Abstract
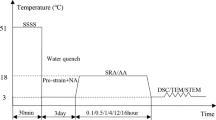
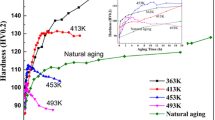
The precipitation behaviors of an Al-Cu-Li-Mn-Zr alloy at different ageing temperatures (120, 160 and 200 °C) were investigated using Vickers hardness measurements and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) characterization. Age hardening curves show an increase in precipitation kinetics with increasing ageing temperature. The results of TEM show that for the samples peak aged at 120 °C, the amount of δ' (Al3Li), GP zones/θ' (Al2Cu) and χ (Al5Cu6Li2) phases is obviously higher than that of T1 (Al2CuLi) precipitates; while the samples peak aged at 160 and 200 °C are usually dominated by T1 phase with a minor fraction of GP zones/θ' and δ', and the χ phase almost does not form. In addition, quantitative analysis on the T1 platelets demonstrates that the samples peak aged at 200 °C have larger plate diameter and smaller area fraction of T1, as compared to the samples peak aged at 160 °C. Correspondingly, the possible reasons for such phenomena are discussed.
摘要
本文采用显微硬度计和透射电子显微镜(TEM)表征手段,研究不同时效温度(120、160、200 °C) 对Al-Cu-Li-Mn-Zr 合金析出行为的影响。通过分析不同时效温度下的时效硬度曲线可以得出,随着 时效温度的升高,析出相的析出速度加快。此外,由TEM 表征结果可知,当时效温度为120 °C 时, 峰值态样品的析出相主要为δ'相(Al3Li)、GP 区/θ'相(Al2Cu)和χ 相(Al5Cu6Li2),其析出量明显高 于T1 相;当时效温度为160 °C 和200 °C 时,样品峰值态的析出相主要为T1 相,并有较少的δ'相和 GP 区/θ'相,而χ 相几乎不存在。对T1 相进行定量统计可知,与时效温度为160 °C 的峰值态样品相比, 时效温度为200 °C 时峰值态样品的主要析出相T1 相的直径更大,且面积分数更小,文本对这些现象 的产生原因进行了阐述和讨论。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RIOJA R J. Fabrication methods to manufacture isotropic Al-Li alloys and products for space and aerospace applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 257(1): 100–107.
LIU Xiao, WANG Zhao, LI Qing, ZHANG Xi, CUI Hao, ZHANG Xiao. Effects of pre-deformation on microstructure and properties of Al–Cu–Mg–Ag heat-resistant alloy [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(5): 1027–1033.
STARKE E A Jr, STALEY J T. Application of modern aluminum alloys to aircraft [J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 1996, 32(2, 3): 131–172.
YU Cheng, YIN Deng, ZHENG Feng, YU Xin. Effects of solution treatment on mechanical properties and microstructures of Al–Li–Cu–Mg–Ag alloy [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(8): 2083–2089.
YOSHIMURA R, KONNO T J, ABE E, HIRAGA K. Transmission electron microscopy study of the evolution of precipitates in aged Al–Li–Cu alloys: The θ' and T1 phases [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(14): 4251–4266.
DECREUS B, DESCHAMPS A, de GEUSER F, DONNADIEU P, SIGLI C, WEYLAND M. The influence of Cu/Li ratio on precipitation in Al–Cu–Li–x alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(6): 2207–2218.
YOSHIMURA R, KONNO T J, ABE E, HIRAGA K. Transmission electron microscopy study of the early stage of precipitates in aged Al–Li–Cu alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(10): 2891–2903.
KHAN A K, ROBINSON J S. Effect of silver on precipitation response of Al–Li–Cu–Mg alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2008, 24(11): 1369–1377.
van SMAALEN S, MEETSMA A, de BOER J L, BRONSVELD P M. Refinement of the crystal structure of hexagonal Al2CuLi [J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1990, 85(2): 293–298.
DONNADIEU P, SHAO Y, de GEUSER F, BOTTON G A, LAZAR S, CHEYNET M, de BOISSIEU M, DESCHAMPS A. Atomic structure of T1 precipitates in Al–Li–Cu alloys revisited with HAADF-STEM imaging and small-angle X-ray scattering [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(2): 462–472.
DWYER C, WEYLAND M, CHANG L Y, MUDDLE B C. Combined electron beam imaging and ab initio modeling of T1 precipitates in Al–Li–Cu alloys [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(20): 201909.
SILCOCK J M. The structural ageing characteristics of aluminium-copper-lithium alloys [J]. J Inst Met, 1960, 88: 357–364.
GUMBMANN E, LEFEBVRE W, de GEUSER F, SIGLI C, DESCHAMPS A. The effect of minor solute additions on the precipitation path of an Al–Cu–Li alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 115(15): 104–114.
HUANG B P, ZHENG Z Q. Independent and combined roles of trace Mg and Ag additions in properties precipitation process and precipitation kinetics of Al–Cu–Li–(Mg)–(Ag)–Zr–Ti alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(12): 4381–4393.
