEM 电镜图片, 推断出 35.40 MPa 是花岗岩的脆塑性转换临界围压; 模型分布参数 F 反映了岩石的平均强度, m 反映了岩石应力–应变曲线的形态特征。 该模型不仅能反映温度、围压对岩石损伤的影响, 而且能较好地反映岩石峰后残余强度阶段变形特征, 模型参数物理意义明确, 适用于复杂应力状态情况, 这对于研究深部岩石损伤软化问题具有重要的意义。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AL-SHAYEA N A, KHAN K, ABDULJAUWAD S N. Effects of confining pressure and temperature on mixed-mode (I-II) fracture toughness of a lime-stone rock [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2000, 37(4): 629–643. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1365-1609(00)00003-4.
ZHAO Yang-sheng, WAN Zhi-jun, FENG Zi-jun, YANG Dong, ZHANG Yuan, QU Fang. Triaxial compression system for rock testing under high temperature and high pressure [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2012, 52: 132–138. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.02.011.
YIN Tu-bing, WANG Pin, LI Xi-bing, SHU Rong-hua, YE Zhou-yuan. Effects of thermal treatment on physical and mechanical characteristics of coal rock [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 22(3): 2336–2345. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3292-9.
GAUTAM P K, VERMA A K, MAHESHWAR S, SINGH T N. Thermomechanical analysis of different types of sandstone at elevated temperature [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(5): 1985–1993. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0797-8.
LI Ming, MAO Xian-biao, CAO Li-li, PU Hai, MAO Rong-rong, LU Ai-hong. Effects of thermal treatment on the dynamic mechanical properties of coal measures sandstone [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(9): 3525–3539. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0981-5.
YANG Sheng-qi, RANJITH P G, JING Hong-wen, TIAN Wen-ling, JU Yang. An experimental investigation on thermal damage and failure mechanical behavior of granite after exposure to different high temperature treatments [J]. Geothermics, 2017, 65: 180–197. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008.
ZHAO Y S, WAN Z J, FENG Z J, XU Z H, LIANG W G. Evolution of mechanical properties of granite at high temperature and high pressure [J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2017, 3(2): 199–210. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-017-0052-8.
YIN T B, WANG P, LI X B, SHU R H, YE Z Y. Effects of thermal treatment on physical and mechanical characteristics of coal rock [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23: 2336–2345. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3292-9.
DOUGILL J W, LAU J C, BURTN J. Toward a theoretical model for progressive failure and softening in rock, concrete and similar materials [J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 1976, 102: 333–355. https://doi.org/www.scopus.com/record/display.uri?eid=2-s2.0-21144445370&origin=inward&txGid=698aa224d687ac2e3f07a616517c3a26.
LI Peng, RAO Qiu-hua, LI Zhuo, MA Wen-bo, MA Bin. Thermal-hydro-mechanical coupling damage model of brittle rock [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(3): 1136–1141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2046-9.
LIU X S, NING J G, TAN Y L, GU Q H. Damage constitutive model based on energy dissipation for intact rock subjected to cyclic loading [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2016, 85: 27–32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.003.
VAN D V, ARASH M, GIANG D N, ABDUL H S. A thermodynamics-based formulation for constitutive modelling using damage mechanics and plasticity theory [J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 143: 22–39. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.04.018.
CERFONTAINE B, CHARLIER R, COLLIN F, TAIEBAT M. Validation of a new elastoplastic constitutive model dedicated to the cyclic behaviour of brittle rock materials [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(10): 2677–2694. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1258-3.
SAHARA D P, SCHOENBALL M, GEROLYMATOU E, KOHL T. Analysis of borehole breakout development using continuum damage mechanics [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2017, 97: 134–143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.04.005.
CAO Wen-gui, ZHAO Ming-hua, LIU Cheng-xue. Study on the model and its modifying method for rock softening and damage based on weibull random distribution [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(19): 3226–3231. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.19.003.
CHEN Jian-wen, YANG Chun-he, GAO Xiao-ping, LI Xiao-hong, JIANG De-yi. Study on the couple damage of temperature and mechanics for salt rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(11): 1986–1991. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.11.027.
LI Xiang, CAO Wen-gui, SU Yong-hua. A statistical damage constitutive model for softening behavior of rocks [J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 143–144: 1–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.05.005.
ZHANG Hui-mei, LEI Li-na, YANG Geng-she. Damage model of rock under temperature and load [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(Supp 2): 3391–3396. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.s2.001.
LI Yu-wei, JIA Dan, RUI Zhen-hua, PENG Ji-yong, FU Chun-kai, ZHANG Jun. Evaluation method of rock brittleness based on statistical constitutive relations for rock damage [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 153: 123–132. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2017.03.041.
DENG Jian, GU De-sheng. On a statistical damage constitutive model for rock materials [J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2011, 37(2): 122–128. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2010.05.018.
LIU Shi, XU Jin-yu. Analysis on damage mechanical characteristics of marble exposed to high temperature [J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2015, 24(8): 1180–1193. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789515570507.
ZHAO Heng, SHI Cai-jun, ZHAO Ming-hua, LI Xi-bing. Statistical damage constitutive model for rocks considering residual strength [J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 17(1): 04016033. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000680.
CAI Mei-feng, HE Man-chao, LIU Dong-yan. Rock mechanics and engineering [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002.
LEMAITRE J. How to use damage mechanics [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1984, 80(2): 233–245. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-5493(84)90169-9.
CAO Rui-lang, HE Shao-hui, WEI Jing, WANG Fang. Study of modified statistical damage softening constitutive model for rock considering residual strength [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(6): 1652–1660. DOI:https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2013.06.018.
XU Xiao-li, GAO Feng, ZHANG Zhi-zhen. Influence of confining pressure on deformation and strength properties of granite after high temperatures [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(12): 2246–2252. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201412012.
XU Xiao-li, GAO Feng, ZHANG Zhi-zhen. Thermomechanical coupling damage constitutive model of rock based on the Hoek–Brown strength criterion [J]. International Journal of Damage Mechanics, 2018, 27(8): 1213–1230. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789517726838.
XU Xiao-li, KARAKUS M. A coupled thermo-mechanical damage model for granite [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 103: 195–204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.01.030.
MOGI K. On the pressure dependence of strength of rocks and the coulomb fracture criterion [J]. Tectonophysics, 1974, 21(3): 273–285. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(74)90055-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51604260, 11802145) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(SKLGDUEK1204) supported by the State Key Laboratory for Geomechanics and Deep Underground Engineering, China; Project(BK20160416) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Xl., Karakus, M., Gao, F. et al. Thermal damage constitutive model for rock considering damage threshold and residual strength. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 2523–2536 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3933-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3933-2