BOUKOS N, FLOUDA E, PAPASTAIKOUDIS C. The effect of Ag additions on the microstructure of aluminium-lithium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1998, 33(12): 3213–3218.
ZHENG Z Q, LIANG S Q, XU H, TAN C Y, YUN D F. Effect of 0.5% silver on the age hardening behaviour of an Al–Li–Cu–Mg–Zr alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1993, 12(14): 1111–1113.
LI Hong, TANG Yi, ZENG Zai, ZHENG Zi, ZHENG Feng. Effect of ageing time on strength and microstructures of an Al–Cu–Li–Zn–Mg–Mn–Zr alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 498(1, 2): 314–320.
CHEN Zhong, ZHAO Kai, FAN Li. Combinative hardening effects of precipitation in a commercial aged Al–Cu–Li–X alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 588: 59–64.
LI Hong, HUANG Da, KANG Wei, LIU Jiao, OU Yang, LI De. Effect of different aging processes on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Novel Al–Cu–Li Alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2016, 32(10): 1049–1053.
PAN Zheng, ZHENG Zi, LIAO Zhong, LI Shi. New cubic precipitate in Al–3.5Cu–1.0Li–0.5In (wt.%) alloy [J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 64(8): 942–944.
BLANKENSHIP C, STARKE E. Structure-property relationships in Al–Li–Cu–Mg–Ag–Zr alloy X2095 [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 42(3): 845–855.
ZHANG Sai, ZENG Wei, YANG Wen, SHI Chun, WANG Hao. Ageing response of a Al–Cu–Li 2198 alloy [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 63: 368–374.
NOBLE B, THOMPSON G E. T1 (Al2CuLi) precipitation in aluminium–copper–lithium alloys [J]. Metal Science Journal, 1972, 6(1): 167–174.
DORIN T, DESCHAMPS A, de GEUSER F, SIGLI C. Quantification and modelling of the microstructure/strength relationship by tailoring the morphological parameters of the T1 phase in an Al–Cu–Li alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 75(15): 134–146.
DENG Yan, BAI Jian, WU Xiao, HUANG Guang, CAO Ling, HUANG Li. Investigation on formation mechanism of T1 precipitate in an Al–Cu–Li alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 723(5): 661–666.
LI Qiong, WAWNER F E. Characterization of a cubic phase in an Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1997, 32(20): 5363–5370.
DESCHAMPS A, GARCIA M, CHEVY J, DAVO B, de GEUSER F. Influence of Mg and Li content on the microstructure evolution of Al–Cu–Li alloys during longterm ageing [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 122(1): 32–46.
TSIVOULAS D, ROBSON J D, SIGLI C, PRANGNELL P B. Interactions between zirconium and manganese dispersoid-forming elements on their combined addition in Al–Cu–Li alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(13, 14): 5245–5259.
DORIN T, DONNADIEU P, CHAIX J-M, LEFEBVRE W, de GEUSER F, DESCHAMPS A. Size distribution and volume fraction of T1 phase precipitates from TEM images: Direct measurements and related correction [J]. Micron, 2015, 78: 19–27.
RODGERS B I, PRANGNELL P B. Quantification of the influence of increased pre-stretching on microstructurestrength relationships in the Al–Cu–Li alloy AA2195 [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 108(15): 55–67.
KANG S J, KIM T H, YANG C W, LEE J I, PARK E S, NOH T W, KIM M. Atomic structure and growth mechanism of T1 precipitate in Al–Cu–Li–Mg–Ag alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 109: 68–71.
CHEN P, BHAT B. Time-temperature-precipitation behavior in Al-Li alloy 2195 [R]. Huntsville: NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, 2002.
LORIMER G, NICHOLSON R. Further results on the nucleation of precipitates in the Al-Zn-Mg system [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1966, 14(8): 1009–1013.
RINGER S P, SOFYAN B T, PRASAD K S, QUAN G C. Precipitation reactions in Al–4.0Cu–0.3Mg (wt.%) alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(9): 2147–2160.
GABLE B M, ZHU A W, CSONTOS A A, STARKE E A Jr. The role of plastic deformation on the competitive microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of a novel Al-Li-Cu-X alloy [J]. Journal of Light Metals, 2001, 1(1): 1–14.
del CASTILLO P E J R D, REISCHIG P, van der ZWAAG S. Tailoring of Ostwald ripening behaviour in multicomponent Al alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52(8): 705–708.
DORIN T, DESCHAMPS A, de GEUSER F, LEFEBVRE W, SIGLI C. Quantitative description of the T1 formation kinetics in an Al–Cu–Li alloy using differential scanning calorimetry, small-angle X-ray scattering and transmission electron microscopy [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2014, 94(10): 1012–1030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2016YFB0300901) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Project(51421001) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2018CDJDCL0019) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Yj., Huang, Gj., Cao, Lf. et al. Effect of ageing temperature on precipitation of Al-Cu-Li-Mn-Zr alloy. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 1340–1349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3830-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3830-8